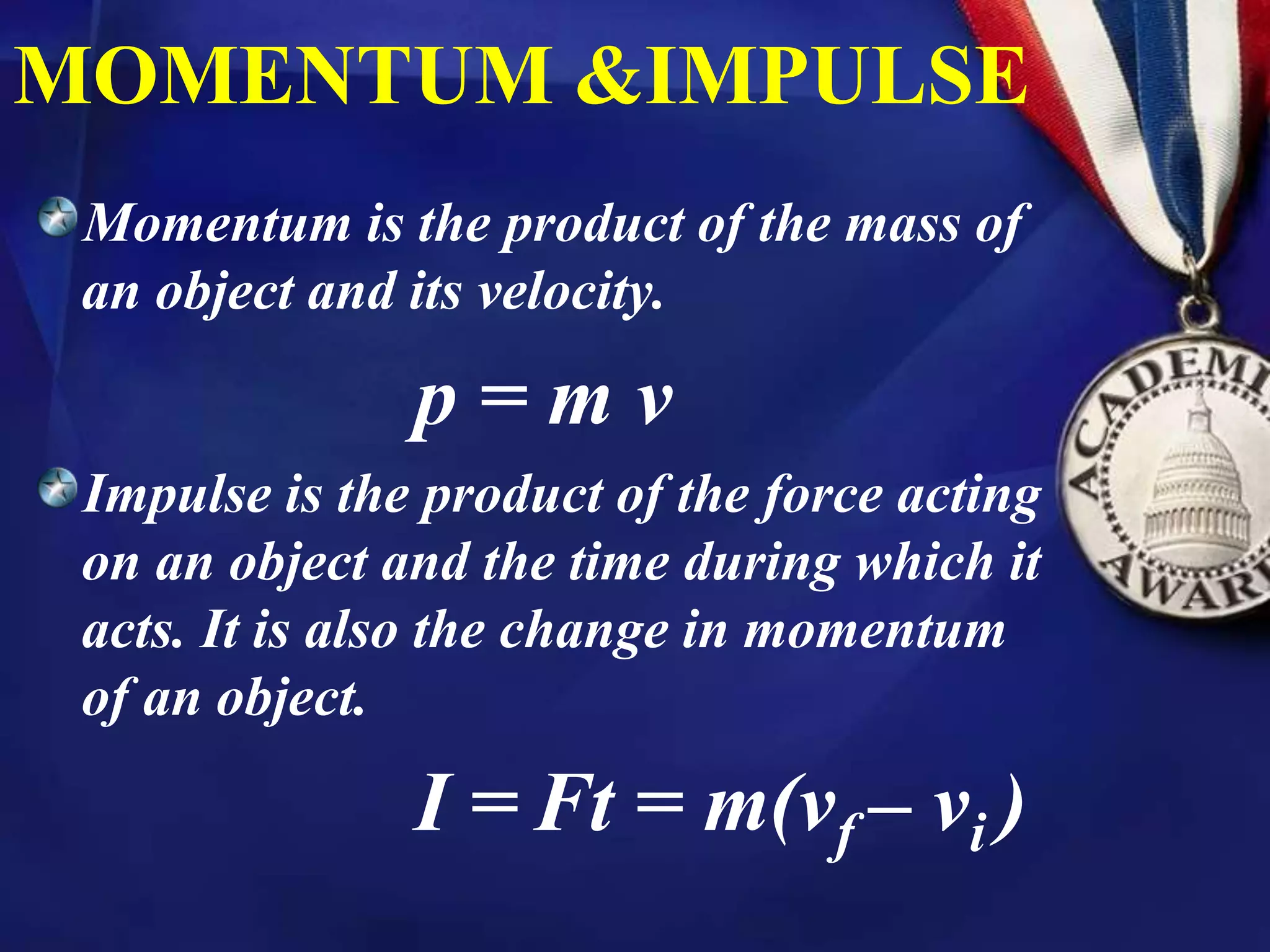
1) Momentum is the product of an object's mass and velocity. Impulse is the product of force acting on an object and the time during which it acts, and is also equal to the change in an object's momentum.
