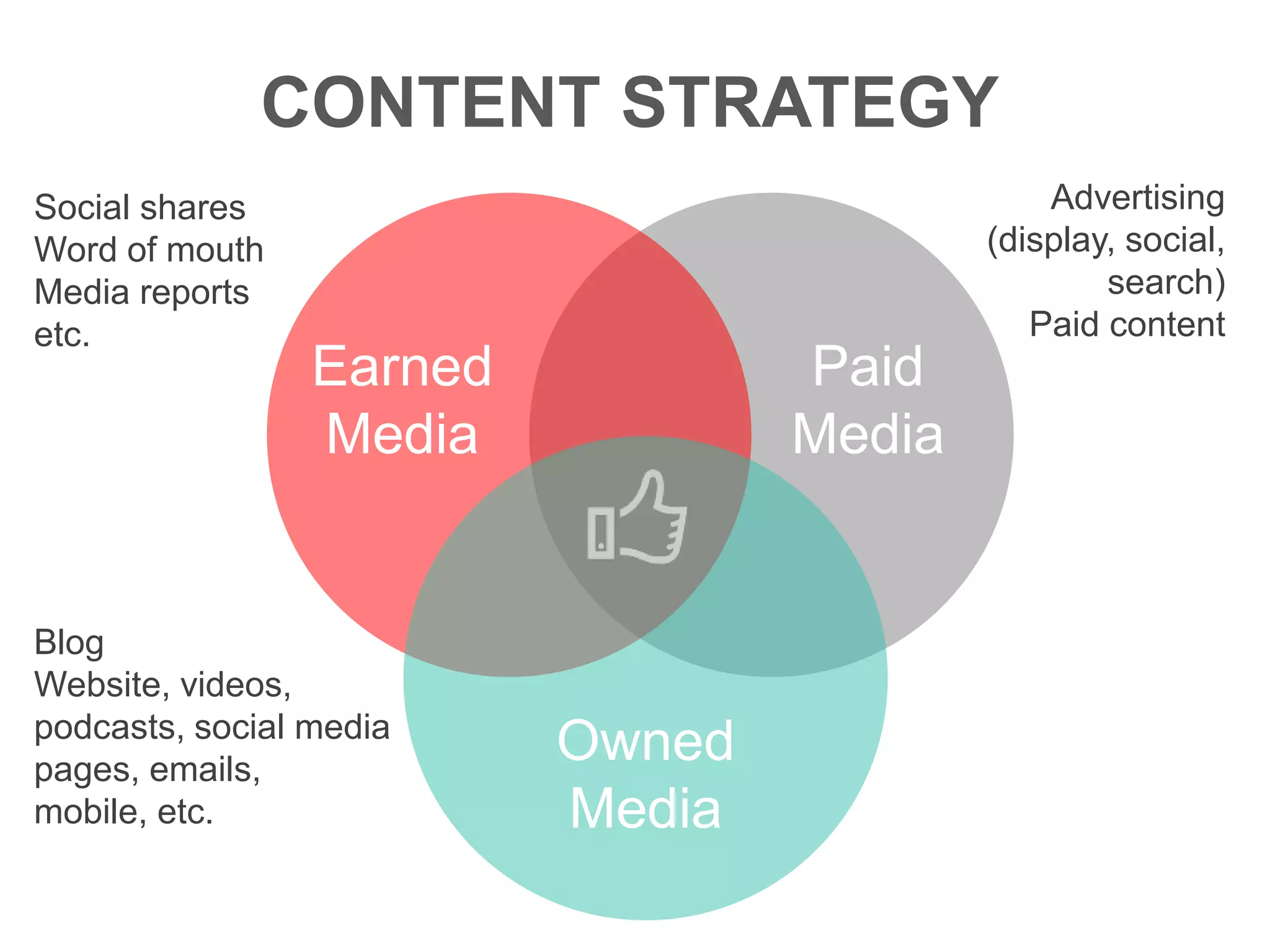
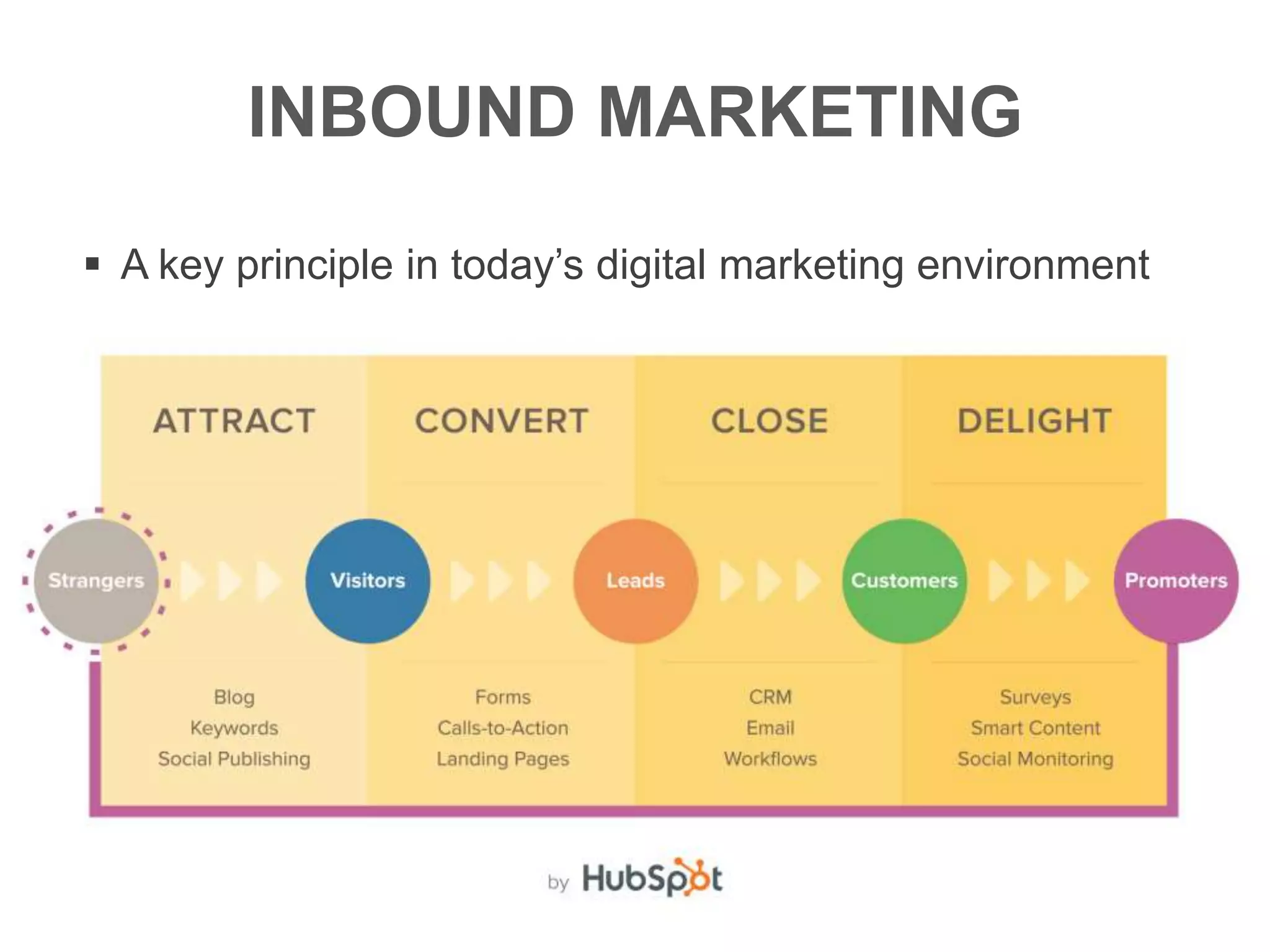
