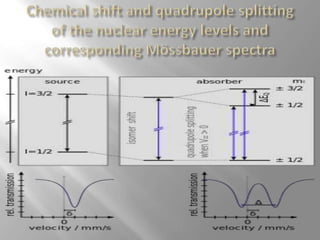
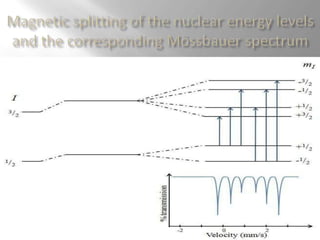
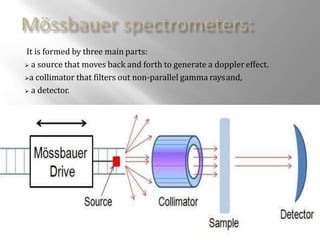
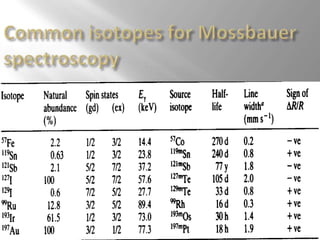
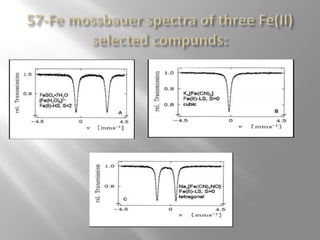
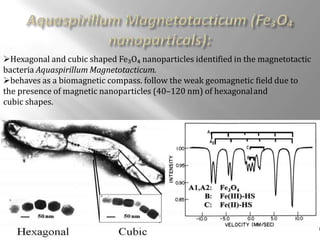
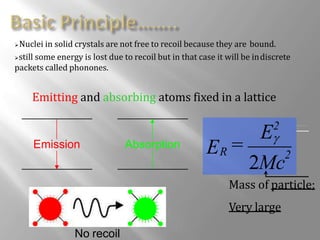
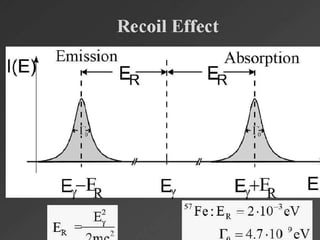
Mossbauer spectroscopy involves probing the nucleus of an atom using gamma rays. It can provide information about the chemical environment and oxidation state of the nucleus. Nuclei in solid crystals do not recoil when absorbing or emitting gamma rays, unlike free nuclei, allowing nuclear resonance to be observed. The technique involves exposing a solid sample to a beam of gamma rays and measuring the intensity of transmitted rays. Differences in chemical environments cause nuclear energy levels to shift, so the Doppler effect is used by accelerating the gamma ray source to produce resonances.








![Chemical Isomer Shift (IS) (): Arises out of the interaction between
nuclear charge density and the surrounding ‘s’ electron charge cloud. IS
can give information about the spin state as well as the co-ordination
number.
Isomer shift (chemical shift, CS) can be expressed using the formula
below:
CS = K (Re
2 – Rg
2) {[Ψs
2(0)]a – [Ψs
2(0)]b}
Physical meaning of this equation:
an increase in s electron density in 57-Fe spectrum gives a negative
shift because the change in the effective nuclear charge isnegative
an increase in s electron density in 119-Sn gives a positive shift due to
a positive change in overall nuclear charge
Oxidised ferric ions (Fe³⁺) have lower isomer shifts than ferrous ions
(Fe²⁺) because s electron density at the nucleus of ferric ions is greater
due to a weaker screening effect by d electrons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mossbauerspectroscopy-131108041016-phpapp021-230710131253-855b1c69/85/mossbauerspectroscopy-131108041016-phpapp02-1-pptx-11-320.jpg)