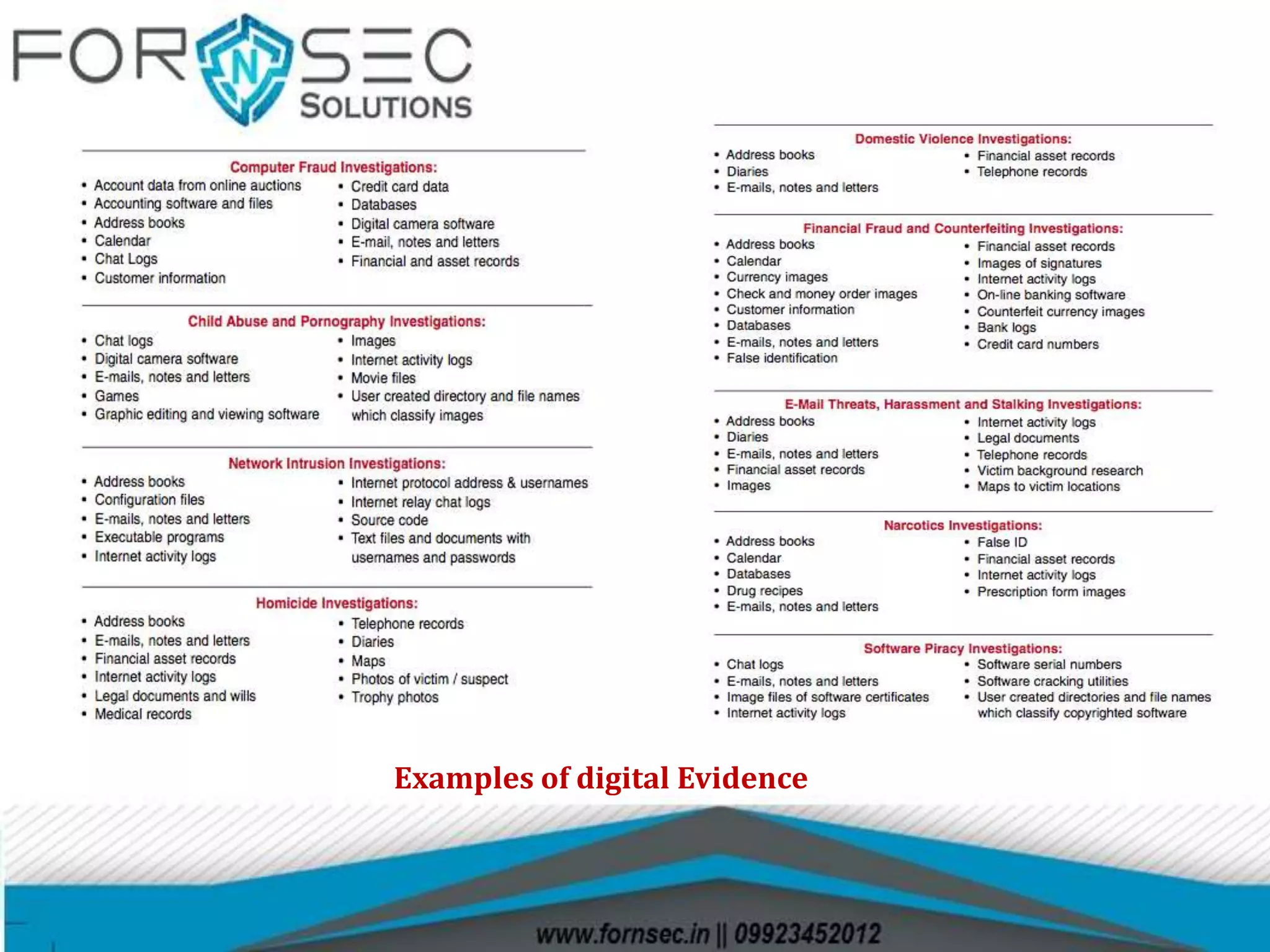
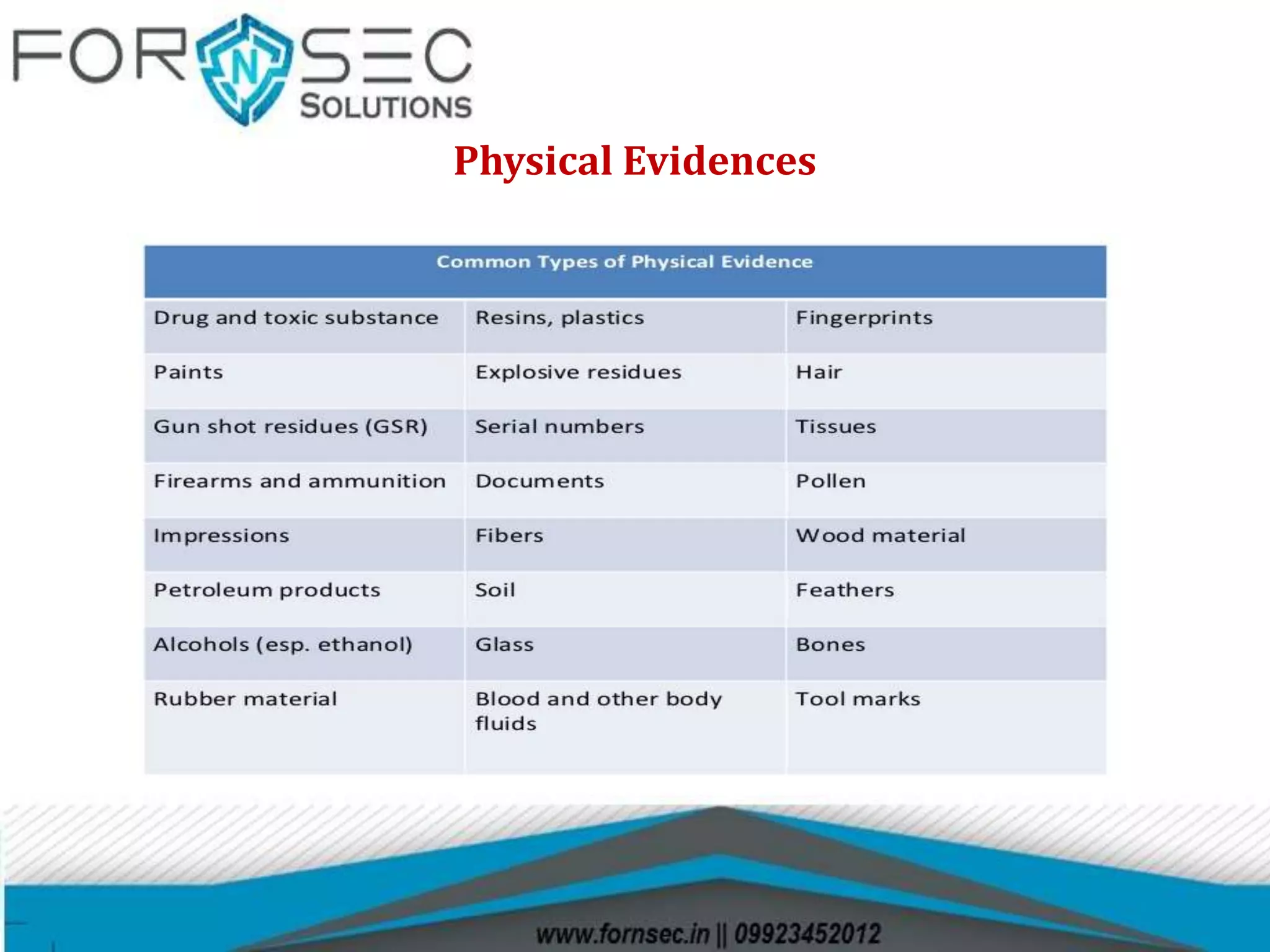
Digital forensics involves the recovery and investigation of digital information from devices such as computers and mobile phones. It has several sub-branches including computer forensics, mobile forensics, and network forensics. Digital evidence must be properly collected, documented, and maintained in the chain of custody to be admissible in court. Common tools used in digital forensic investigations include forensic software for imaging, data recovery, and analysis.