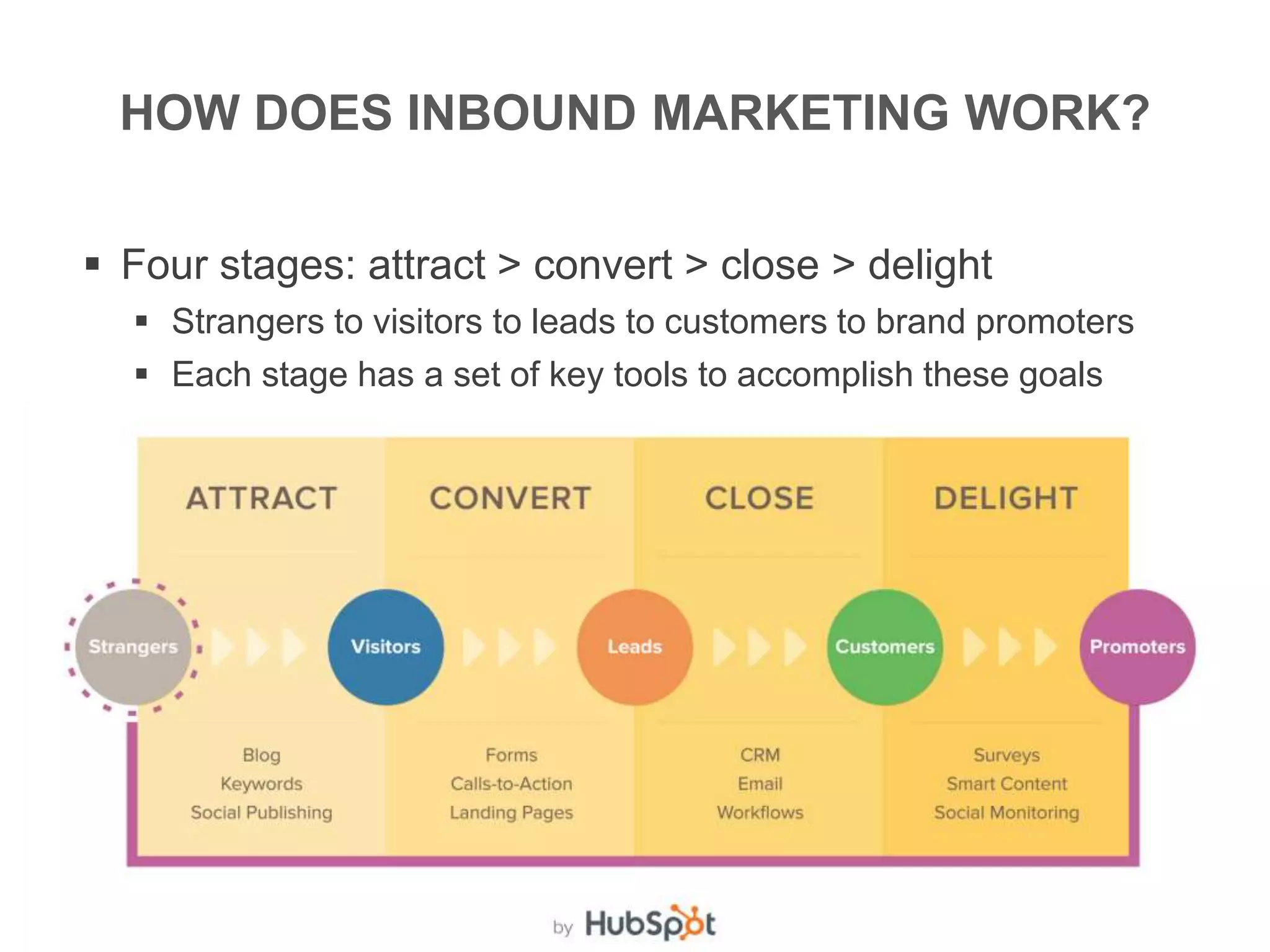
