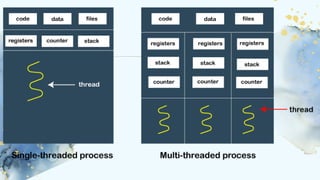
This document discusses multithreading processors, which can execute multiple tasks simultaneously to improve performance and efficiency. It highlights the benefits of multithreading such as increased throughput, improved responsiveness, and efficient resource utilization, as well as challenges like thread safety and complexity. The document also covers different types and models of multithreading, future trends, and concludes that multithreading is vital for advanced computer performance.