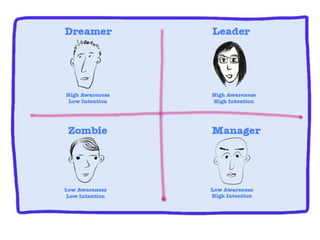
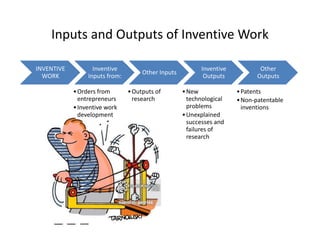
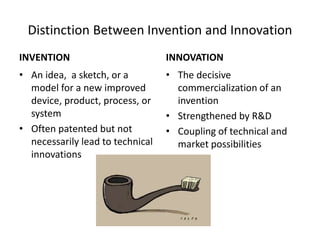
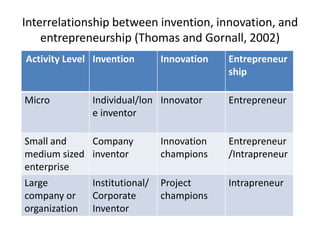
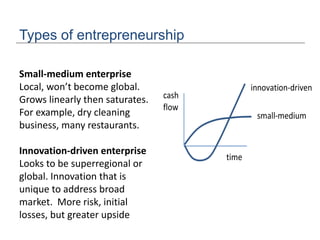
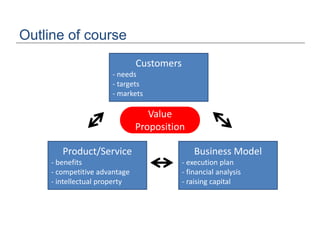
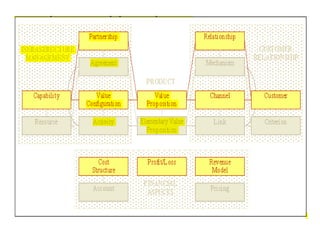
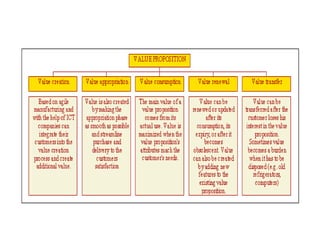
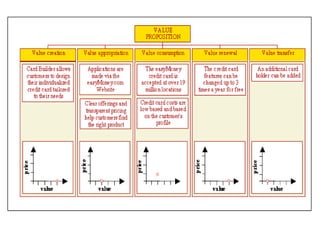
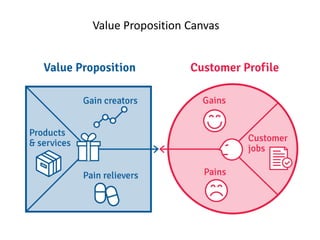
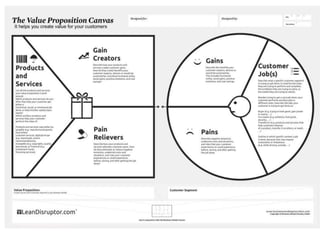
The document discusses the importance of technological innovation for small business survival, emphasizing the distinction between invention, innovation, and entrepreneurship. It outlines types of innovation and value propositions, detailing how to effectively address customer needs with a compelling offering. Additionally, it includes strategies for creating elevator pitches that articulate the value of a product or service.