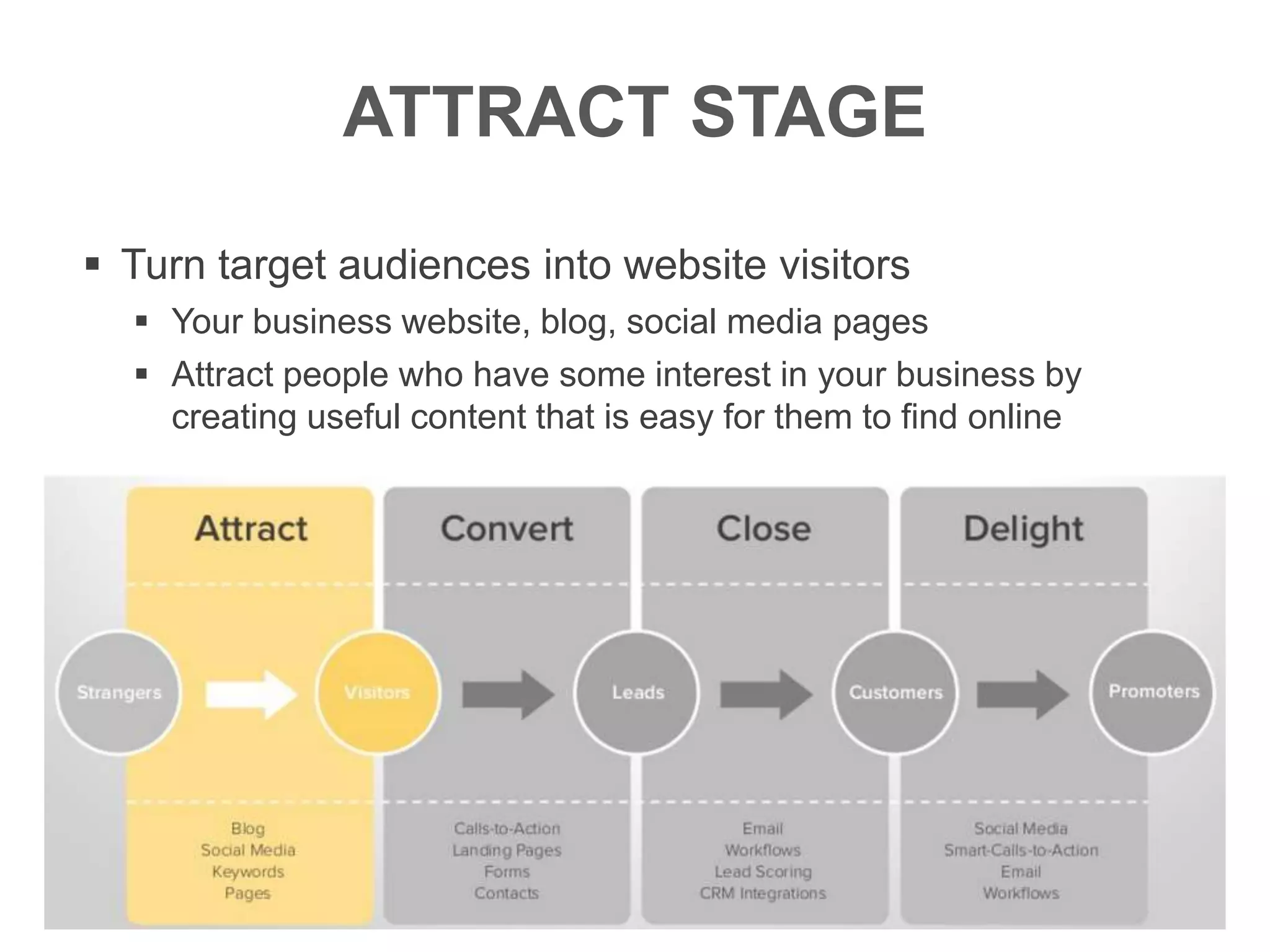
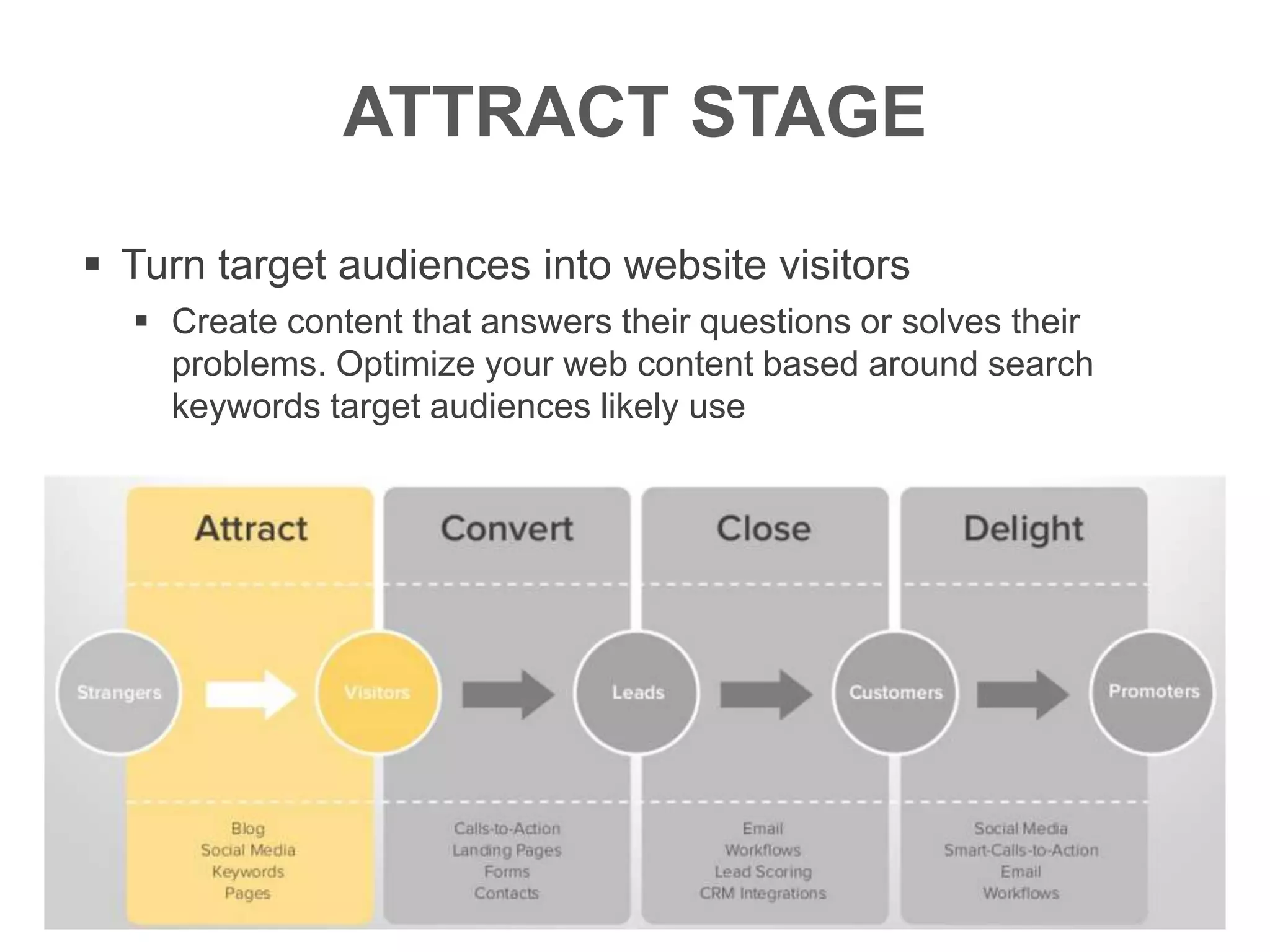
