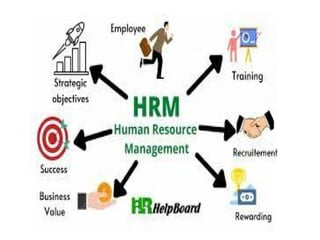
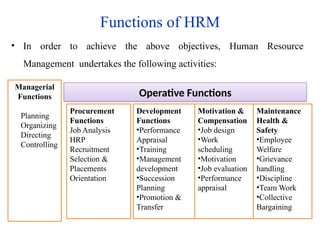
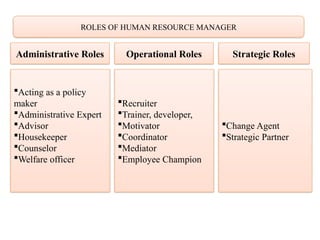
The document provides an overview of Human Resource Management (HRM), outlining its definition, functions, objectives, and scope. It highlights the importance of HRM in managing skilled workforce effectively to achieve organizational goals while addressing various aspects such as personnel management, welfare, industrial relations, and employee development. Additionally, it distinguishes HRM from Human Resource Development (HRD), emphasizing that HRD focuses on employee growth and training within the framework established by HRM.