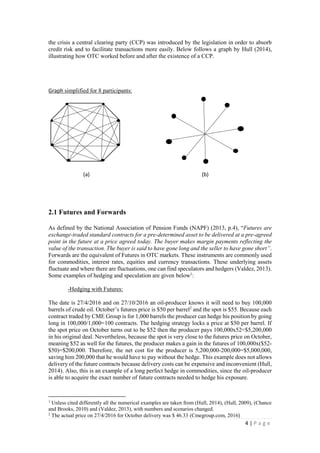
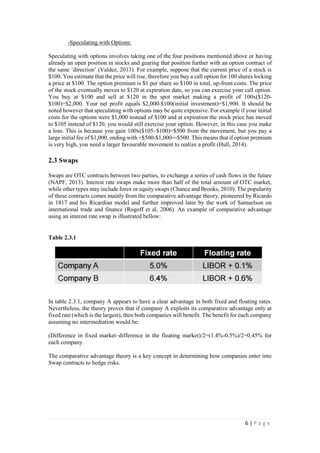
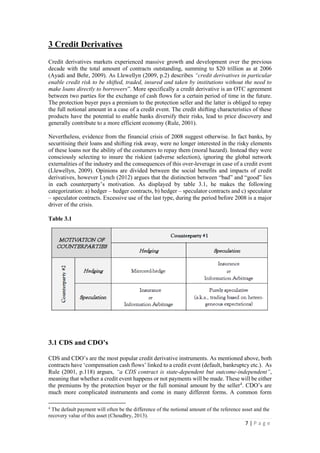
This document discusses how derivative instruments can be used for hedging risks or speculative positions. It provides examples of how futures, forwards, options, swaps, credit default swaps (CDS), and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) can be used for both hedging and speculation. For hedging, examples show how an oil producer can lock in future prices using futures to offset price risk. For speculation, examples demonstrate how anticipating future price movements allows gains by taking positions in derivative markets. The document also discusses debates around whether firms truly hedge or speculate with derivatives, and categorizes different types of counterparties in credit derivative markets.





![9 | P a g e
5 References
Acharya, V. and Richardson, M. (2009). Restoring financial stability. Hoboken, N.J.: John
Wiley & Sons.
Adam, T. and Fernando, C. (2003). Are there speculative components in corporate hedging
and do they add value?. [online] Repository.ust.hk. Available at: http://repository.ust.hk
/ir/Record/1783.1-217 [Accessed 26 Apr. 2016].
Allayannis, G. and Ofek, E. (2001). Exchange rate exposure, hedging, and the use of foreign
currency derivatives. Journal of International Money and Finance, 20(2), pp.273-296.
Ayadi, R. and Behr, P. (2009). On the necessity to regulate credit derivatives markets. J Bank
Regul, 10(3), pp.179-201.
Brown, G., Crabb, P. and Haushalter, D. (2003). Are Firms Successful at 'Selective' Hedging?.
SSRN Electronic Journal.
Call-options.com. (2016). European Call Option, European Put Options. [online] Available at:
http://www.call-options.com/european-call-option.html [Accessed 29 Apr. 2016].
Cassidy, J. (2013). Why Do Banks Go Rogue: Bad Culture or Lax Regulation? - The New
Yorker. [online] The New Yorker. Available at:
http://www.newyorker.com/news/johncassidy/why-do-banks-go-rogue-bad-culture-or-lax-
regulation [Accessed 2 May 2016].
Chance, D. and Brooks, R. (2010). An introduction to derivatives and risk management.
Mason, OH: Thomson/South-Western.
Chernenko, S. and Faulkender, M. (2011). The Two Sides of Derivatives Usage: Hedging and
Speculating with Interest Rate Swaps. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 46(06),
pp.1727-1754.
Choudhry, M. (2013). An introduction to credit derivatives. Oxford, UK: Elsevier Butterworth-
Heinemann.
Cmegroup.com. (2016). Crude Oil Futures - CME Group. [online] Available at:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mscproject-hedgingvsspeculatingwithderivativeinstruments-161205183802/85/Msc-Project-Hedging-vs-Speculating-with-derivative-instruments-9-320.jpg)
![10 | P a g e
http://www.cmegroup.com/trading/energy/crude-oil/light-sweet-crude.html [Accessed 27 Apr.
2016].
Comstock, C. (2016). The Complete Story Of What Really Happened Between Goldman,
Paulson, ACA, IKB, And ABN. [online] Business Insider. Available at:
http://www.businessinsider.com/a-timeline-of-goldmans-abacus-trade-with-paulson-aca-
ikband-2010-4?op=1&IR=T [Accessed 2 May 2016].
Fincad.com. (2016). Types of Credit Derivatives | Derivatives Risk Management Software &
Pricing Analytics | FINCAD. [online] Available at:
http://www.fincad.com/resources/resource-library/wiki/types-credit-derivatives [Accessed 30
Apr. 2016].
Fletcher, G. (2013). Hazardous Hedging: The (Unacknowledged) Risks of Hedging with Credit
Default Swaps. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Hentschel, L. and Kothari, S. (2001). Are Corporations Reducing or Taking Risks with
Derivatives?. The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 36(1), p.93.
Hull, J. (2009). Solutions manual [to accompany] Options, futures, and other derivatives.
Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Hull, J. (2014). Fundamentals of Futures and Option Markets. 8th ed. Upper Saddle River, N.J.:
Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Llewellyn, D. (2009). Financial Innovation and the economics of banking and the financial
system, financial innovation in retail and corporate banking. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
Lynch, T. (2012). Gambling by Another Name? The Challenge of Purely Speculative
Derivatives. SSRN Electronic Journal.
NAPF, (2013). Derivatives and risk management made simple. Cheapside House 138
Cheapside London EC2V 6AE: The National Association of Pension Funds Limited 2013.
Ricardo, D. (2001). On the principles of political economy and taxation. London: Electric
Book Co.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mscproject-hedgingvsspeculatingwithderivativeinstruments-161205183802/85/Msc-Project-Hedging-vs-Speculating-with-derivative-instruments-10-320.jpg)
![11 | P a g e
Rogoff, Kenneth, Aron Gottesman, Lall Ramrattan, and Michael Szenberg. 2006. “Paul
Samuelson's Contributions to Economics.” Samuelsonian Economics and the Twenty-First
Century. Oxford University Press.
Rule D. (2001) “Credit Derivatives Market: Its Development and Possible Implications for
Financial Stability”, Bank of England, Financial Stability Review, June, 2001
Stout, Lynn A., Derivatives and the Legal Origin of the 2008 Credit Crisis (June, 29 2011).
Harvard Business Law Review, Vol. 1, pp. 1-38, 2011; UCLA School of Law, Law-Econ
Research Paper No. 11-11. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1874806
Turbeville, W. (2013). Derivatives: Innovation In The Era of Financial Deregulation | Demos.
[online] Demos.org. Available at: http://www.demos.org/publication/derivatives-
innovationera-financial-deregulation [Accessed 26 Apr. 2016].
Valdez, S. (2013). An introduction to global financial markets. New York, NY: Palgrave
Macmillan.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mscproject-hedgingvsspeculatingwithderivativeinstruments-161205183802/85/Msc-Project-Hedging-vs-Speculating-with-derivative-instruments-11-320.jpg)