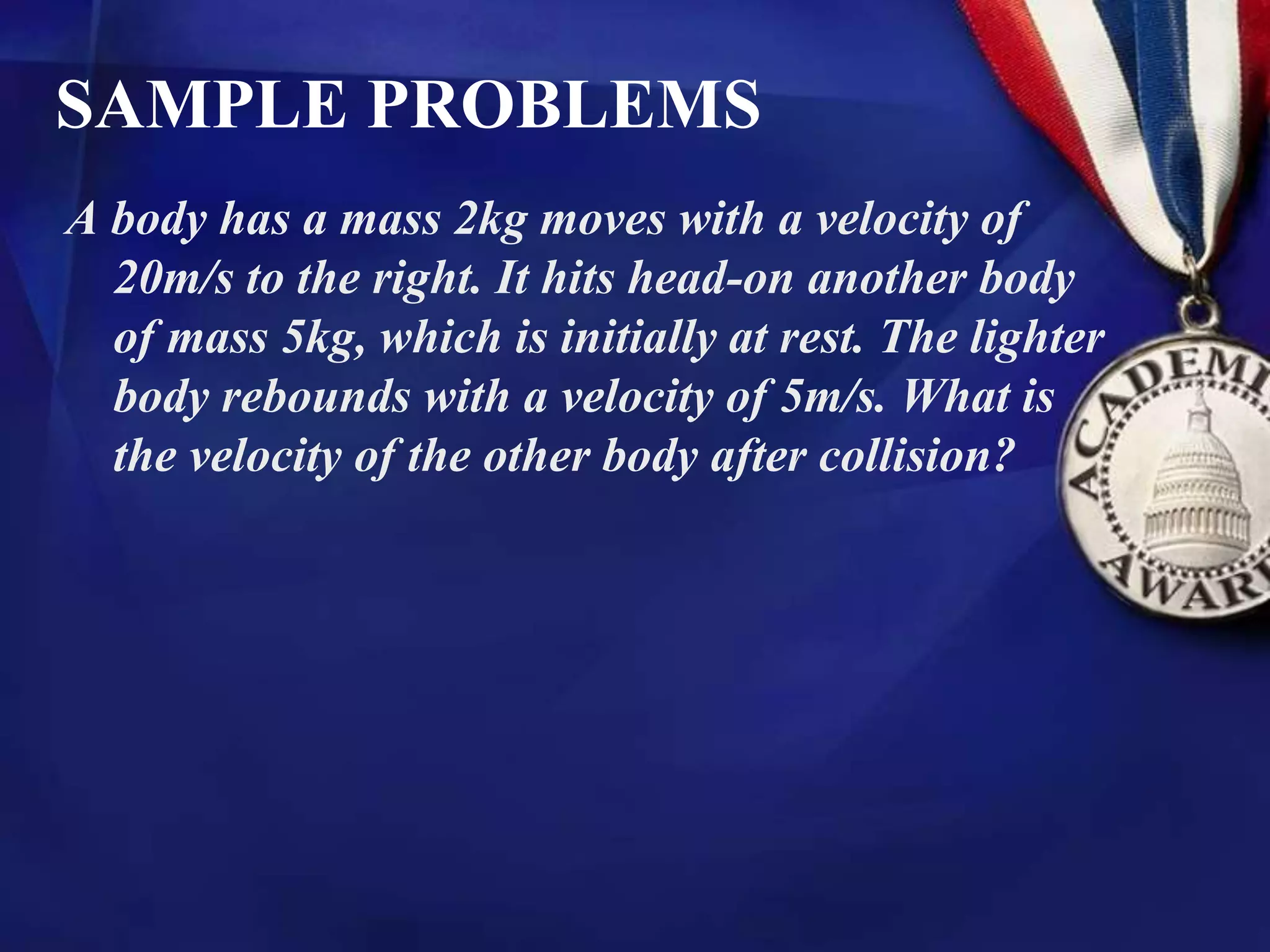
2) The document provides examples of calculating momentum, impulse, and changes in momentum for various scenarios involving objects with different masses and velocities.
