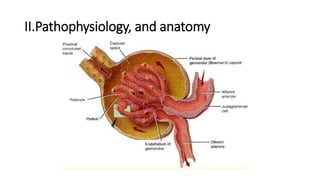
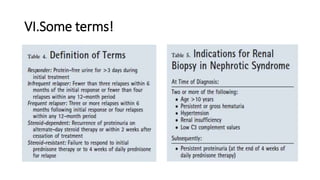
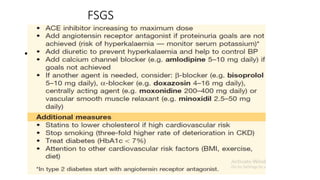
Nephrotic syndrome is a condition characterized by heavy proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia. It is caused by damage to the glomerular capillary wall that increases permeability and allows large molecules like albumin to pass into the urine. The main types are minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and membranous glomerulonephritis. Treatment involves managing edema, restricting protein intake, and potentially using steroids, immunosuppressants, or diuretics depending on the specific cause and severity. Complications can include infection, thrombosis, hyperlipidemia, and end-stage renal disease if left untreated.