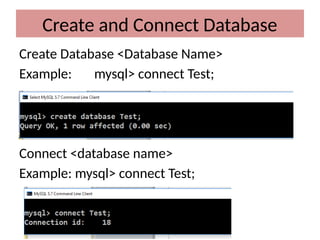
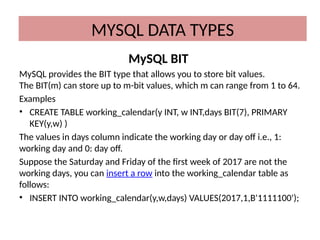
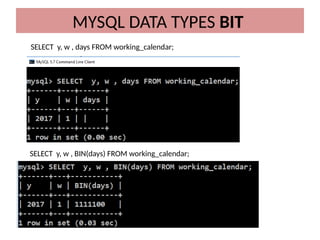
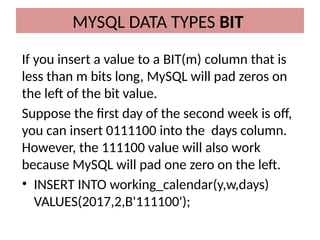
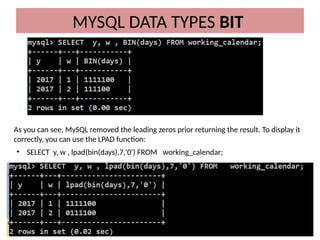
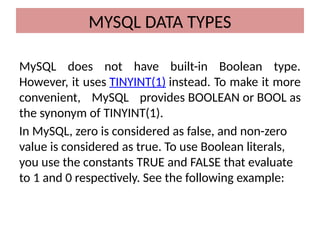
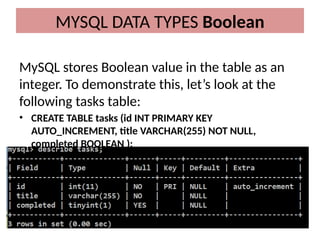
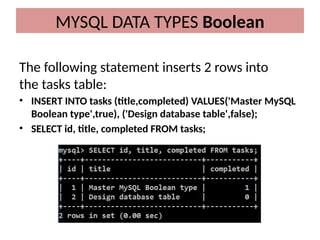
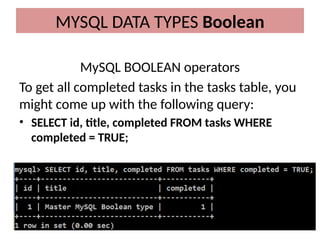
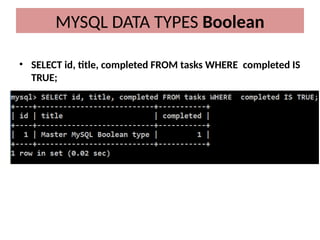
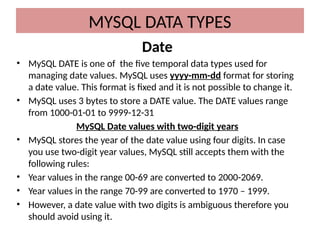
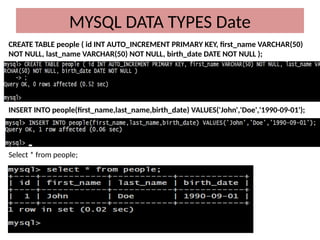
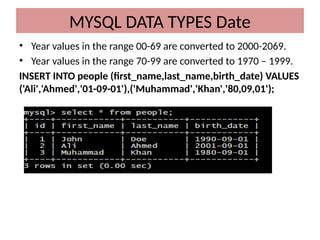
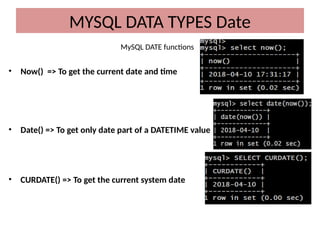
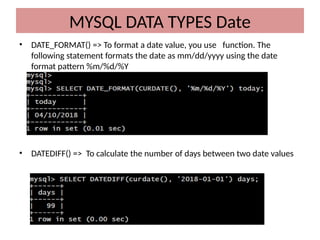
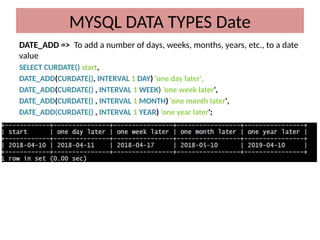
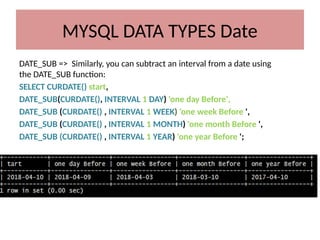
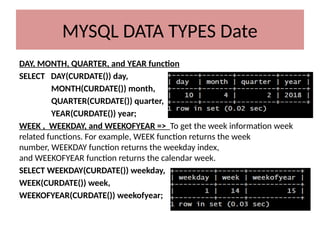
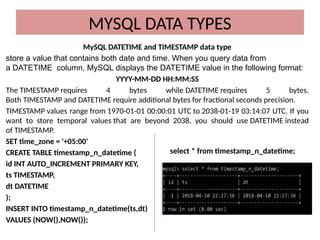
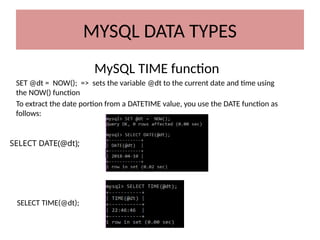
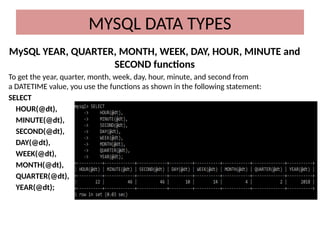
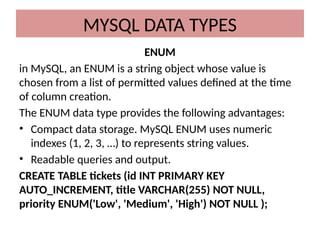
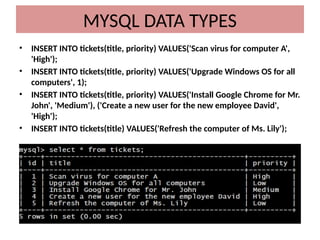
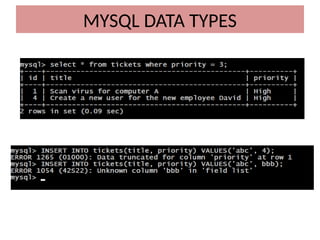
This document discusses various MySQL data types, including bit, boolean, date, datetime, timestamp, and enum. It provides examples of how to create tables, insert values, and query data using these types, as well as details on formatting and function usage for date manipulations. Additionally, it explains MySQL's conventions for handling boolean values and dates, emphasizing specific formats and storage requirements.