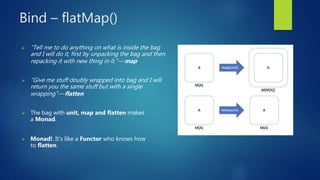
Monads are functional design patterns that wrap objects and provide two operations: identity (unit) and bind (flatMap). They follow three laws: left-identity, right-identity, and associativity. Common monads in Scala include List, Option, Future, and Try. Monads allow calculations to be chained together by passing the output of one as the input to the next.


![Identity - Unit ()
“Give me anything and I will hand it over to you wrapped in a bag. That’s my job.”—Unit
In case of our monad trait, if we give it a value of type A, it will return a value of type M[A].
In Scala, Unit is usually the apply method, a special method that doesn’t need to be named. A.apply()
is the same as A() which is the same as A{}.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monad-200926165817/85/Monad-3-320.jpg)
![Monad Laws
Left-identity law unit(x).flatMap(f) == f(x)
Right-identity law Monad[X].flatMap(unit) == Monad[X]
Associativity law m.flatMap(f).flatMap(g) == m.flatMap(x ⇒ f(x).flatMap(g))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monad-200926165817/85/Monad-5-320.jpg)
![Monads
List
Option
Future
Try
class mPackaging{
def flatMapOp(firstList : List[String], secondList : List[String] ):
List[String]= {
firstList.flatMap { x => secondList
.map { y => x + y }
}
}
}
object mPackaging{
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val monad = List("unit","bind")
val gift = List("packaging","opaeration")
println(apply.flatMapOp(monad, gift))
}
def apply: mPackaging = new mPackaging()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/monad-200926165817/85/Monad-6-320.jpg)