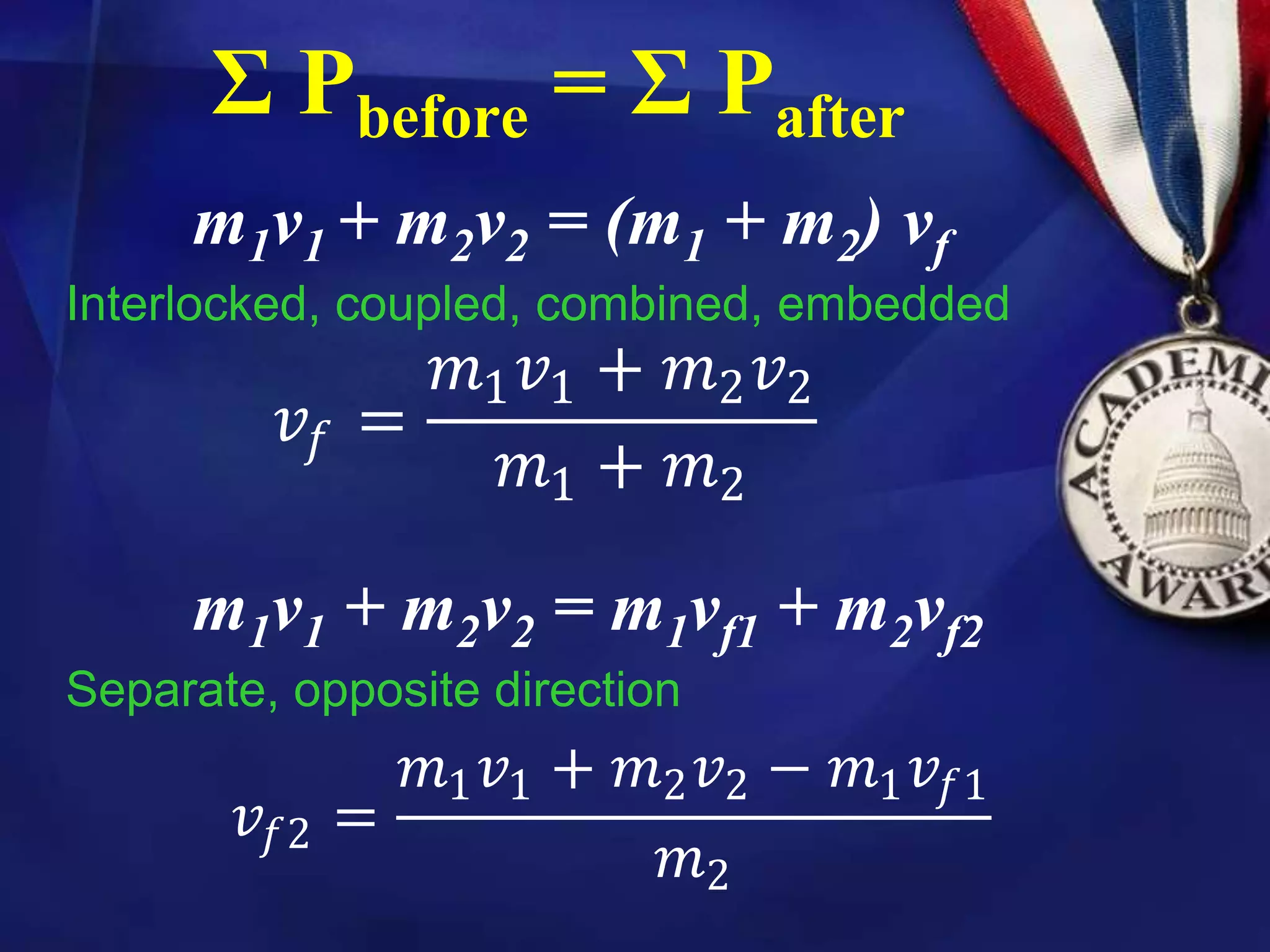
3) The law of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant, meaning the total momentum before an event involving only internal forces equals the total momentum after the event.