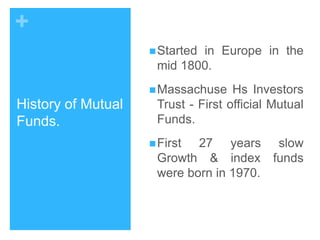
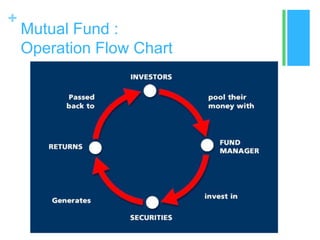
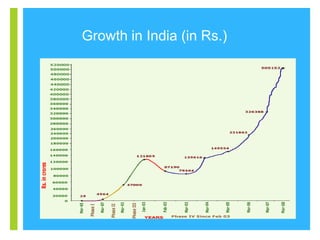
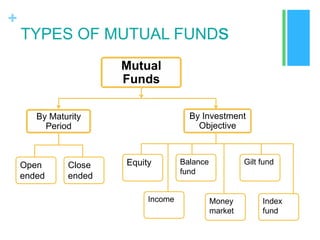
Mutual funds are investment trusts that pool money from various investors to invest in capital market instruments, offering different types such as equity, debt, balanced, and money market funds. The industry began in Europe in the mid-1800s, with significant growth in India starting in 1963, and is regulated by SEBI for investor protection. Investing in mutual funds provides diversification, professional management, and potential tax benefits, though risks like market fluctuations and credit risks should be considered.