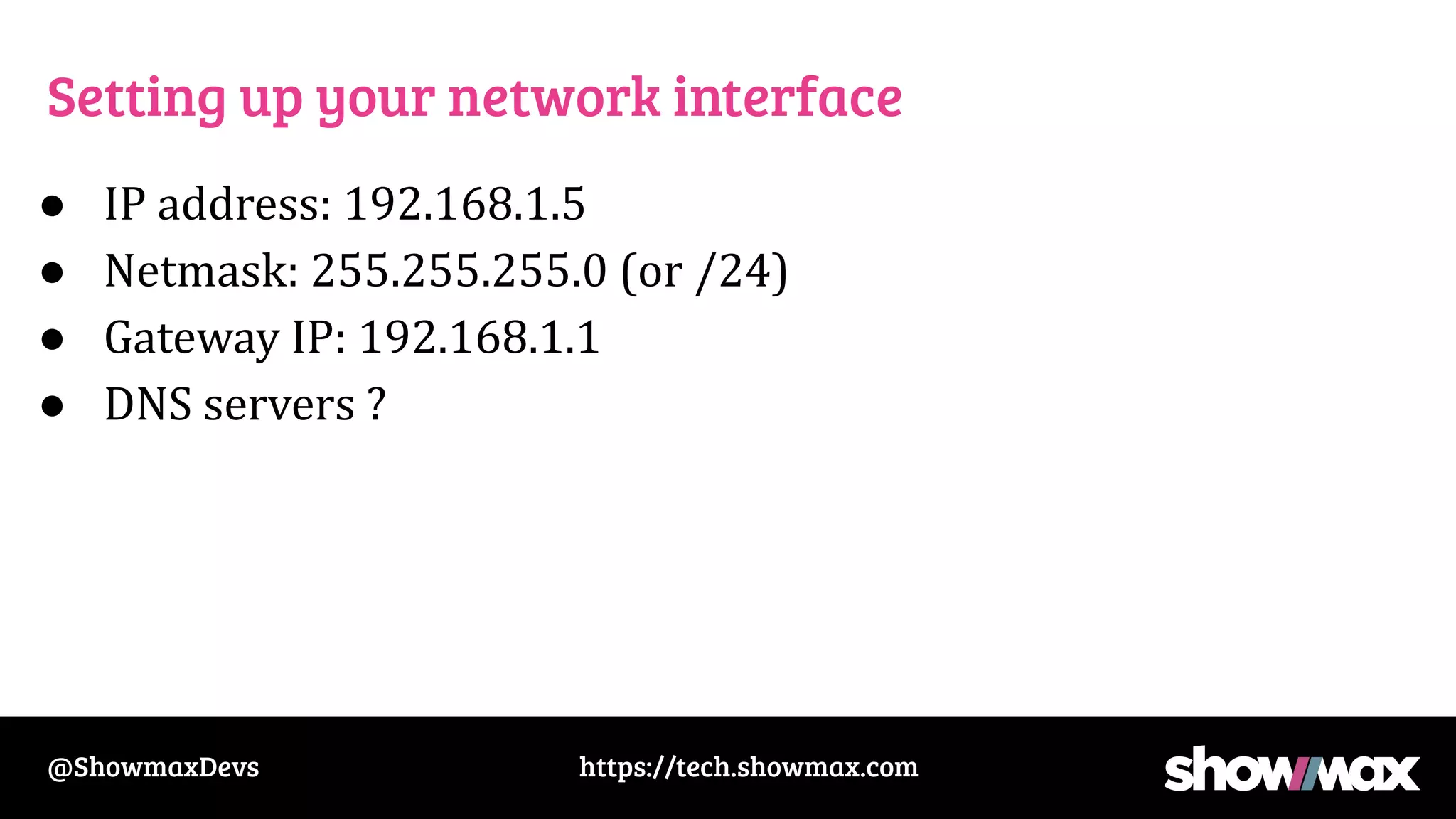
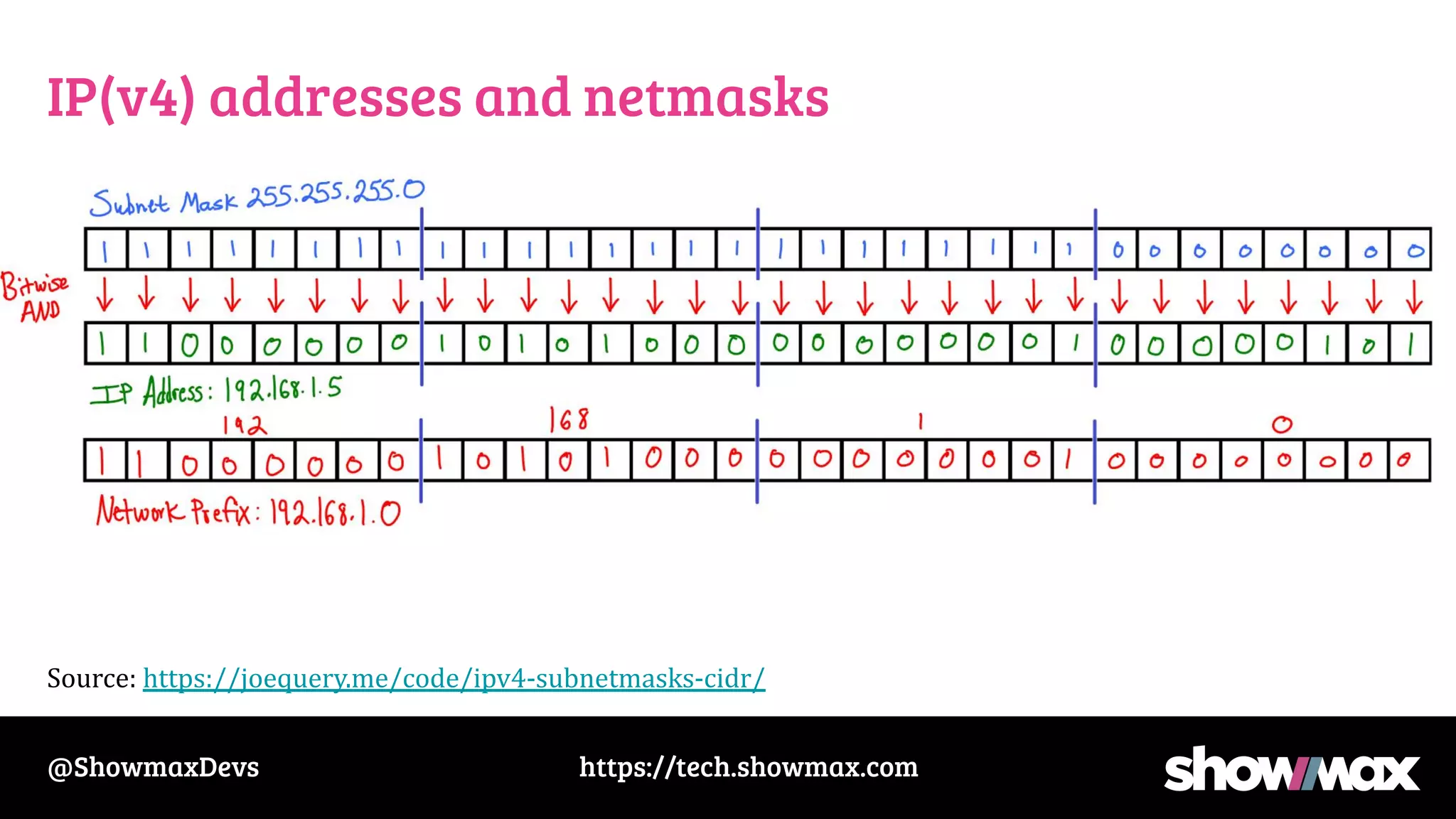
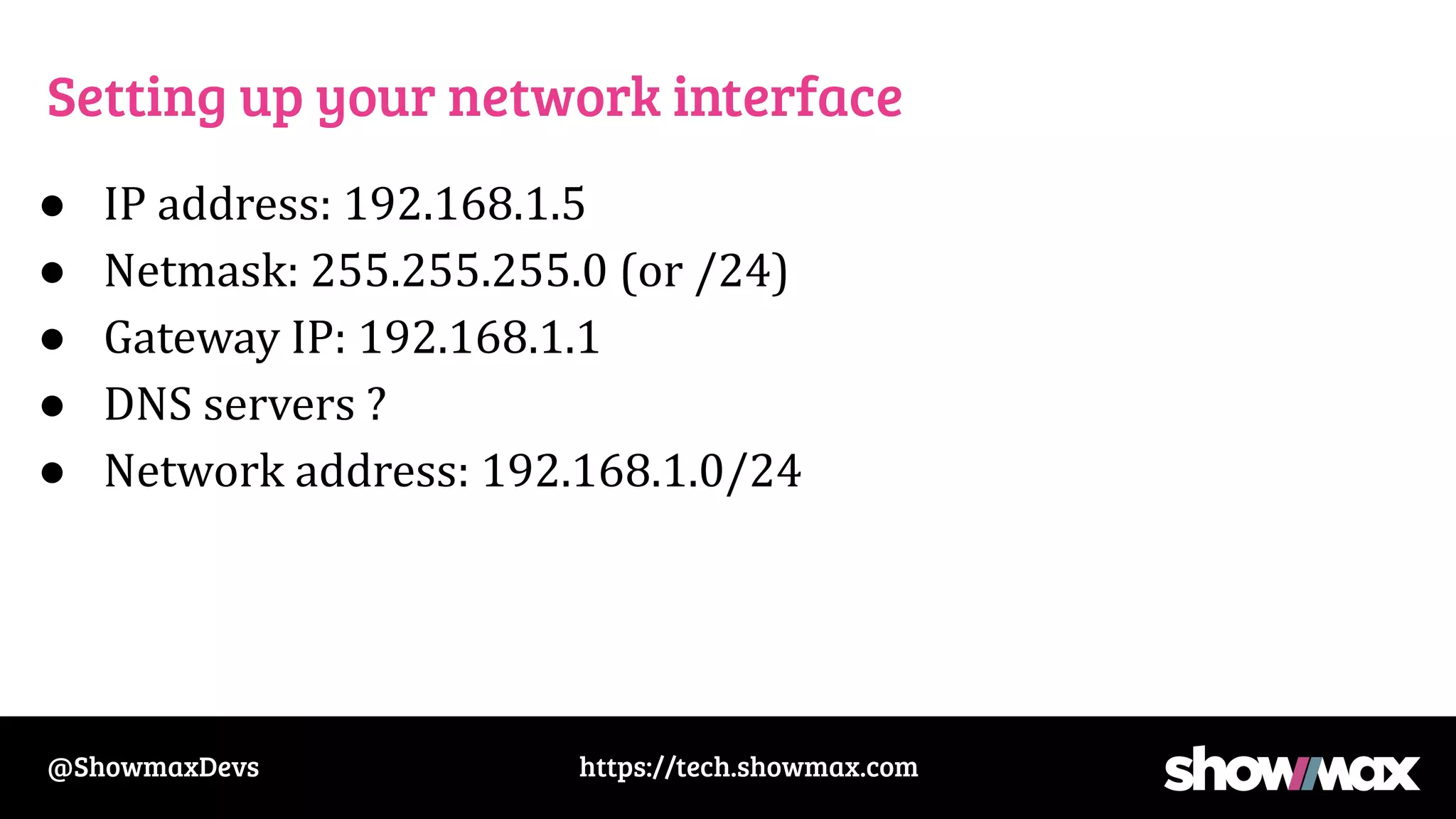
