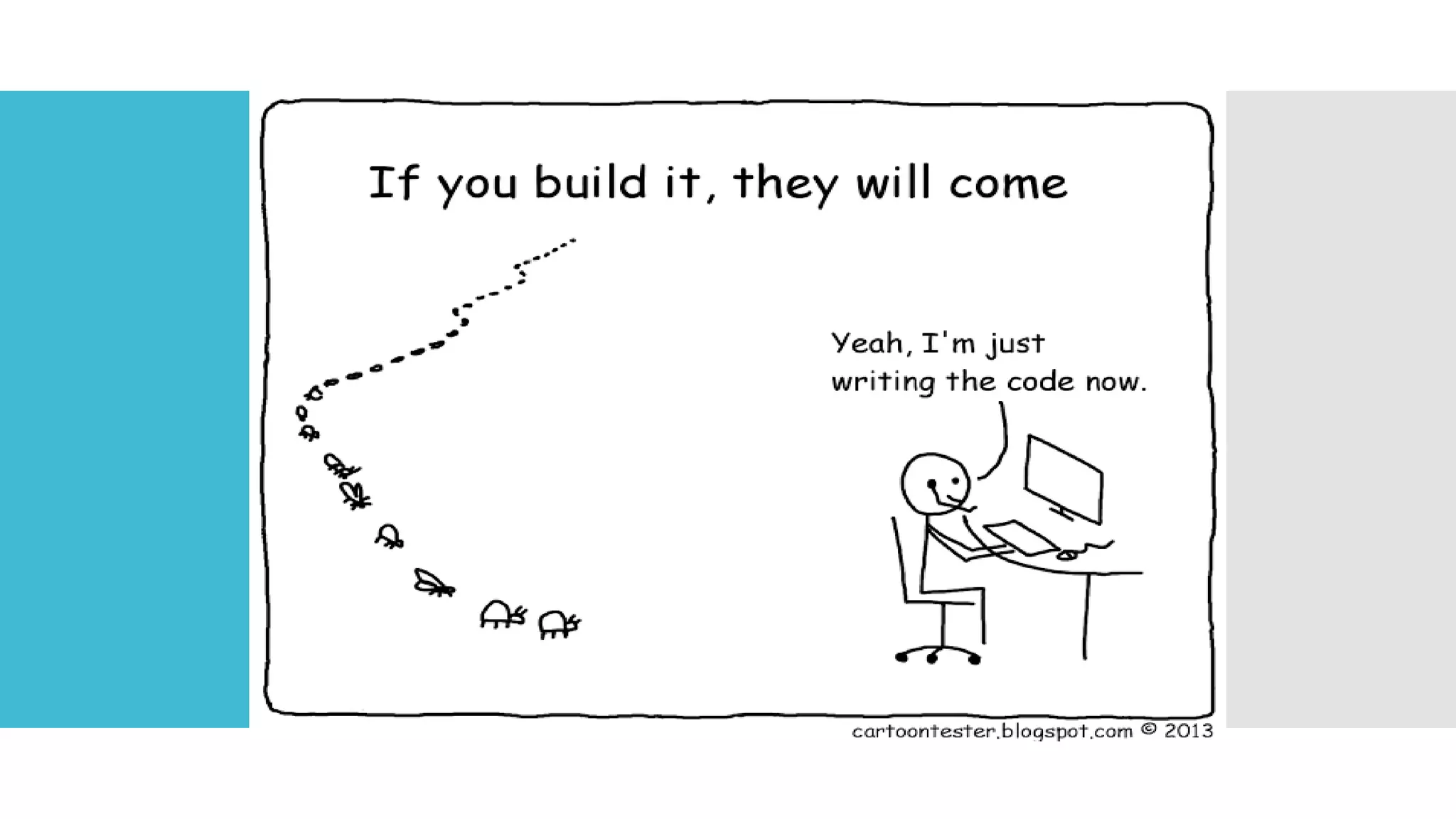
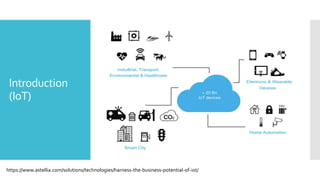
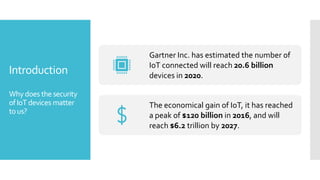
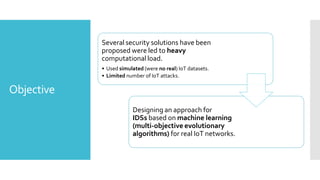
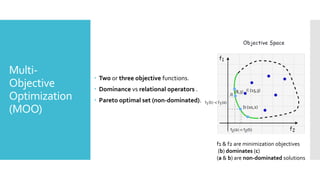
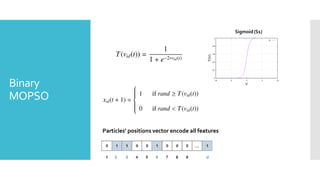
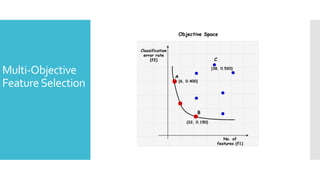
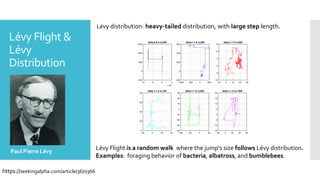
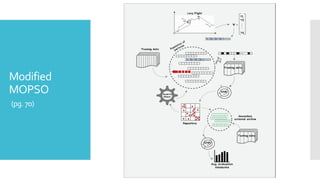
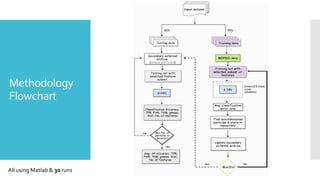
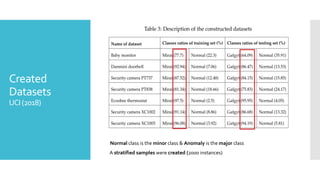
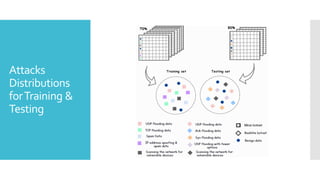
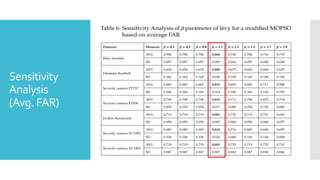
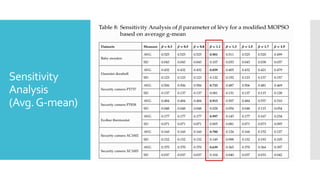
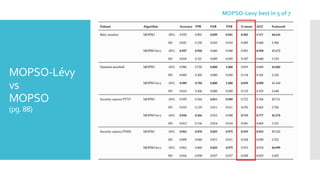
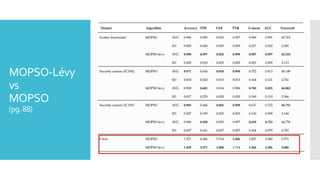
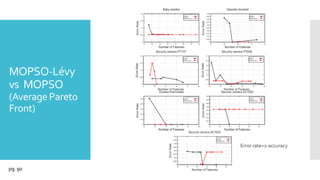
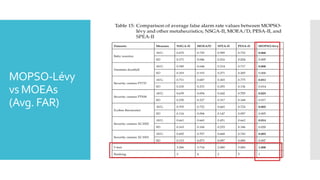
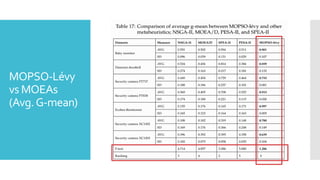
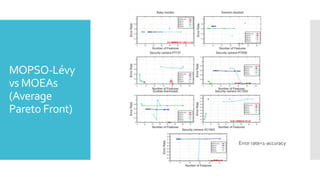
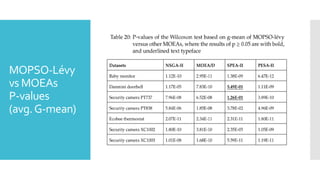
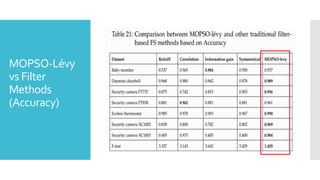
The document discusses a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm-based approach to intrusion detection for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, highlighting the increasing importance of IoT security due to the projected growth of connected devices. It compares the effectiveness of a modified Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) against traditional methods, emphasizing its superior performance in identifying anomalies in IoT networks. The study concludes that the proposed machine learning-based IDS is a promising solution for enhancing IoT security.