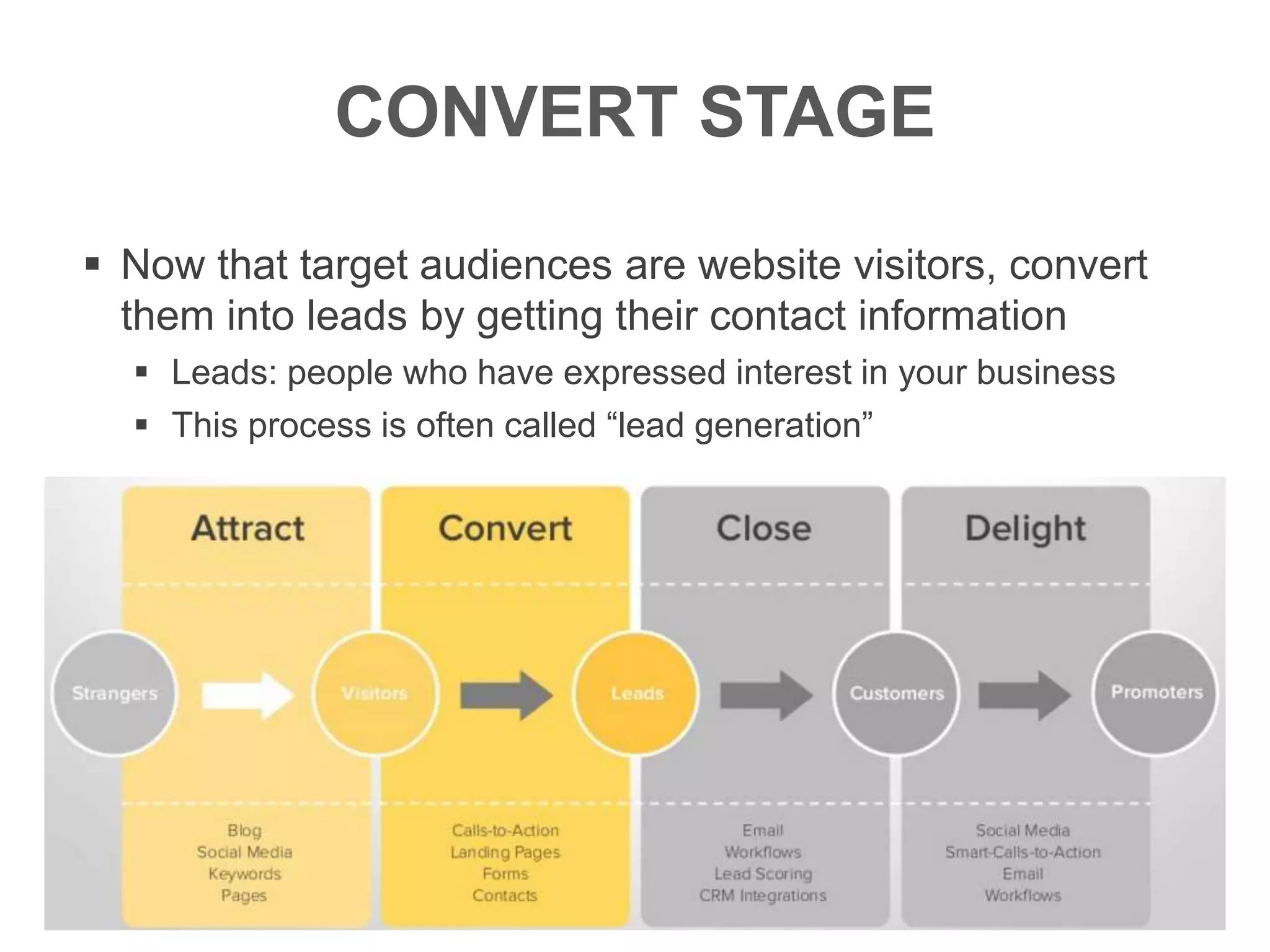
