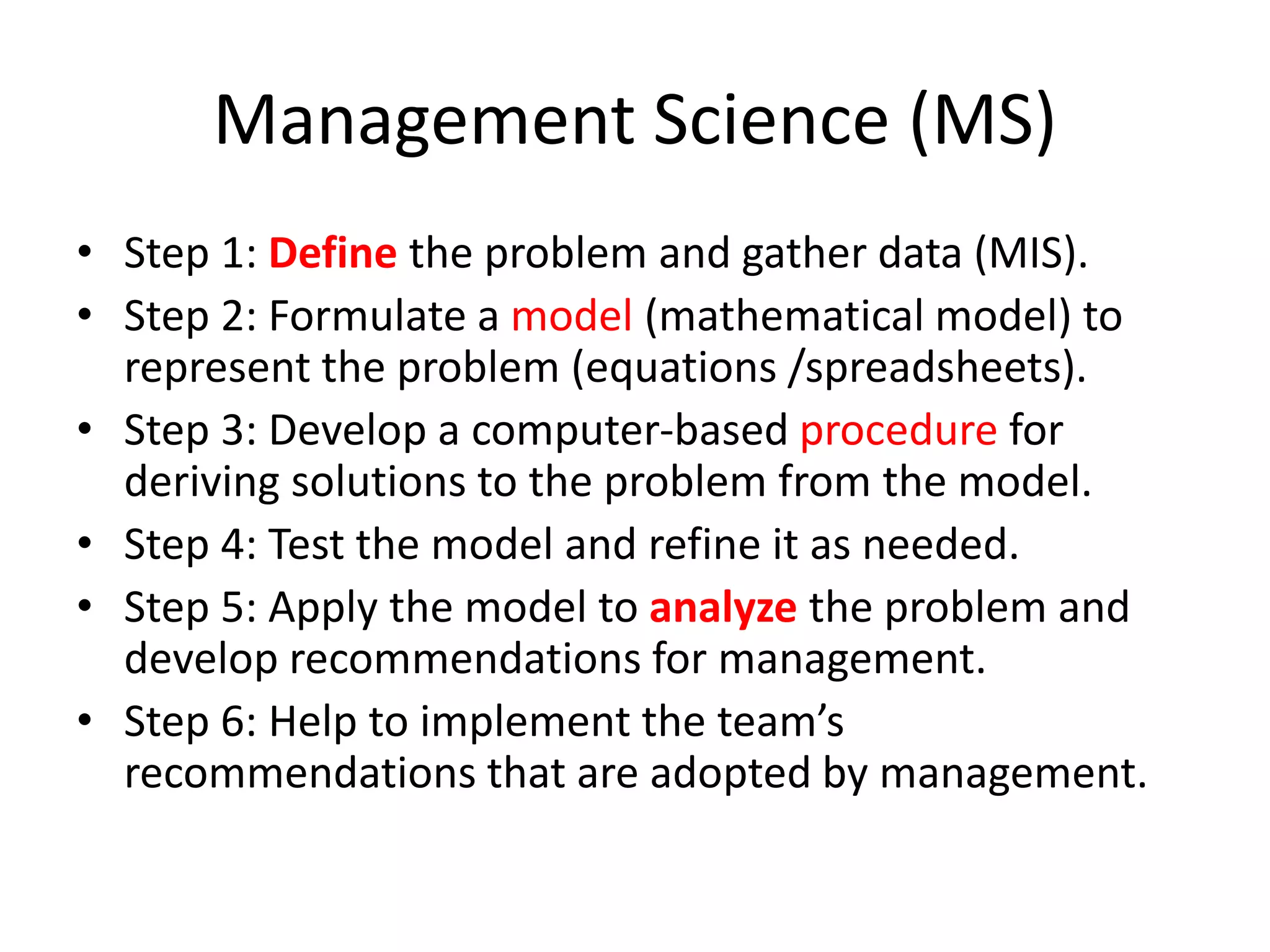
Management science (MS) is a discipline that uses scientific approaches to help managers make quantitative decisions. It involves developing mathematical models to represent problems, deriving solutions, and making recommendations to managers. While MS only considers quantitative factors, managers also weigh qualitative factors in their final decisions. The impact of MS includes improving organizational efficiency through applications in areas like transportation, healthcare, and the military.