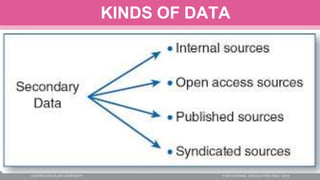
This document provides an overview of data including definitions of key terms like data, information, primary and secondary data sources, qualitative and quantitative data, and discrete and continuous variables. It discusses the importance of data for decision making, problem solving, innovation and more. The evolution of data storage technologies from the 1960s to present is reviewed, from punch cards to modern cloud storage. Primary data sources include surveys, interviews, observations and questionnaires, while secondary data comes from published sources like books, journals, newspapers and websites.