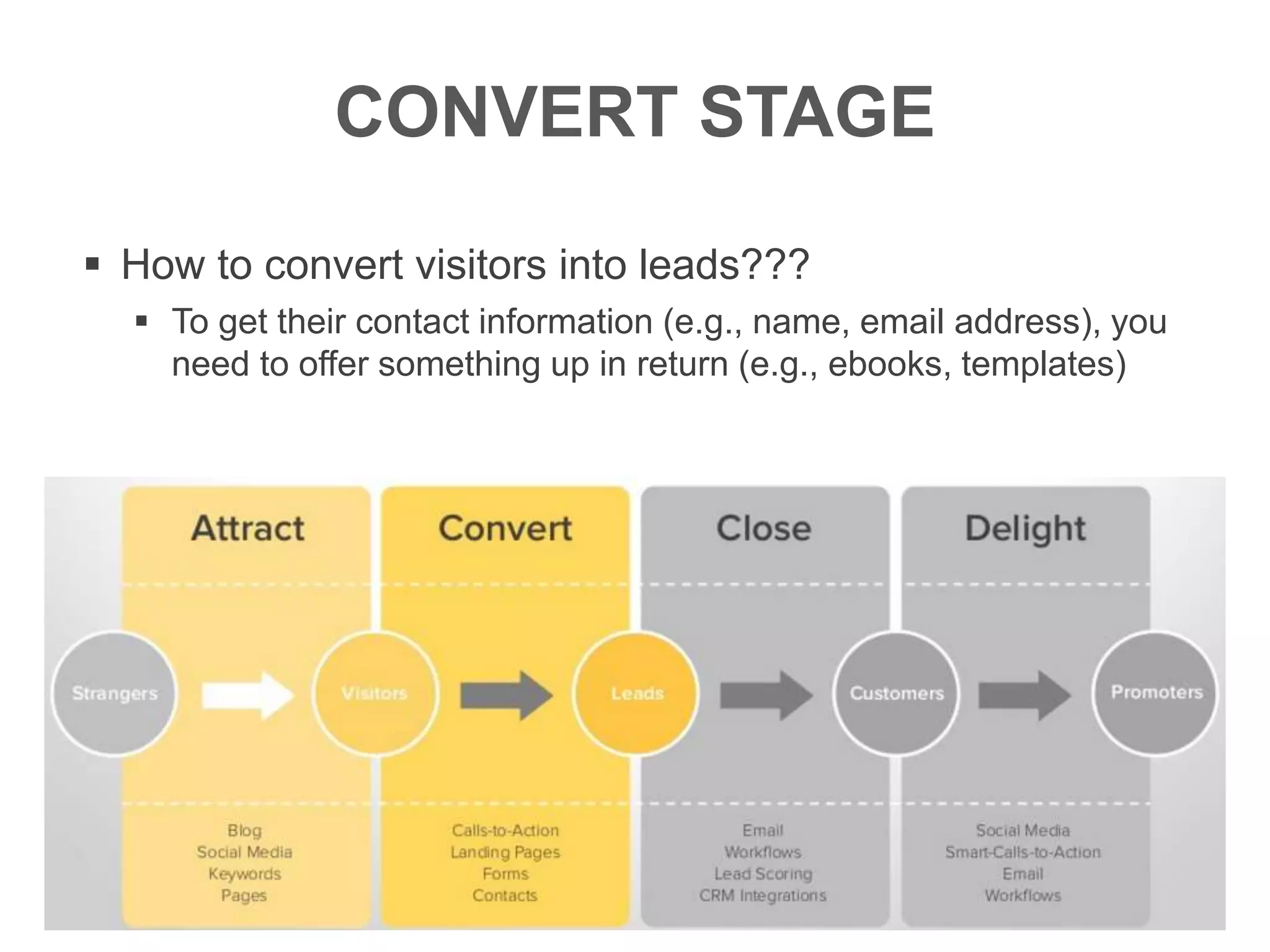
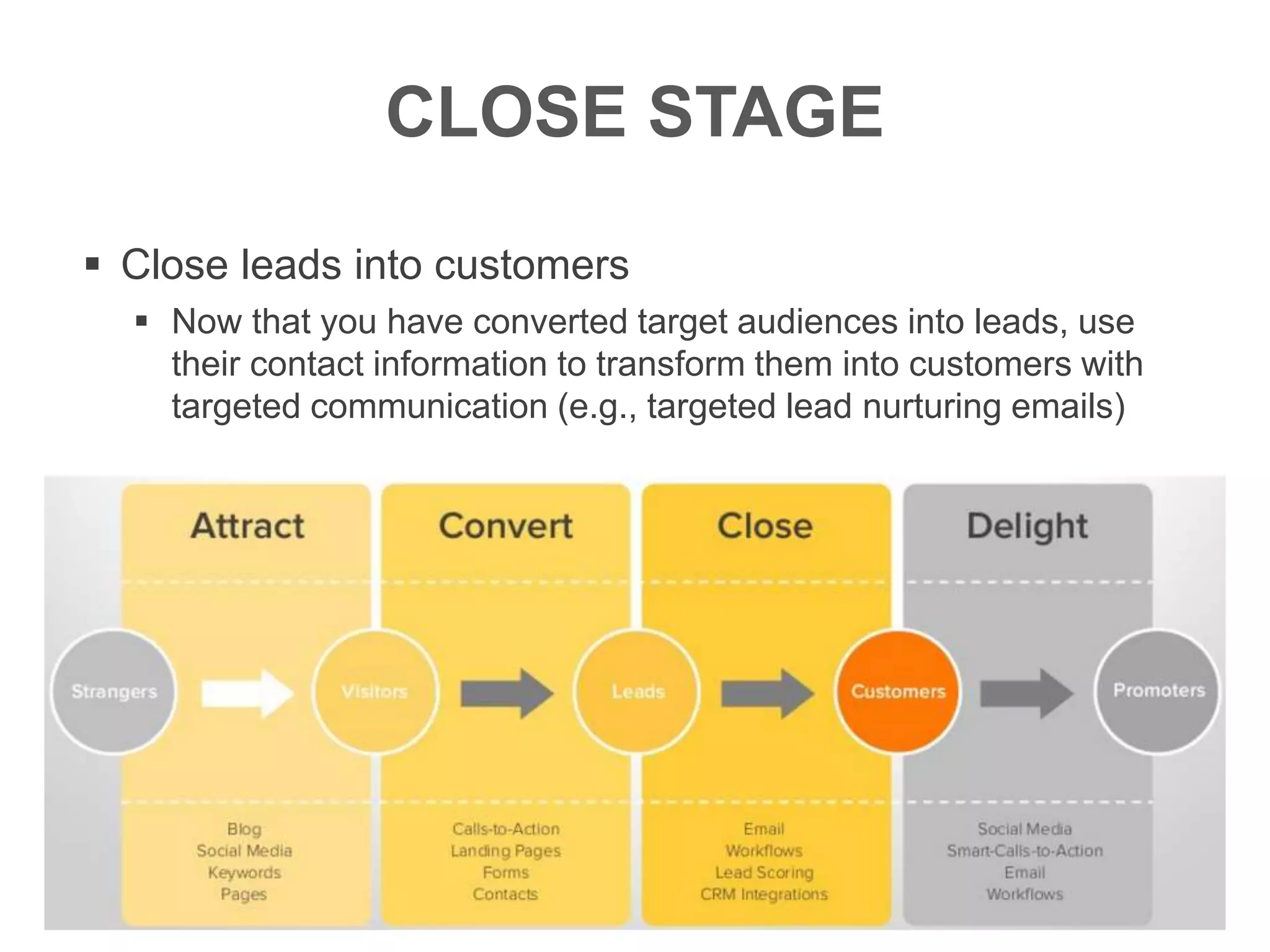