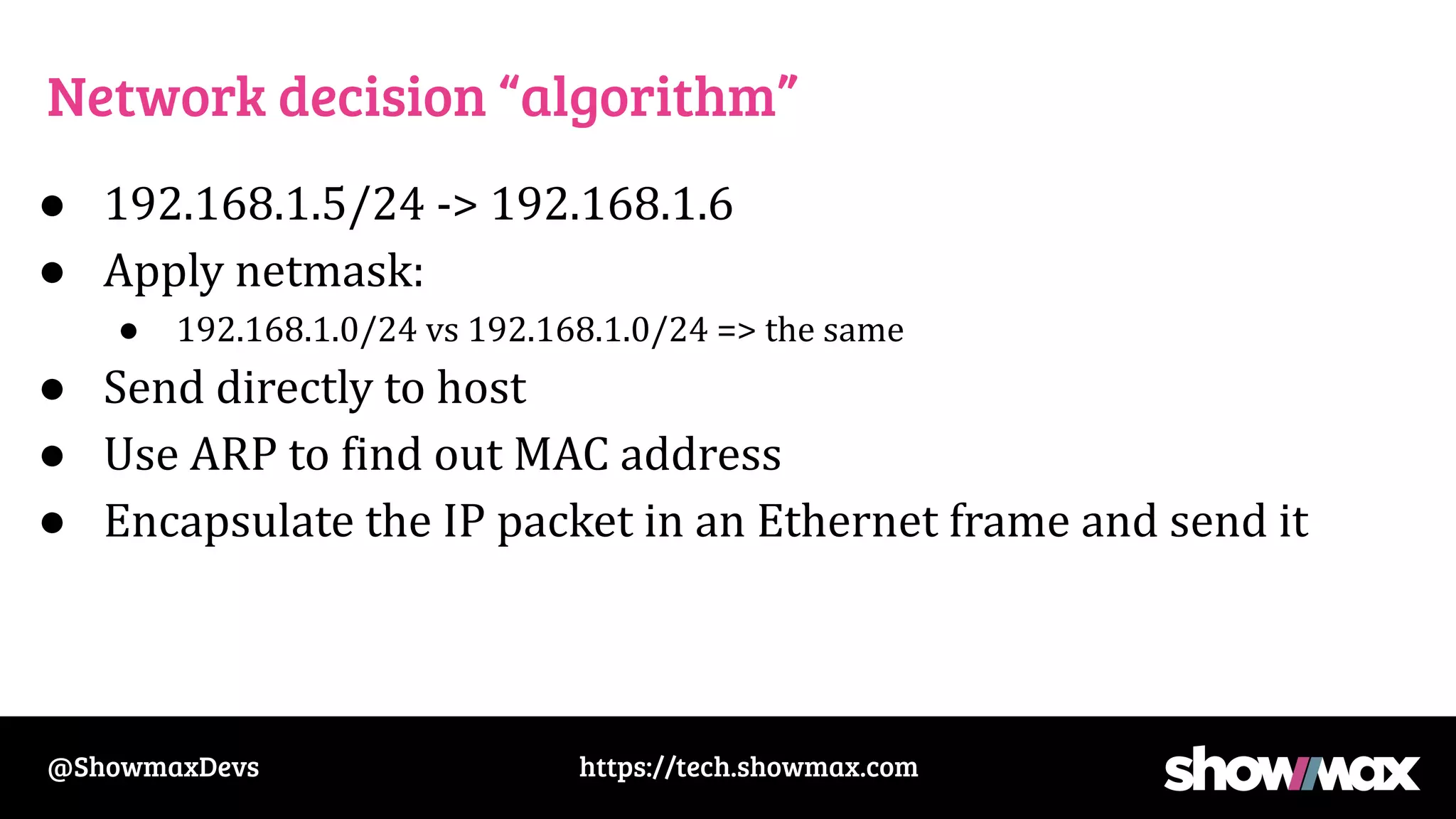
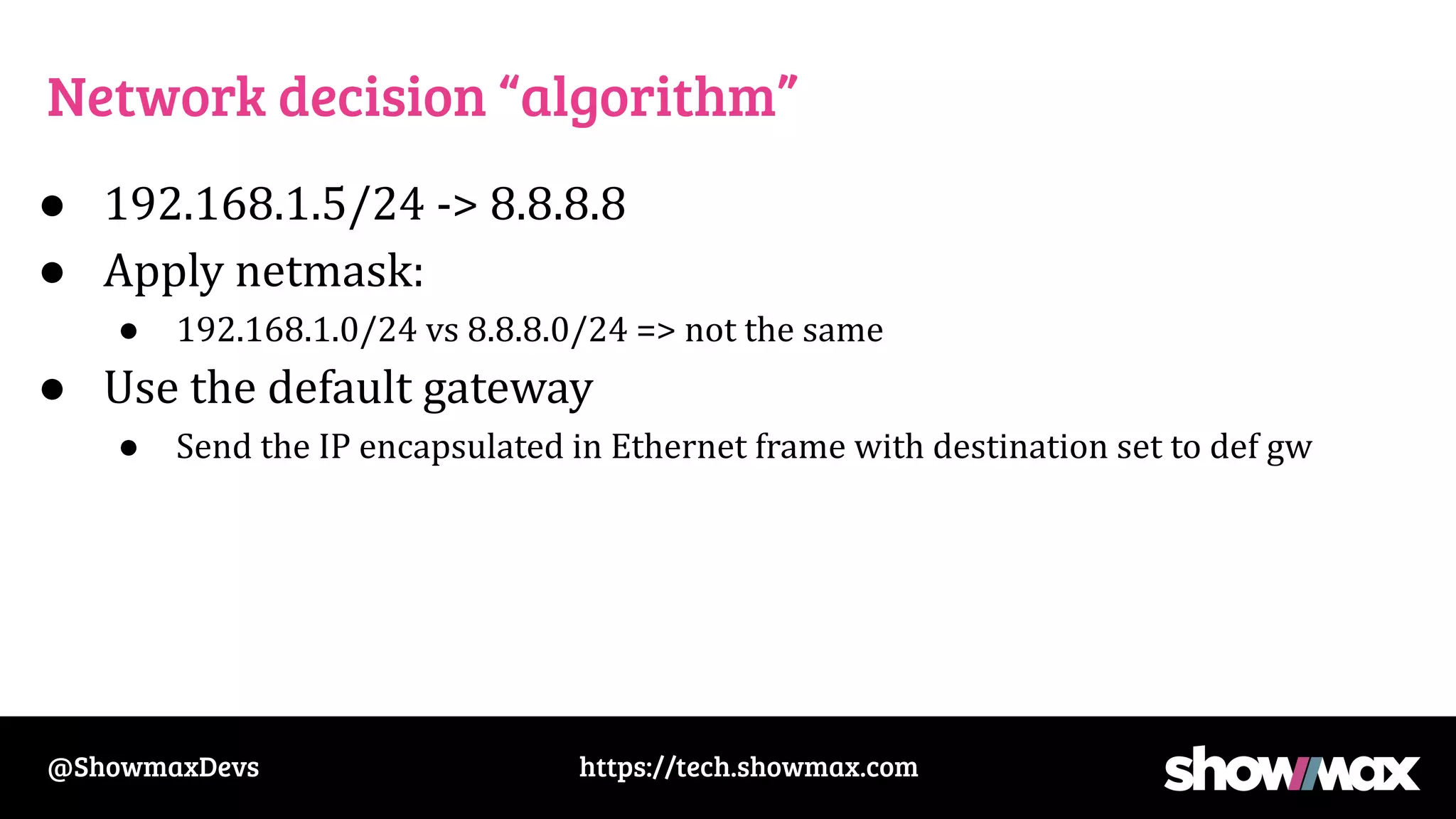
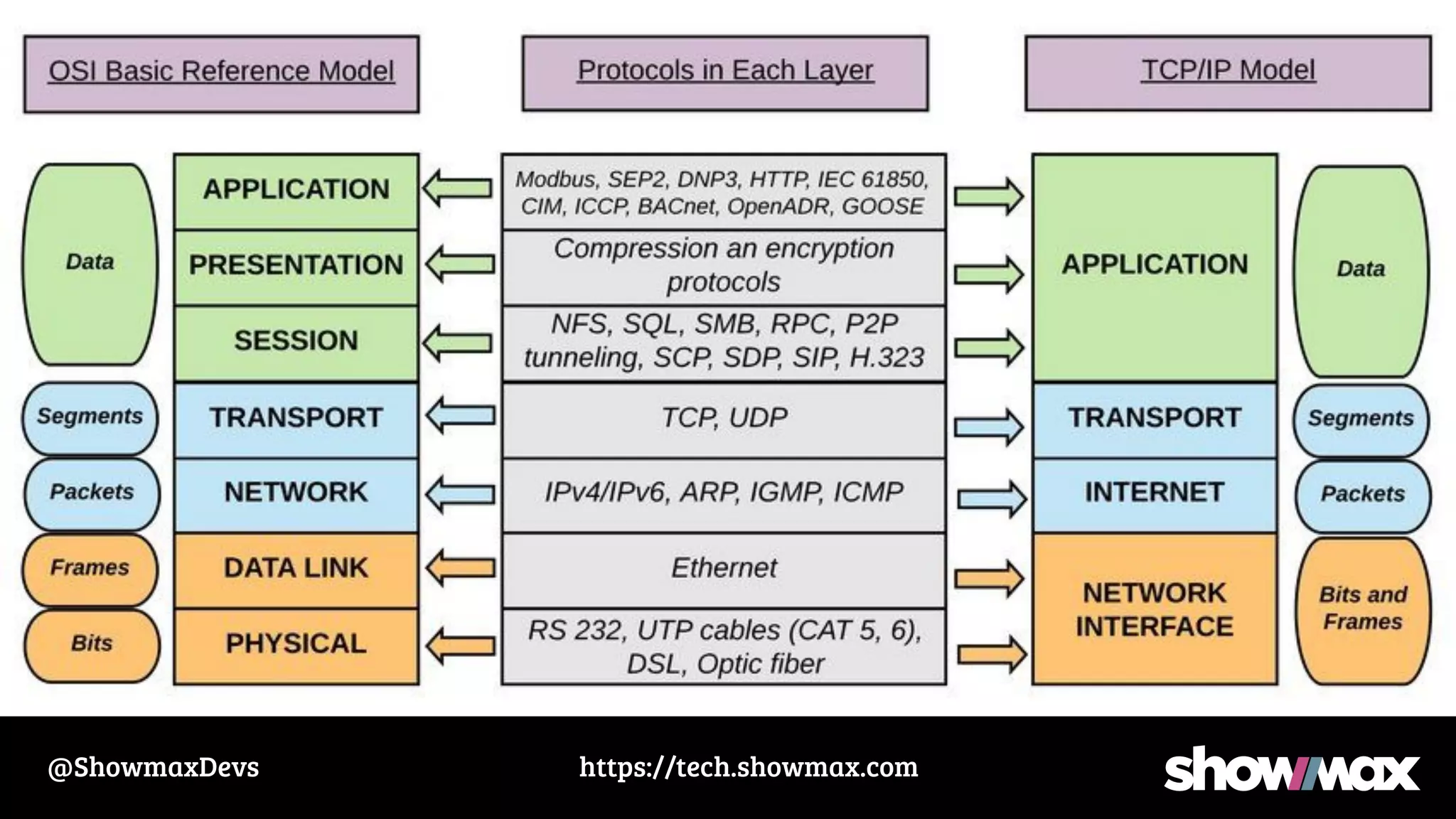
