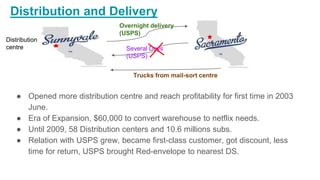
Netflix started as a DVD rental service in 1997 and transformed into a leading streaming platform. In 2011, Netflix took a major gamble by splitting its DVD and streaming services into separate plans priced at $8/month each. This risked losing subscribers but positioned the company to focus on online streaming. Netflix was successful due to its personalized recommendations, growing library of content through negotiations with studios, and innovation in streaming technology and integration with TVs.