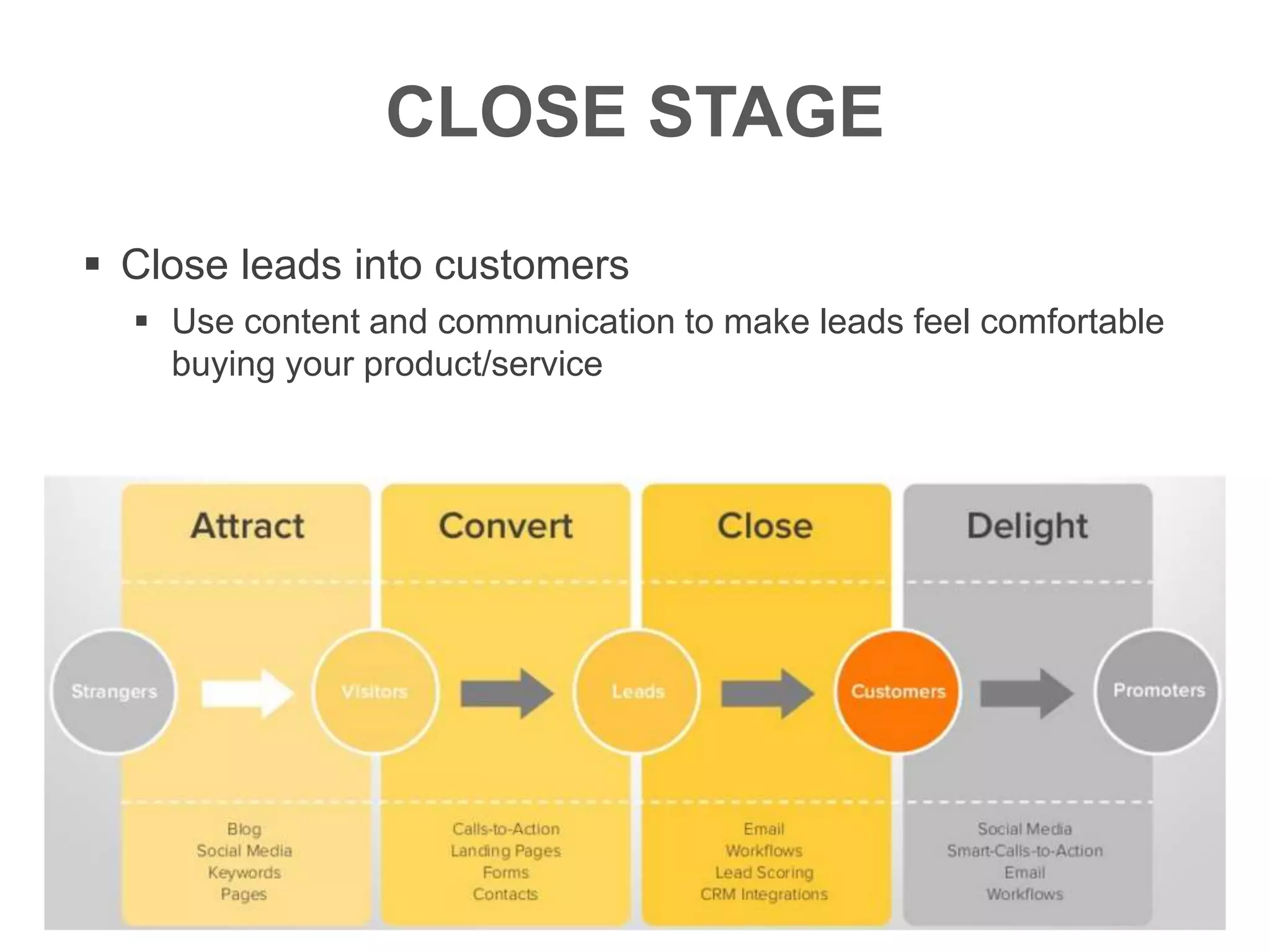
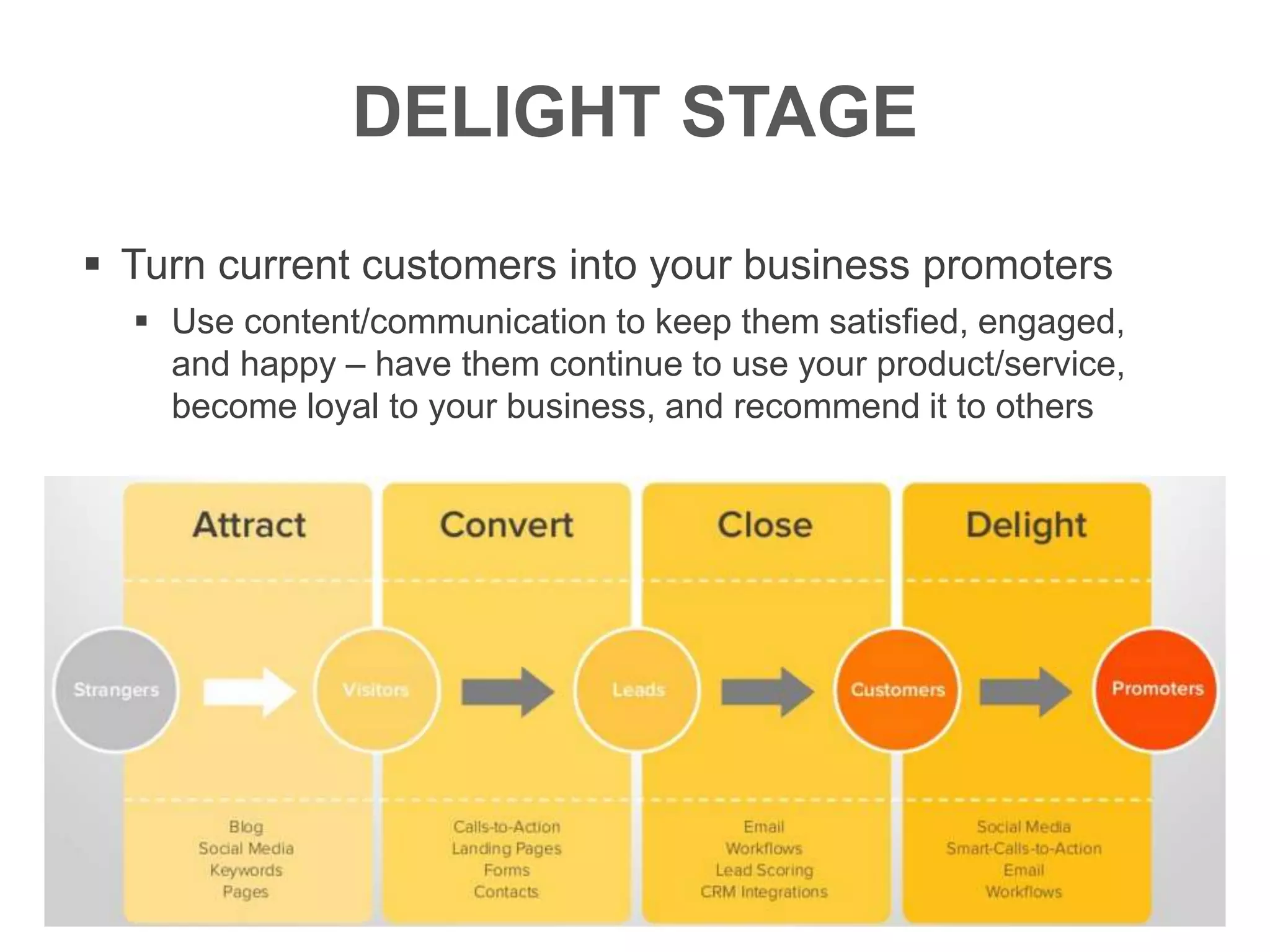
