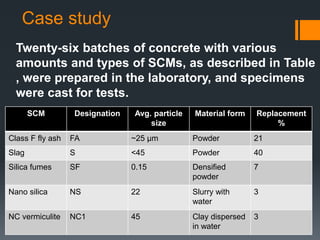
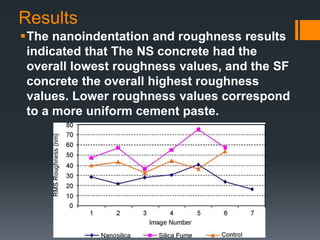
This document discusses the use of nano materials in concrete. It describes that nano materials, which are less than 100 nanometers in size, can significantly change the mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical properties of concrete. Common nano materials used include nano silica, carbon nano tubes, and titanium oxide. The document outlines the advantages these materials provide such as increased strength and durability. It also summarizes the results of a laboratory study that found nano silica concrete produced the most uniform microstructure and lowest surface roughness.