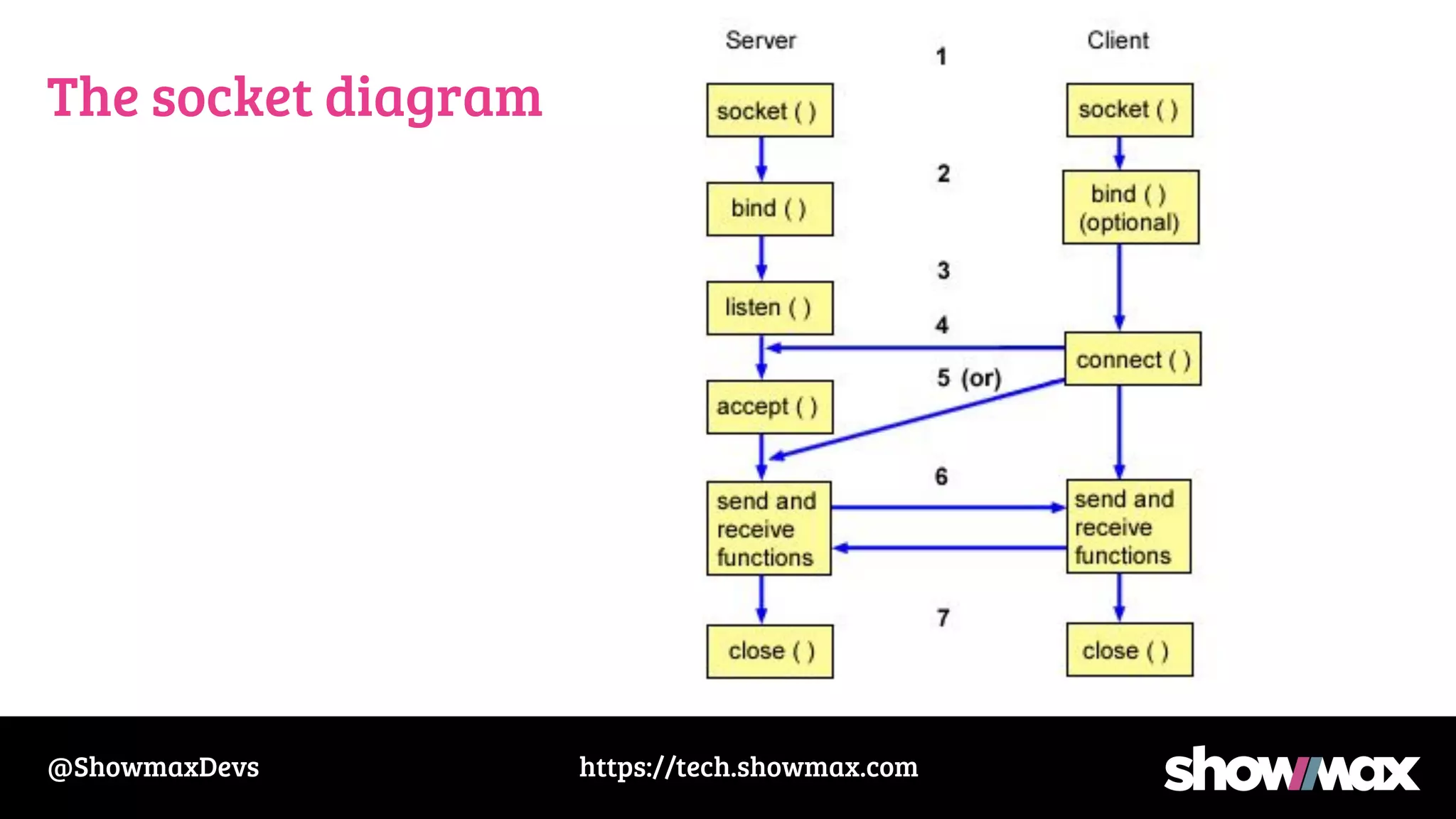
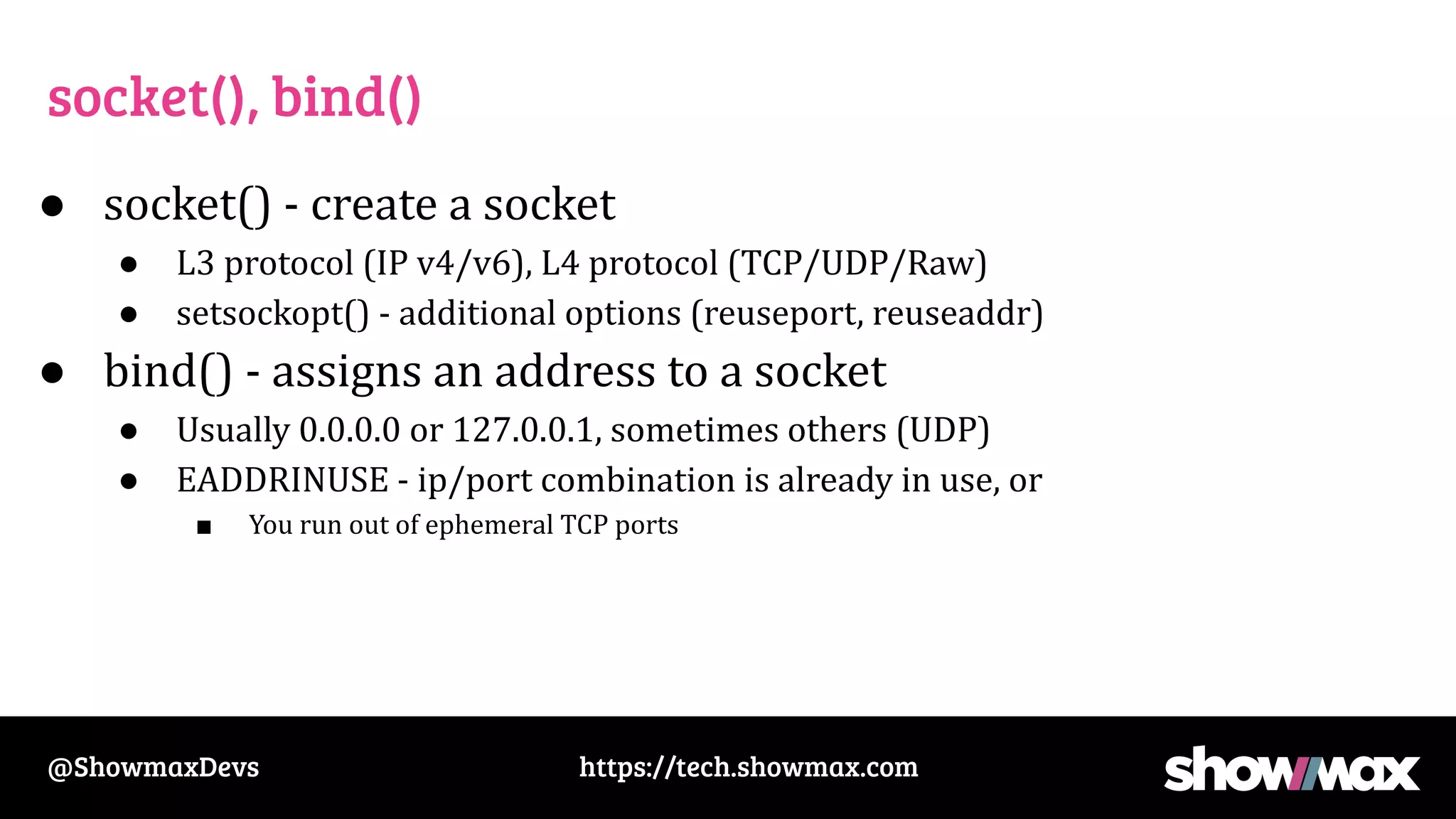
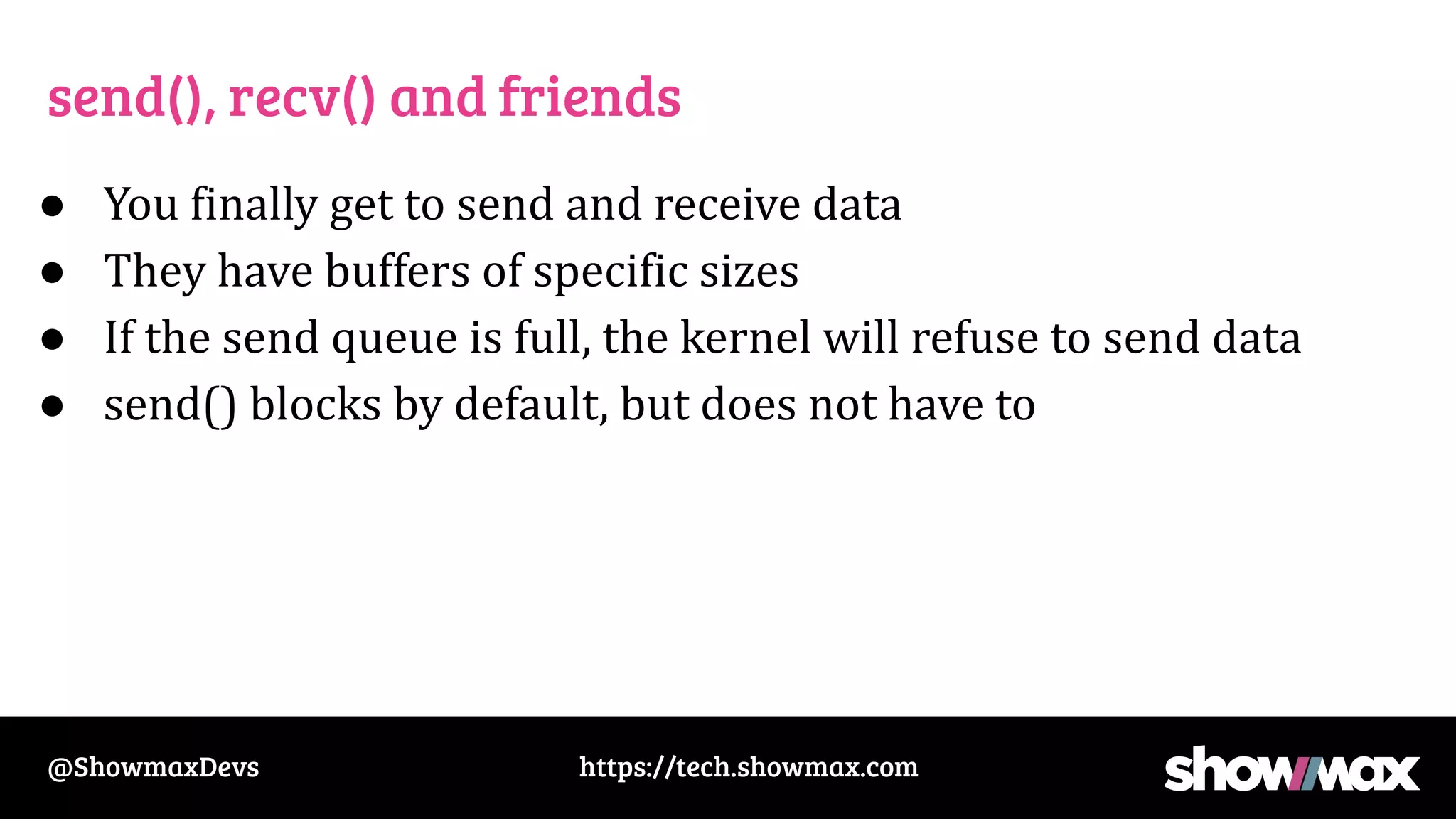
