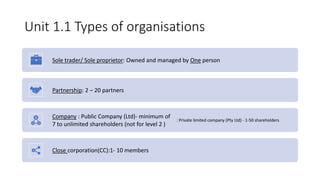
This document discusses different types of business organizations in South Africa, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, private limited companies, and close corporations. It outlines the key advantages and disadvantages of each structure. Sole proprietorships have advantages like no required registration and sole ownership of profits, but the owner is personally liable for all debts. Partnerships allow for shared profits but also shared personal liability for debts. Private limited companies and close corporations provide liability protections but have membership limits and other requirements. Understanding the pros and cons of each structure is important for competitive business planning.