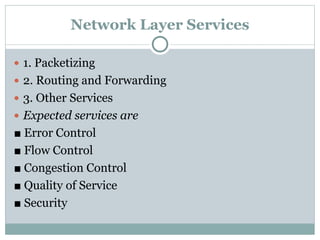
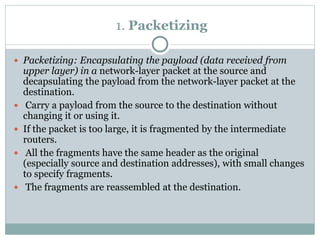
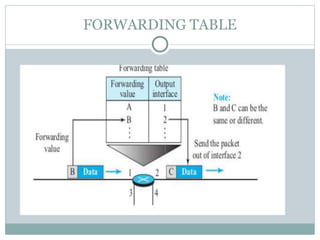
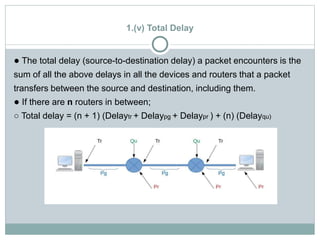
The document discusses network layer services and performance. It describes the key services as packetizing, routing, forwarding and other services like error control, flow control and congestion control. It then discusses various delays in network layer performance like transmission delay, propagation delay, processing delay and queuing delay. The total delay a packet experiences is the sum of these delays across all the devices and routers between source and destination.