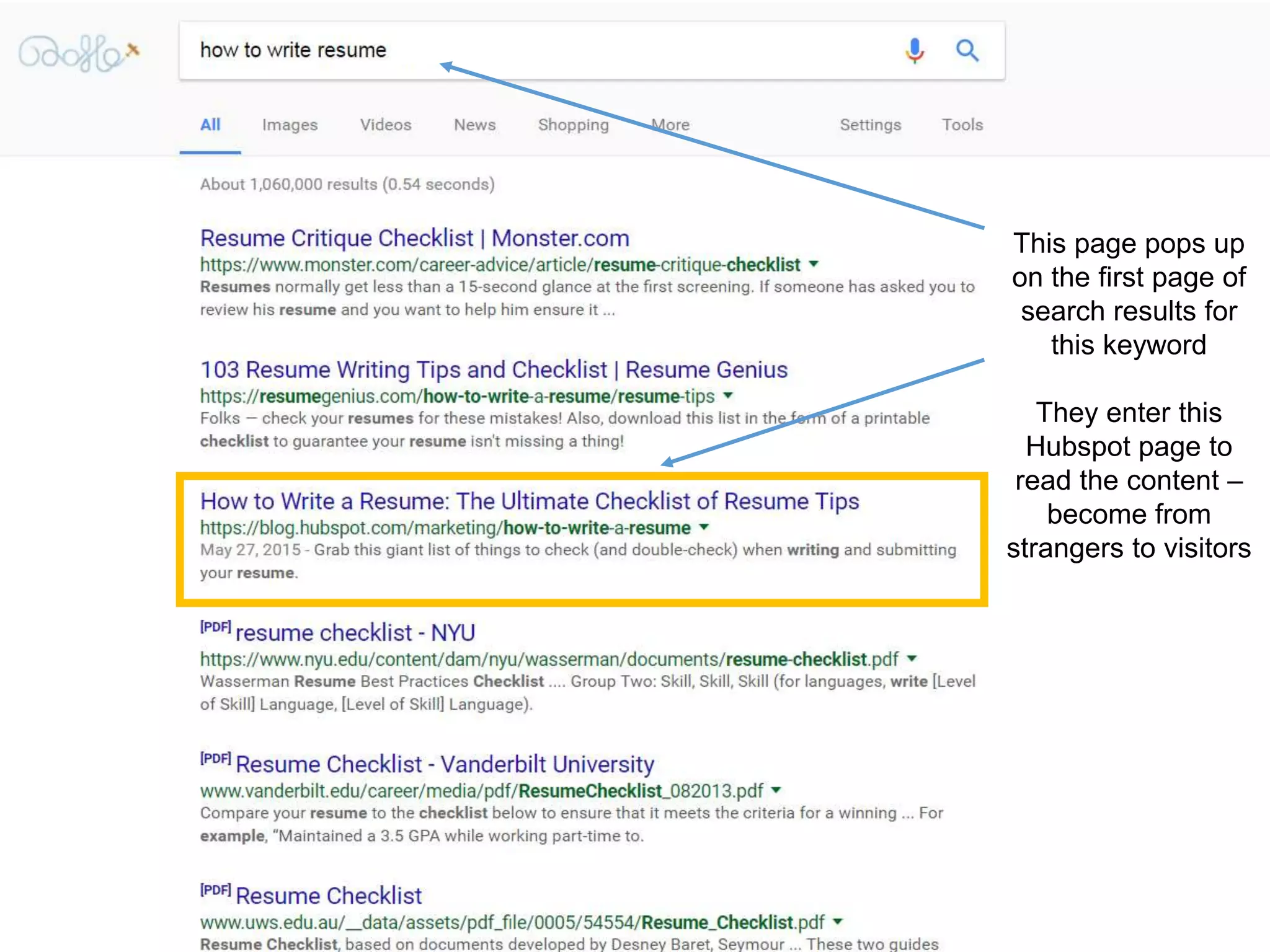
