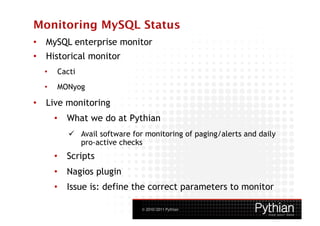
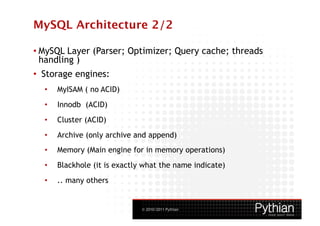
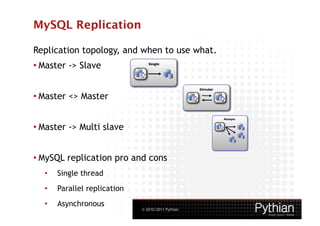
The document provides a high-level overview of MySQL in 3 sentences:
MySQL is a popular open source database management system. It allows users to manage and query relational databases and is commonly used for both small and large-scale projects. MySQL works across many operating systems and provides transactional support and flexibility through different storage engines.







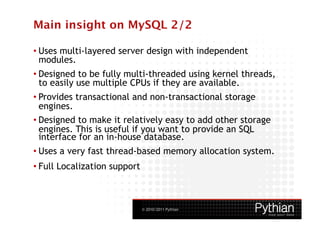



![MySQL Storage engine more details 2/2
1. MySQL Cluster
• No geospatial support; no foreign-key; no “Temporary” tables; partition only by
[LINEAR] KEY; only the READ COMMITTED isolation level is supported; no partial roll-
back (full or nothing); a Select on Blob or Text fields will create a READ LOCK on the
table to guarantee consistency.
• Fully ACID; share nothing architecture; single point of failure; write scale by node-
group; thread requests parallelization; and a lot more …
20
1 © 2010/2011 Pythian
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythianmysqloverview-130128151040-phpapp01/85/MySQL-overview-14-320.jpg)








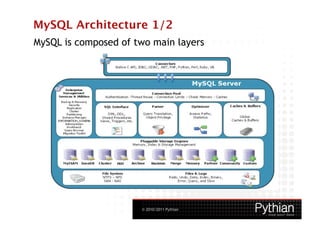
![MySQL HA solution
How many nines do you need?
9 0. 0 0 0 % (36 days) MySQL Replication
9 9. 0 0 0 % (8 hours) Linux Heartbeat with DRBD
9 9. 0 0 0 % (8 hours) Linux Heartbeat with Shared Storage
(Active/Passive)
9 9. 0 0 0 % (8 hours) Linux Heartbeat with Shared Storage
(Active/Active)
9 9. 9 0 0 % (52 minutes) Linux Heartbeat with DRBD and Replication
9 9. 9 0 0 % (52 minutes) Linux Heartbeat with Shared Storage and
Replication
9 9. 9 9 9 % (5 minutes) MySQL Cluster
9 9. 9 9 9 % (5 minutes) MySQL Cluster & Replication
9 9. 9 9 9 % (5 minutes) MySQL Cluster Carrier Grade Edition
[Time is possible outage per year]
20
2 © 2010/2011 Pythian
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythianmysqloverview-130128151040-phpapp01/85/MySQL-overview-25-320.jpg)