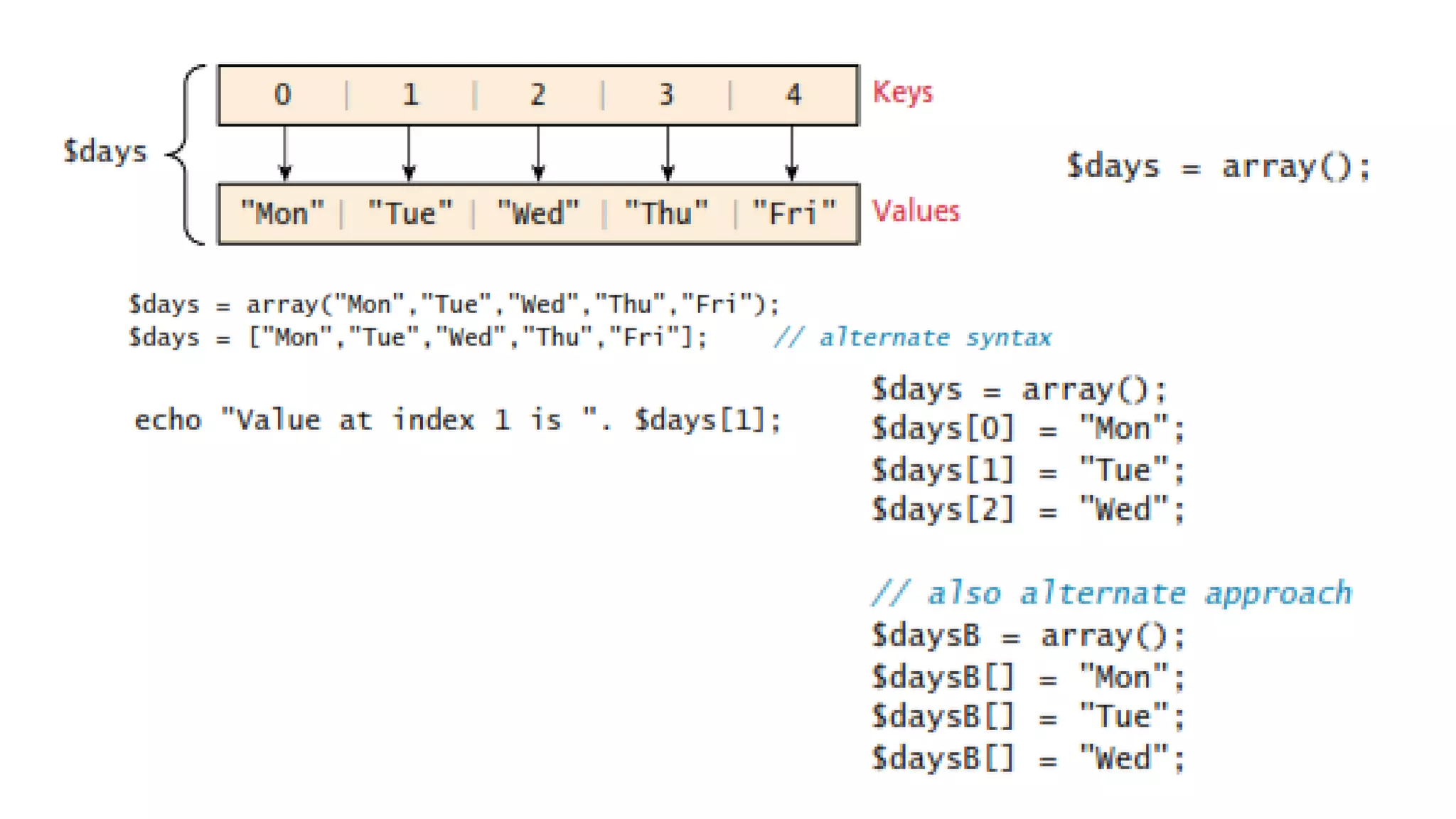
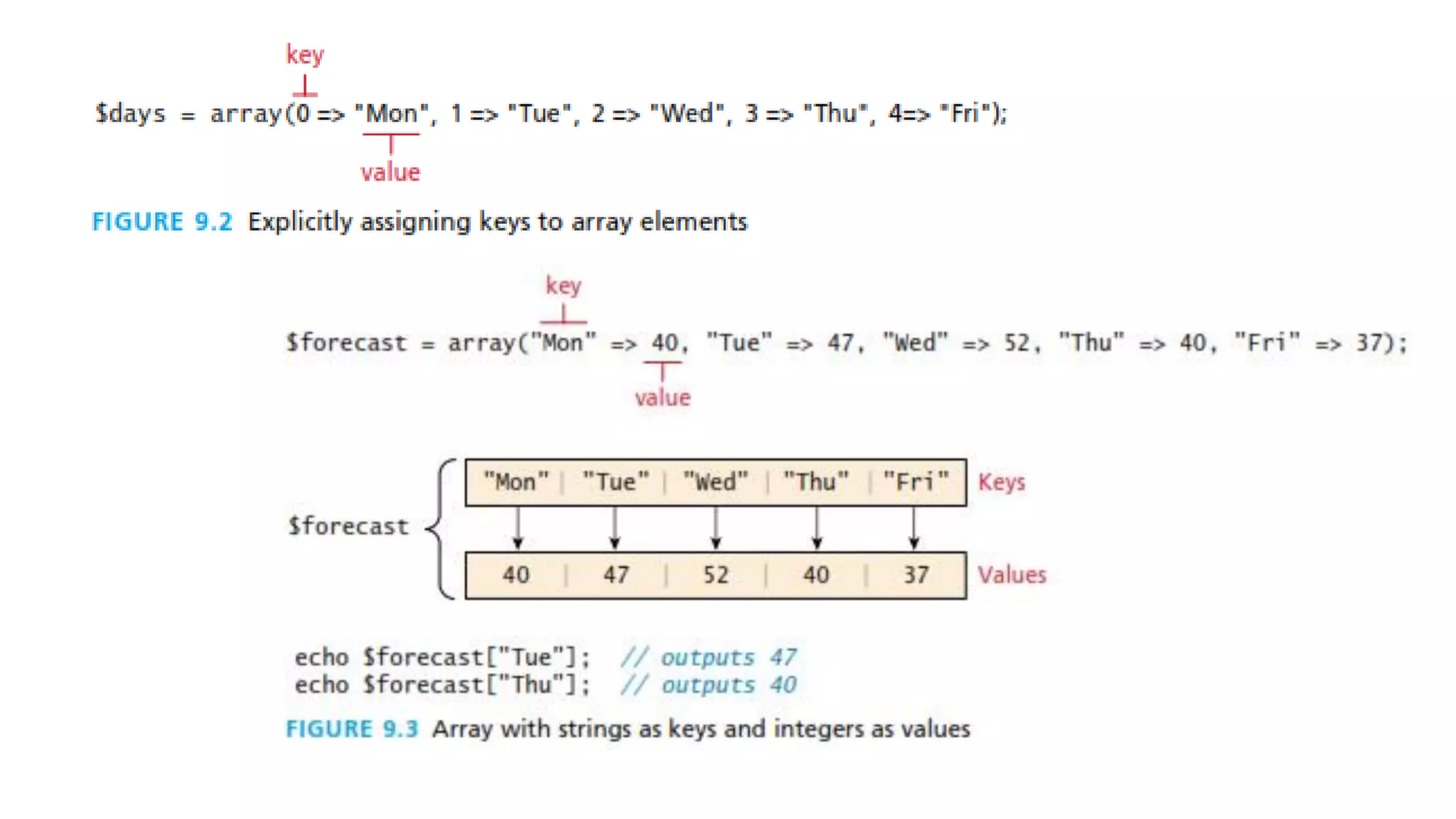
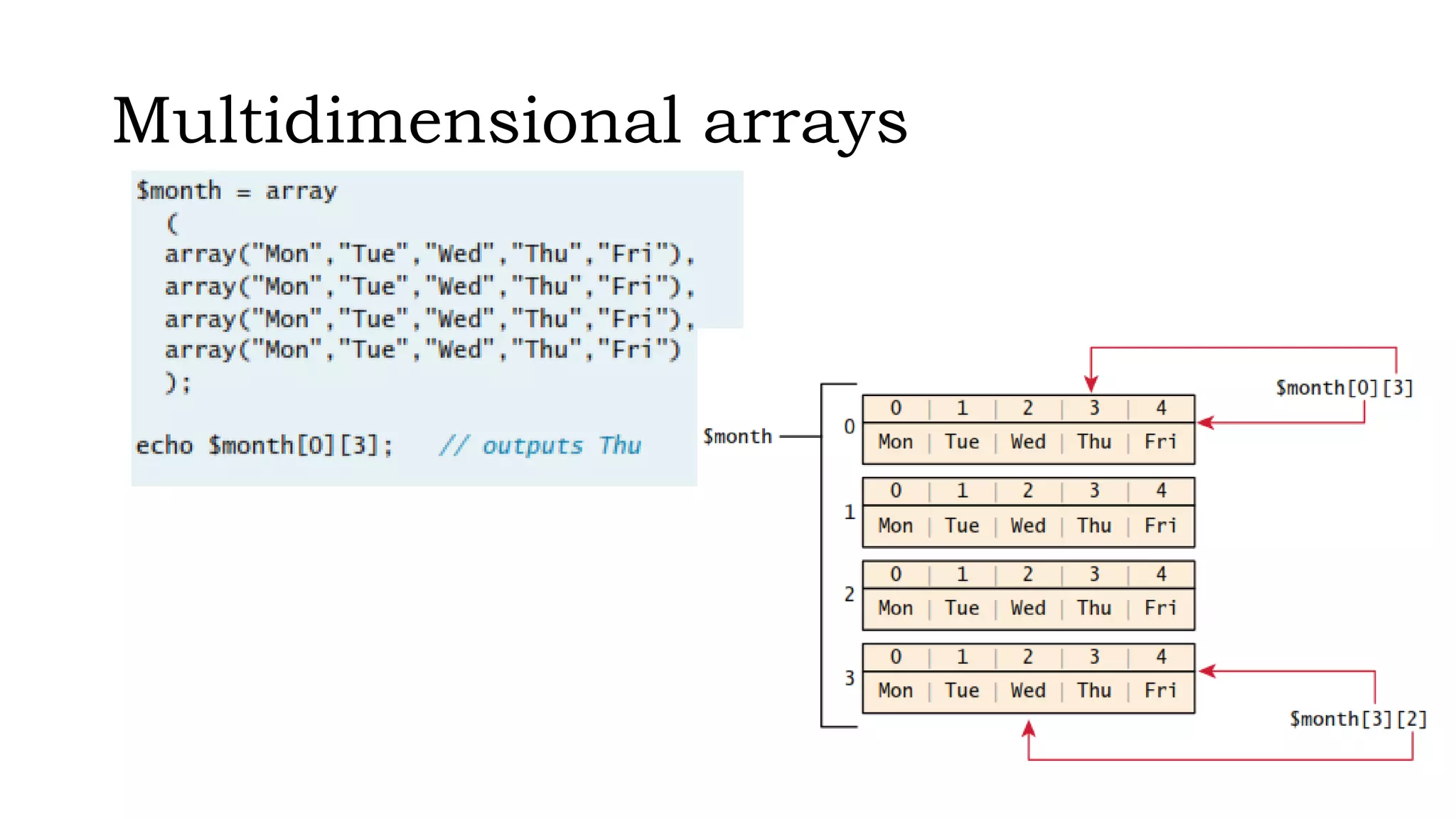
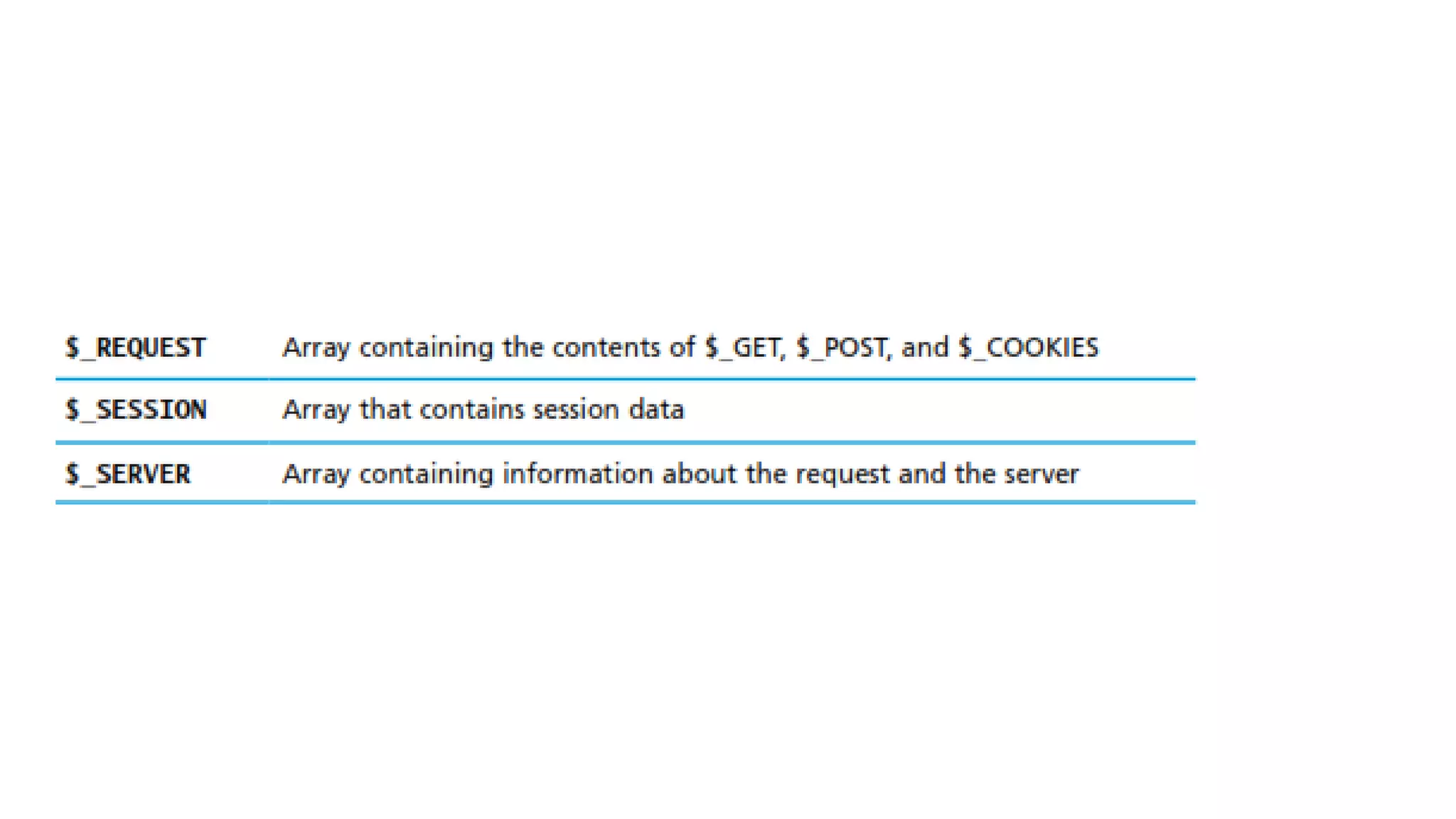
The document outlines the structure and functionality of PHP arrays, including multidimensional and superglobal arrays, which are always in scope for easy access. It explains error and exception handling in PHP, categorizing errors into expected errors, warnings, and fatal errors, and discusses error reporting settings and mechanisms for handling runtime errors. Additionally, it touches upon custom exception handlers to improve user experience and provide relevant application information during errors.