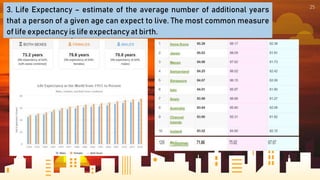
The document provides information about global cities and their characteristics. It begins by defining what a global city is, including that they are major nodes for information and money flows and facilitate specialized businesses. It then discusses characteristics of global cities such as having a large population, major international airport and advanced transportation systems. The document also identifies different tiers of global cities based on various indices that measure factors like business activity, human capital and cultural institutions. It concludes by discussing concepts in demography like birth rate, mortality rate and fertility rate.