Embed presentation
Download to read offline



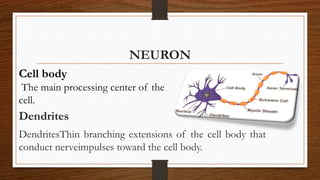



The nervous system is comprised of interconnected systems and subsystems that work together to maintain homeostasis in the human body. It receives information from sensory receptors about internal and external changes through neurons, which are cells that transmit signals through branched dendrites and a single axon. There are three main types of neurons: efferent neurons which conduct motor signals, afferent neurons which conduct sensory signals, and interneurons which connect between neurons.