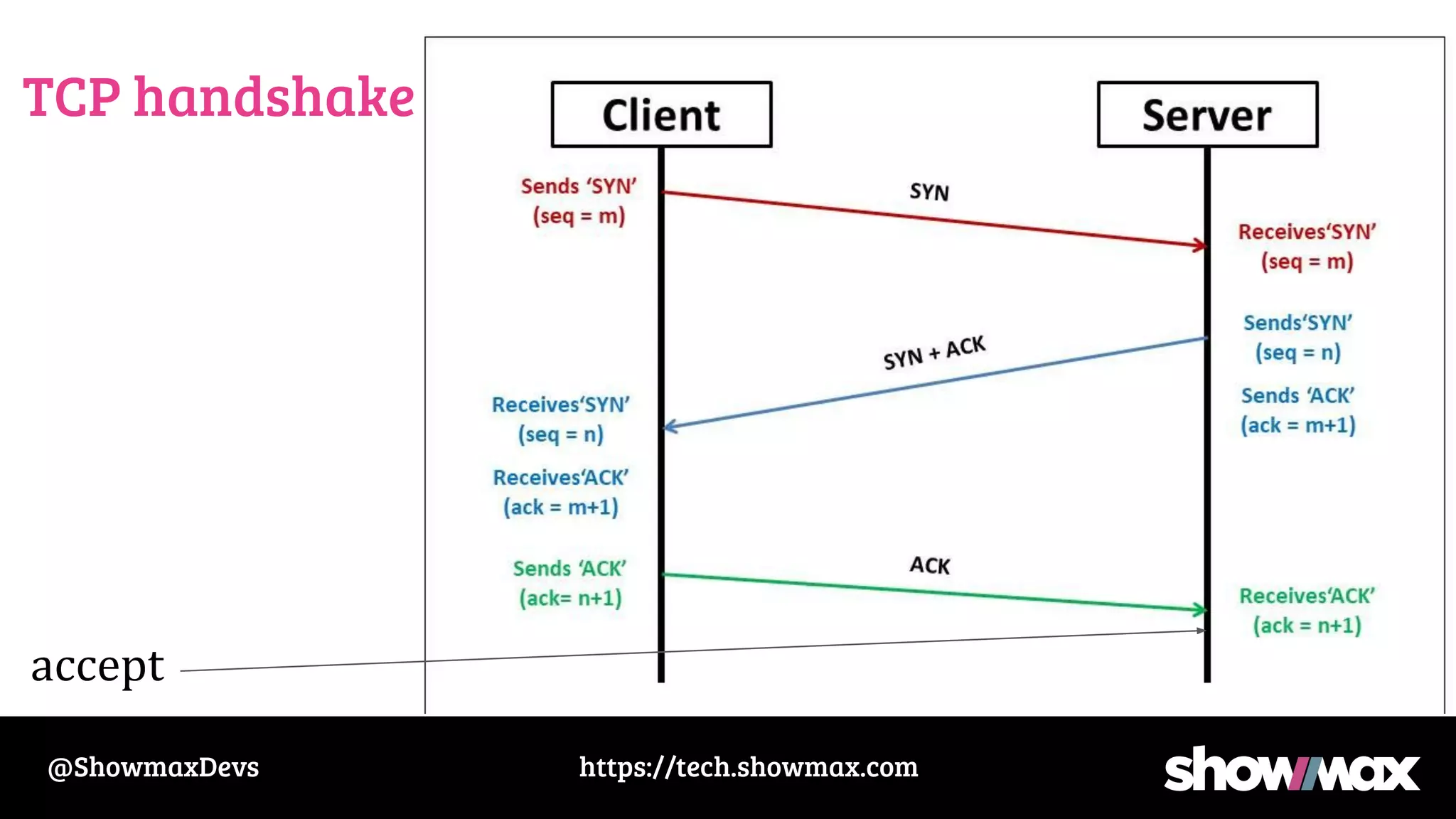
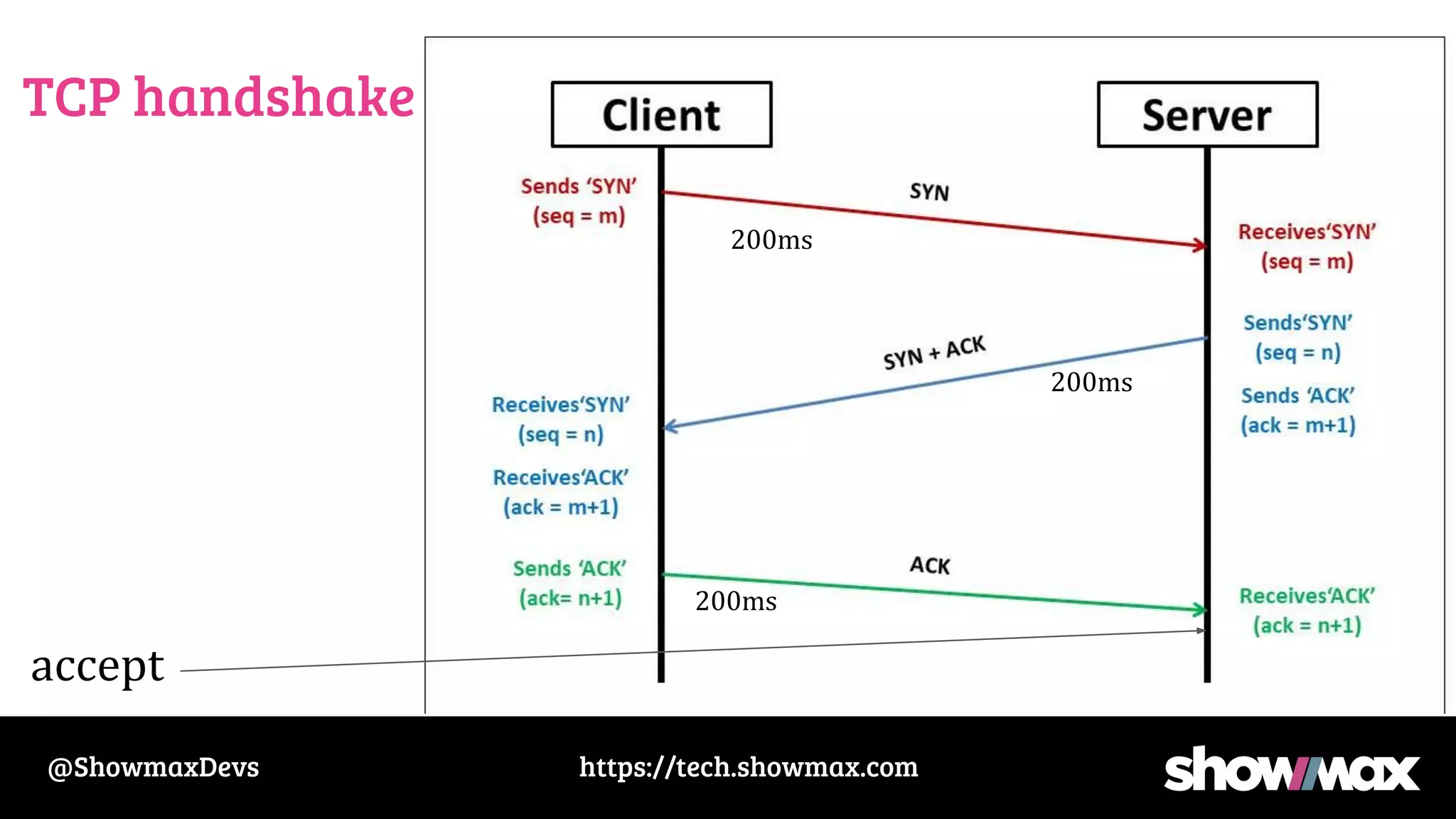
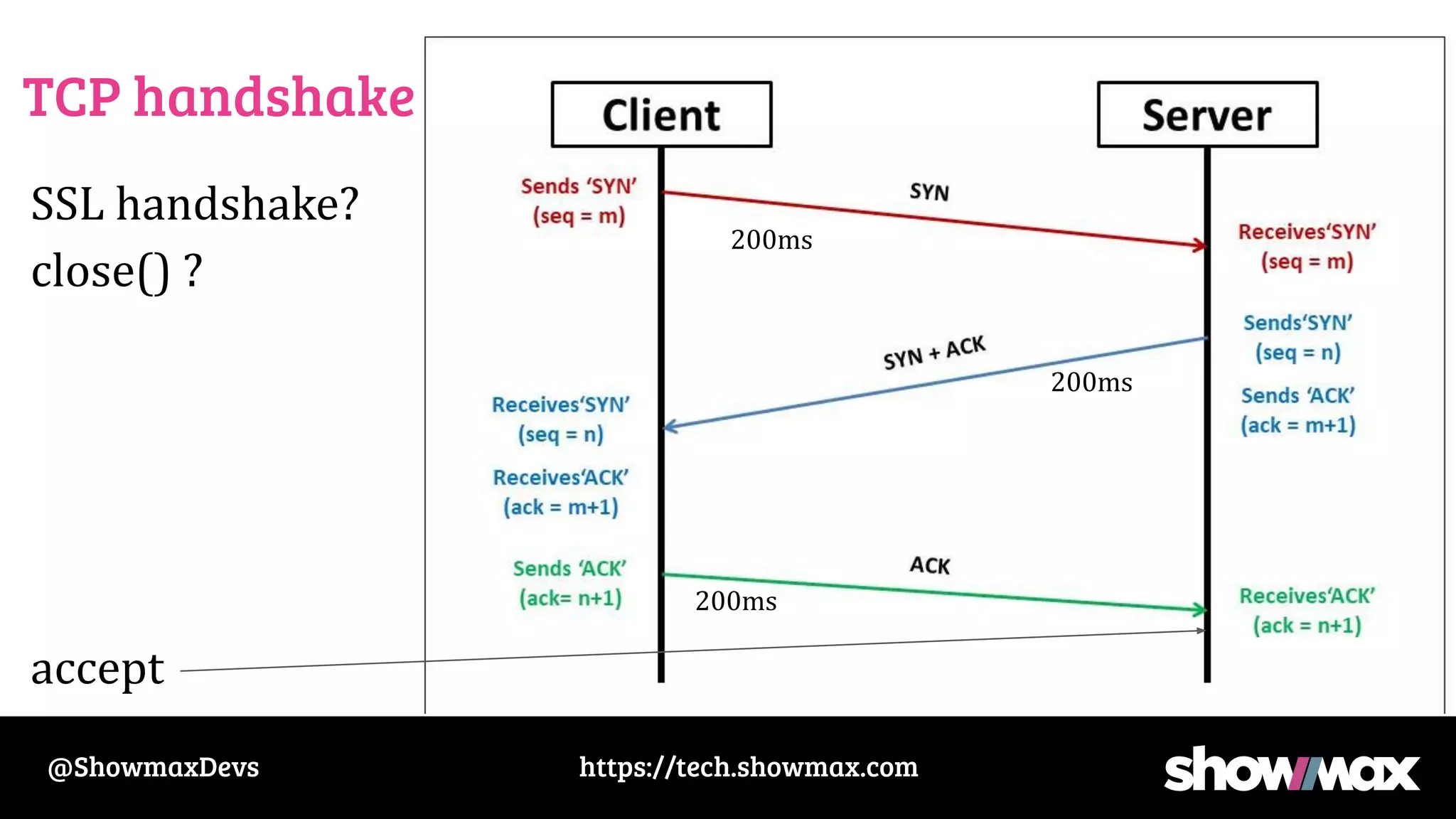
