Embed presentation
Download to read offline





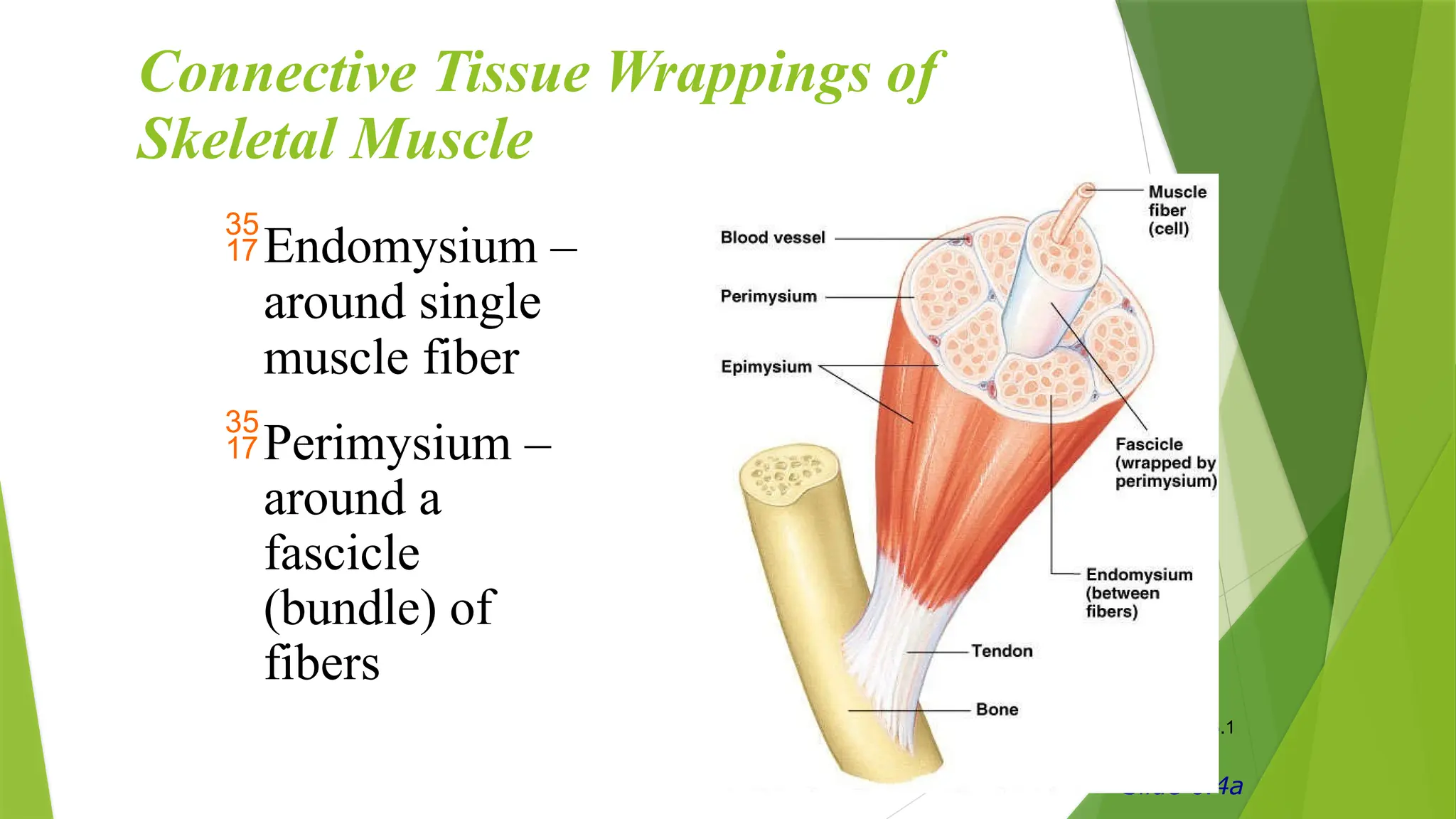
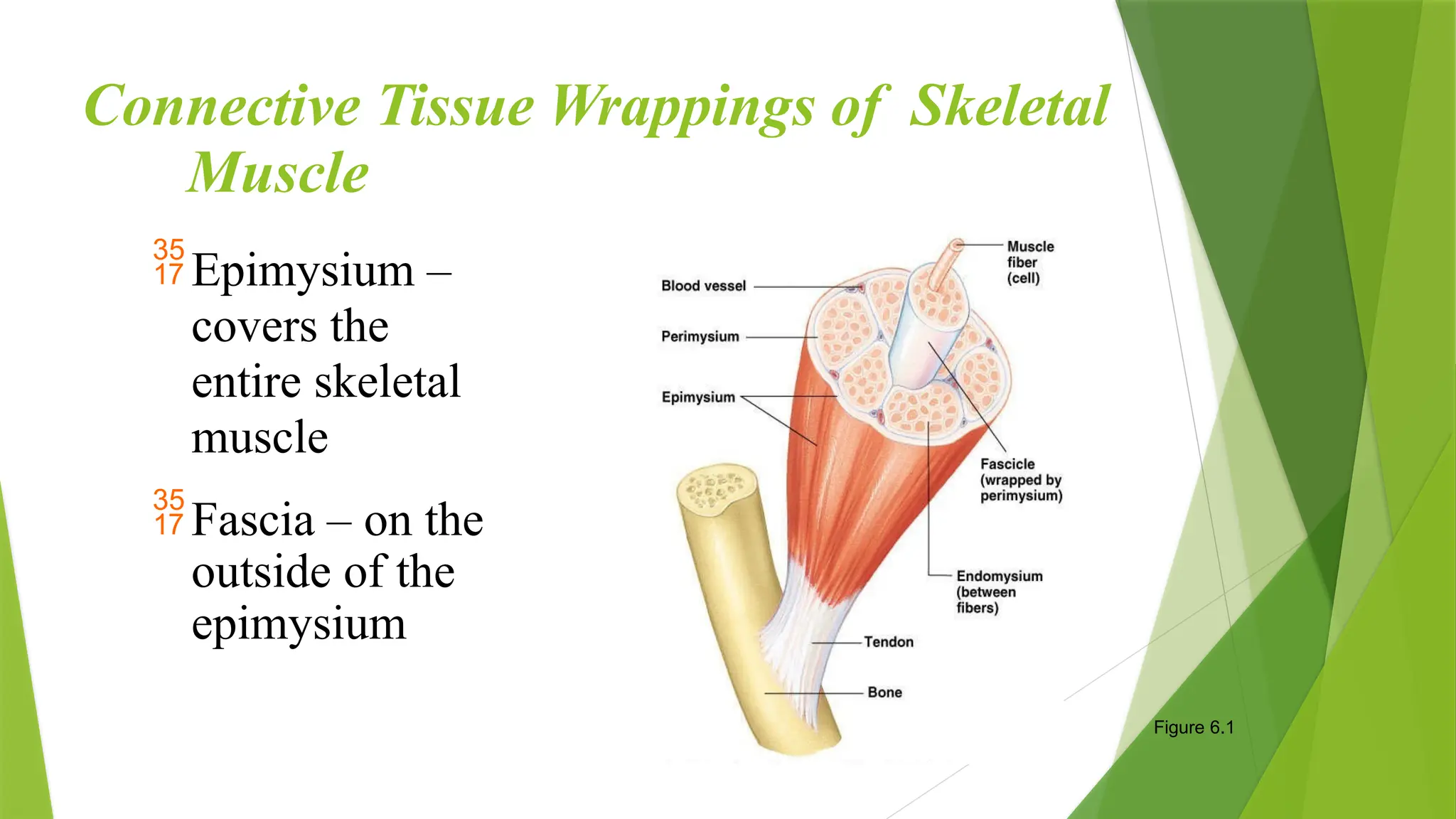






The muscular system is essential for body movement, with three main types of muscle: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscles, which constitute 40-50% of body weight, facilitate functions such as locomotion, posture maintenance, respiration, and heat production. Key characteristics of skeletal muscle include multinucleate cells, striated appearance, and voluntary control, surrounded by connective tissue wrappings.












