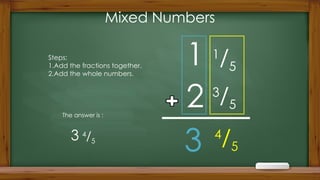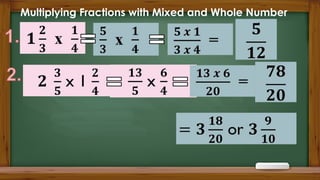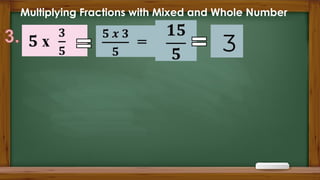The document provides a comprehensive guide on performing arithmetic operations on rational numbers, specifically focusing on addition and subtraction of both like and unlike fractions, as well as operations involving mixed numbers. It outlines step-by-step procedures for simplifying fractions and includes various activities for practice. Additionally, it explains multiplication and division of fractions, emphasizing the importance of simplification and cancellation.