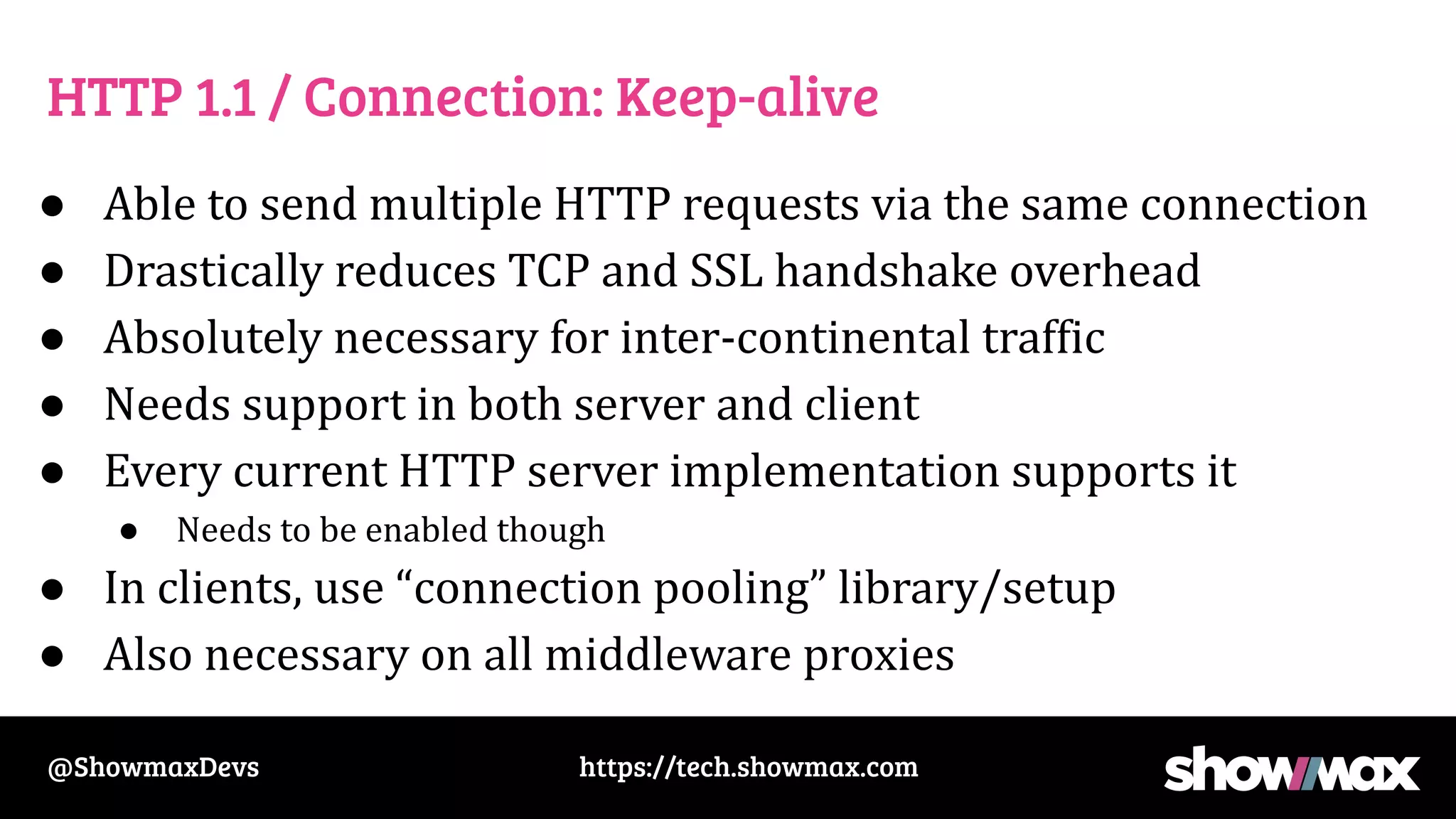
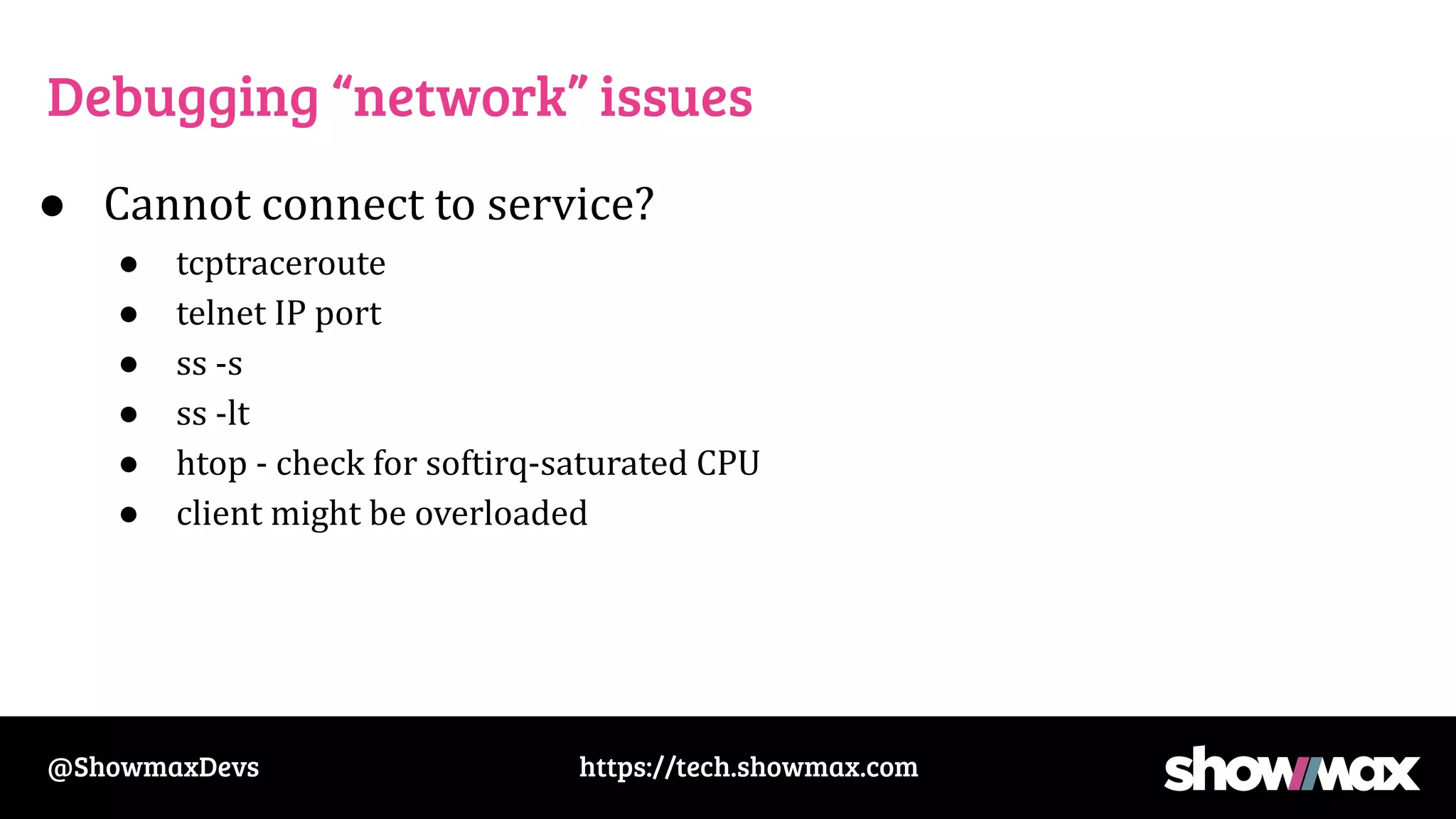
The document provides a comprehensive overview of networking fundamentals, including IP addresses, network masks, routing, and the TCP/IP stack. It covers the setup of network interfaces, the socket API, and the TCP handshake process, while also addressing debugging techniques for network issues. Various command usage and performance considerations in networking are also discussed.