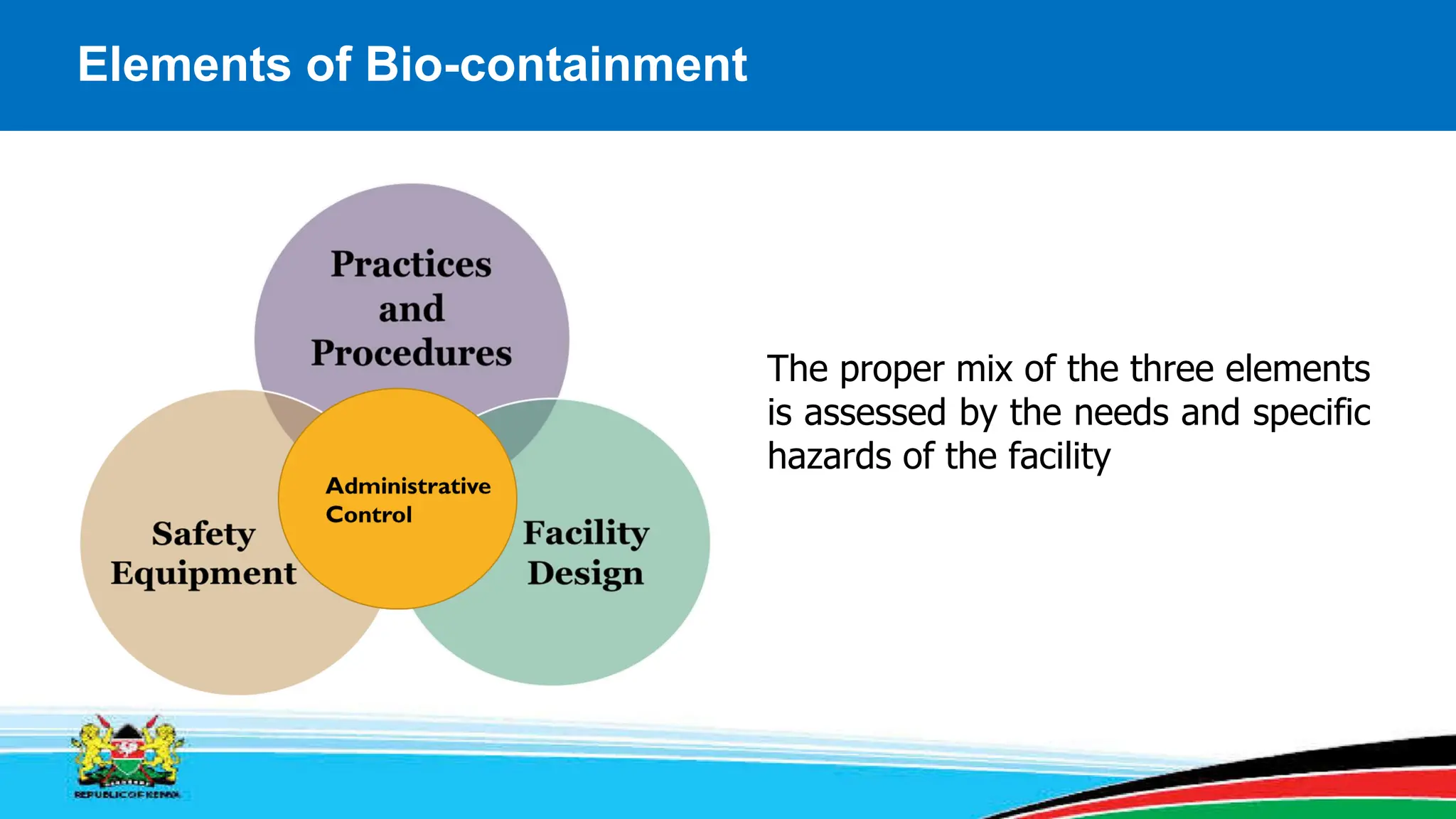
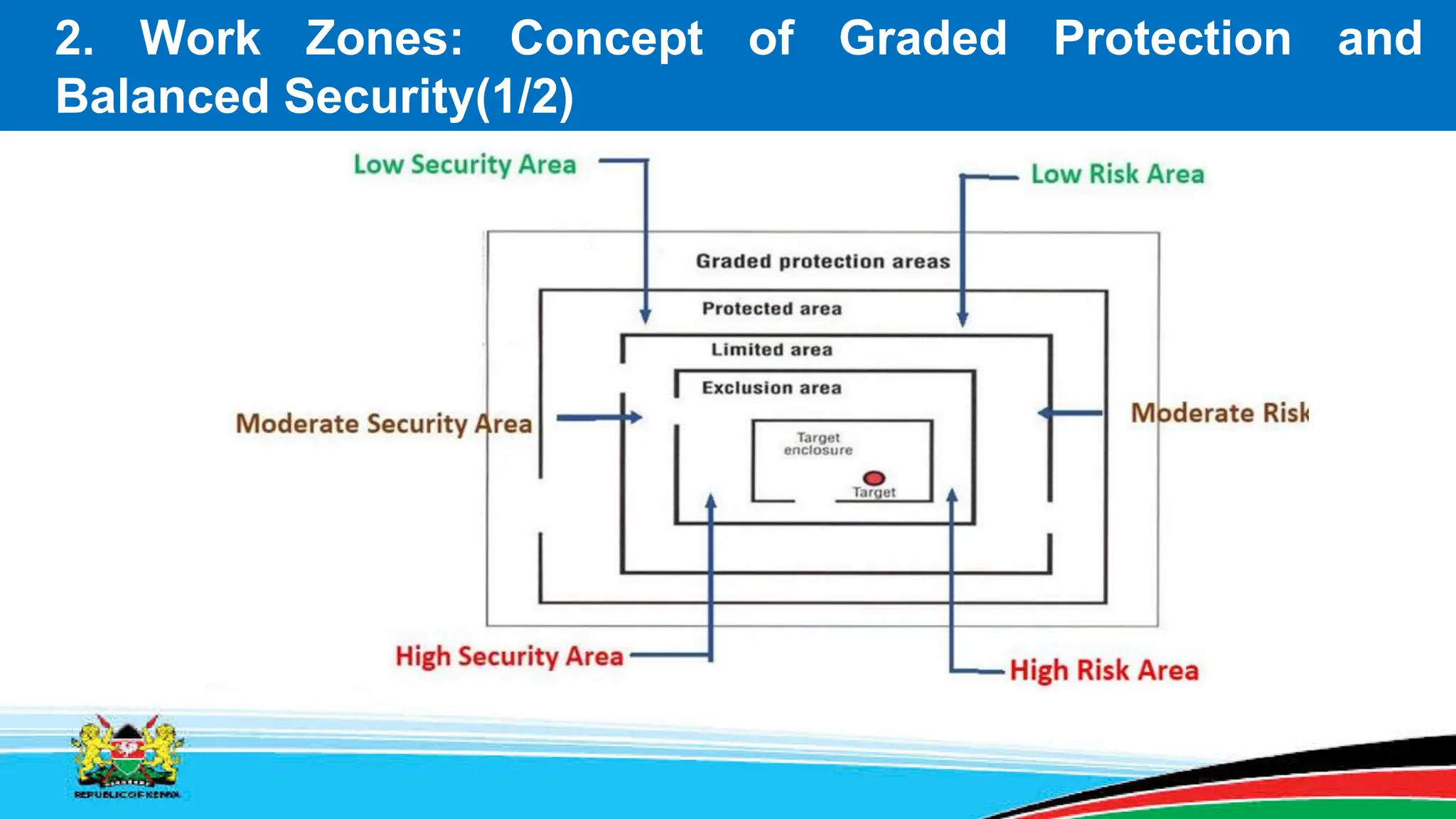
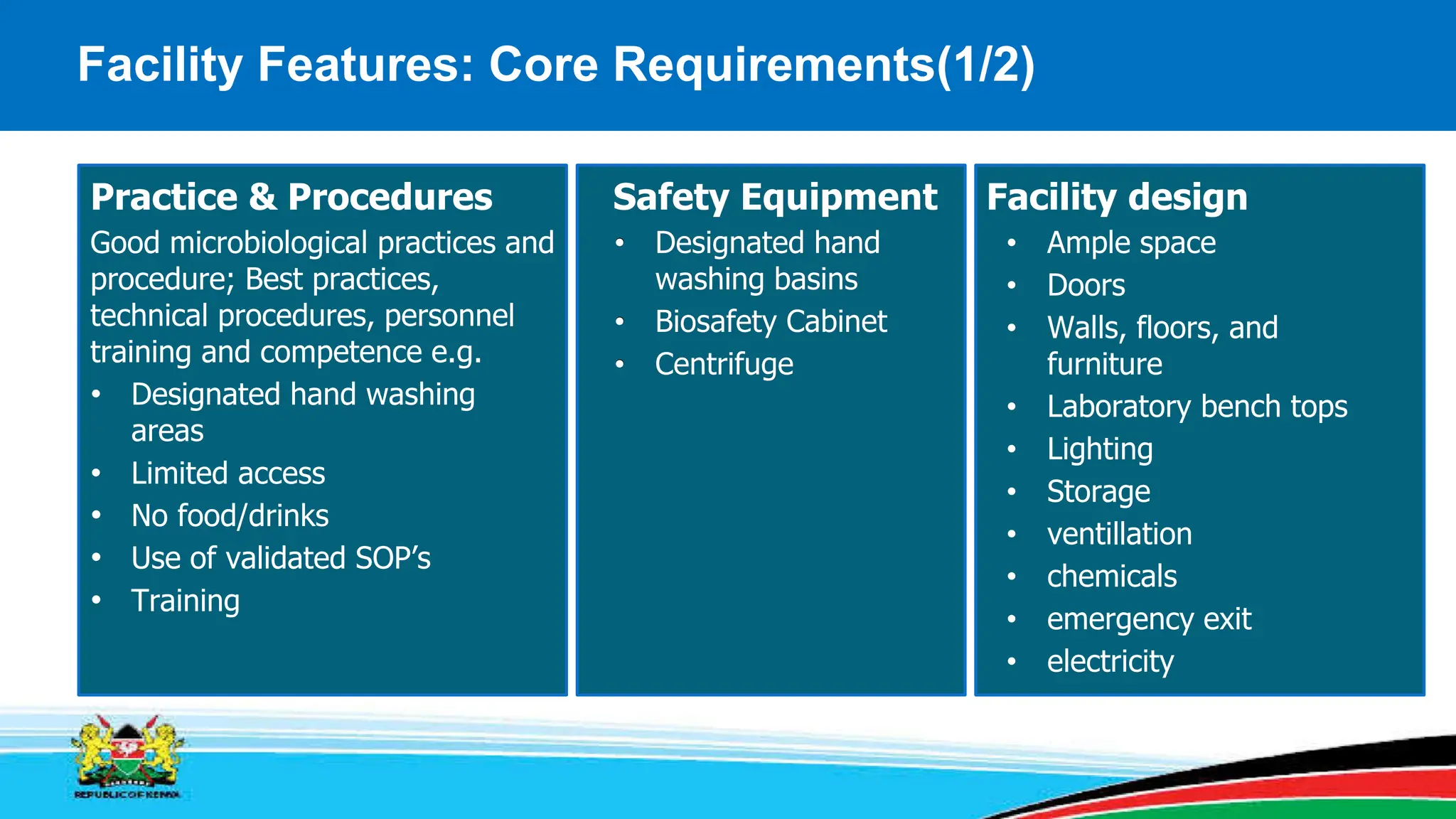
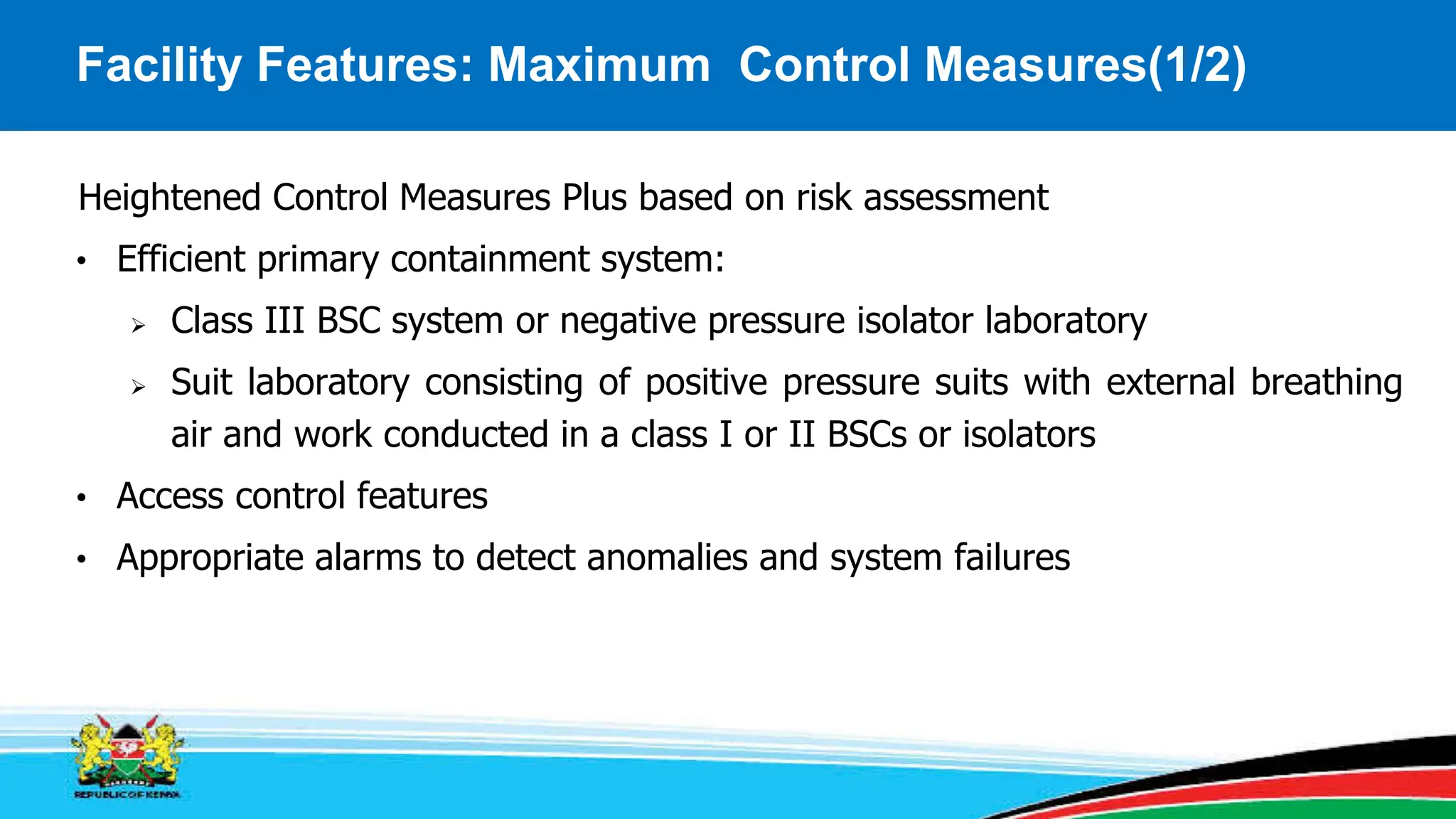
This module covers containment requirements in biocontainment, aiming to help learners define key terms, explain containment elements, and select appropriate facilities based on risk assessments. It details the elements of biocontainment, such as containment barriers and graded protection, while outlining facility design requirements for various containment levels. Participants are encouraged to engage in quizzes and discussions to reinforce learning outcomes.