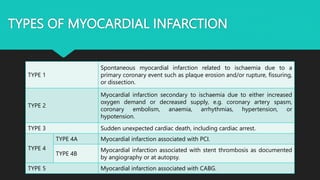
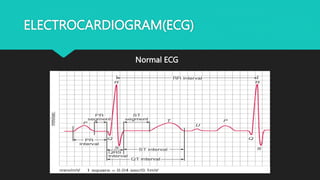
Myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack, is caused by ischemia due to an imbalance between the supply and demand of blood to the heart. It is the leading global cause of death, taking over 17 million lives each year. Indians have some of the highest rates of coronary artery disease in the world. Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, abnormal heart rhythms, anxiety, and fatigue. There are five types of myocardial infarction defined by their causes.