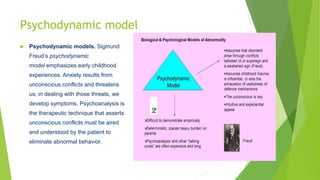
Normal behavior is defined as behavior that allows for satisfactory social adjustment and relationships. It represents optimal individual functioning that benefits the group. Abnormal behavior deviates from social norms in a pathological way that impairs individual and group well-being. Psychological abnormalities can be explained by various models, including biological models that emphasize genetic and neurological factors, psychodynamic models that focus on unconscious conflicts and early experiences, and behavioral models centered on learning through conditioning and consequences.