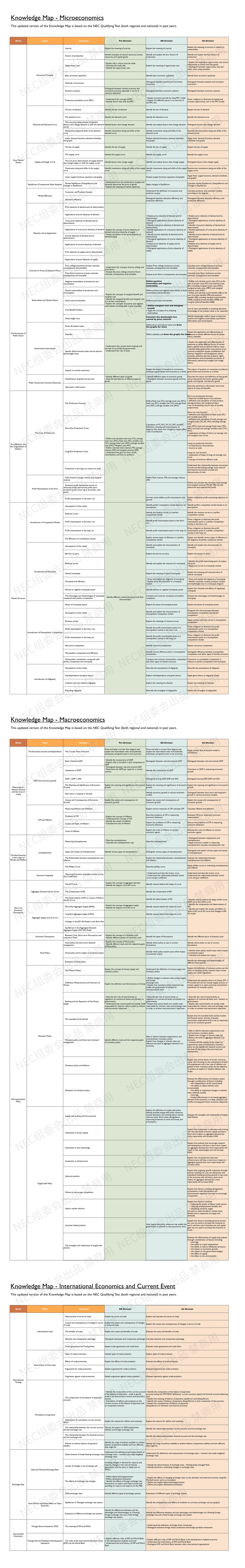
The document outlines key concepts in economics, including scarcity, opportunity cost, demand and supply, market equilibrium, elasticity, public goods, firm behavior, as well as monetary and fiscal policies. It delves into various economic models, the measurement of national income, inflation, unemployment, and economic inequality while also addressing different market structures such as perfect competition, monopoly, and oligopoly. The text serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding major economic principles and their applications in analyzing real-world economic scenarios.