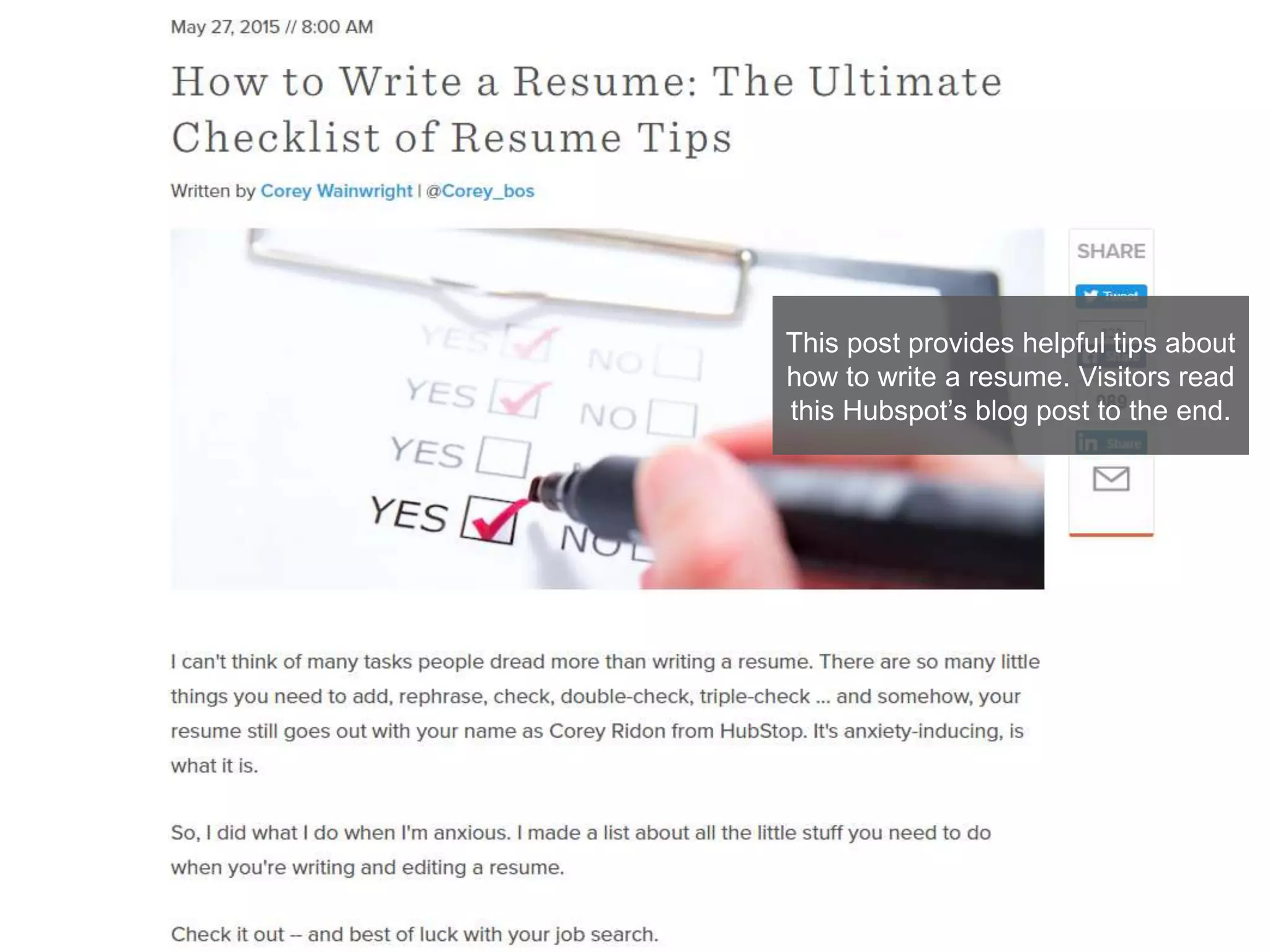
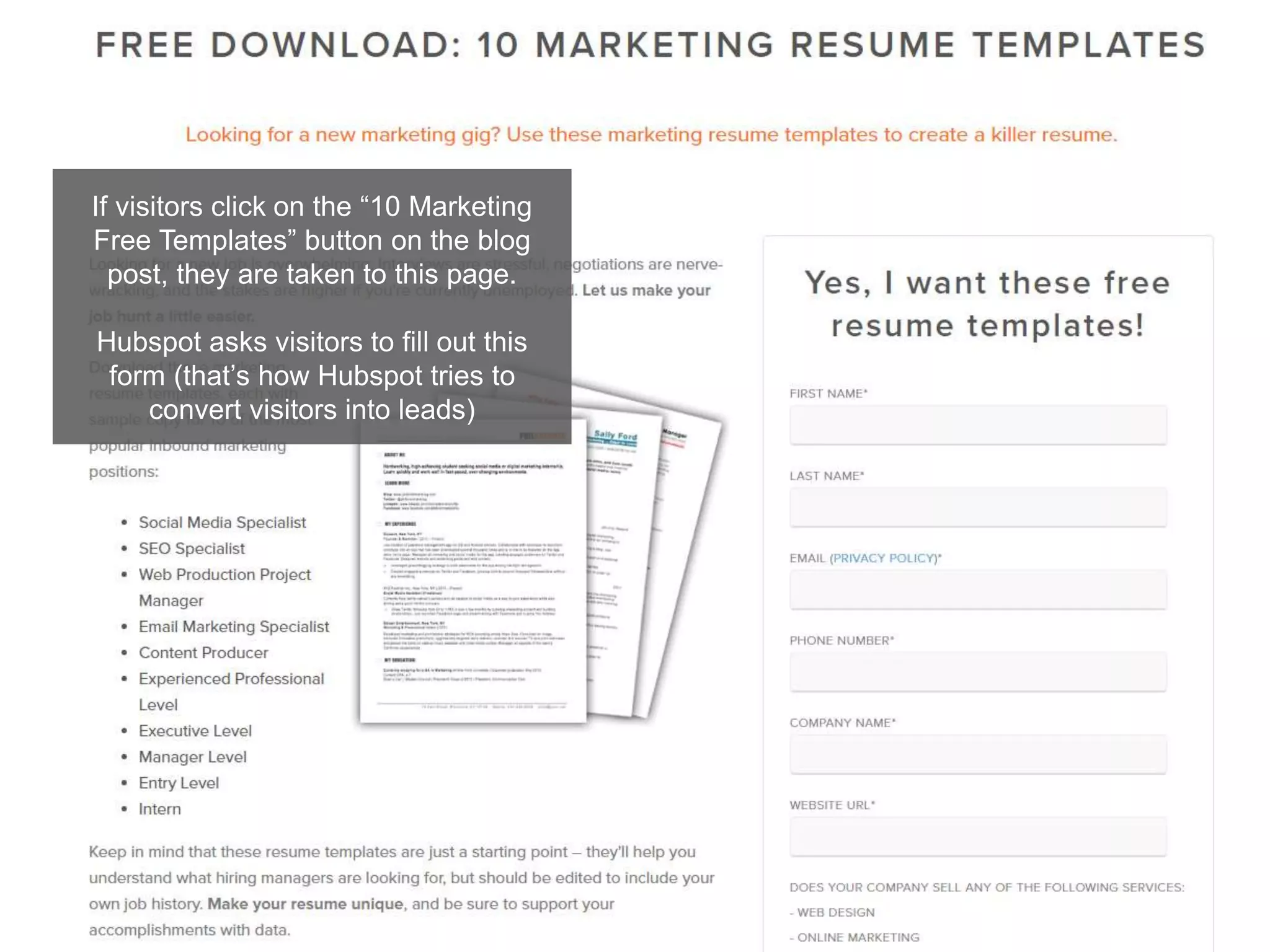
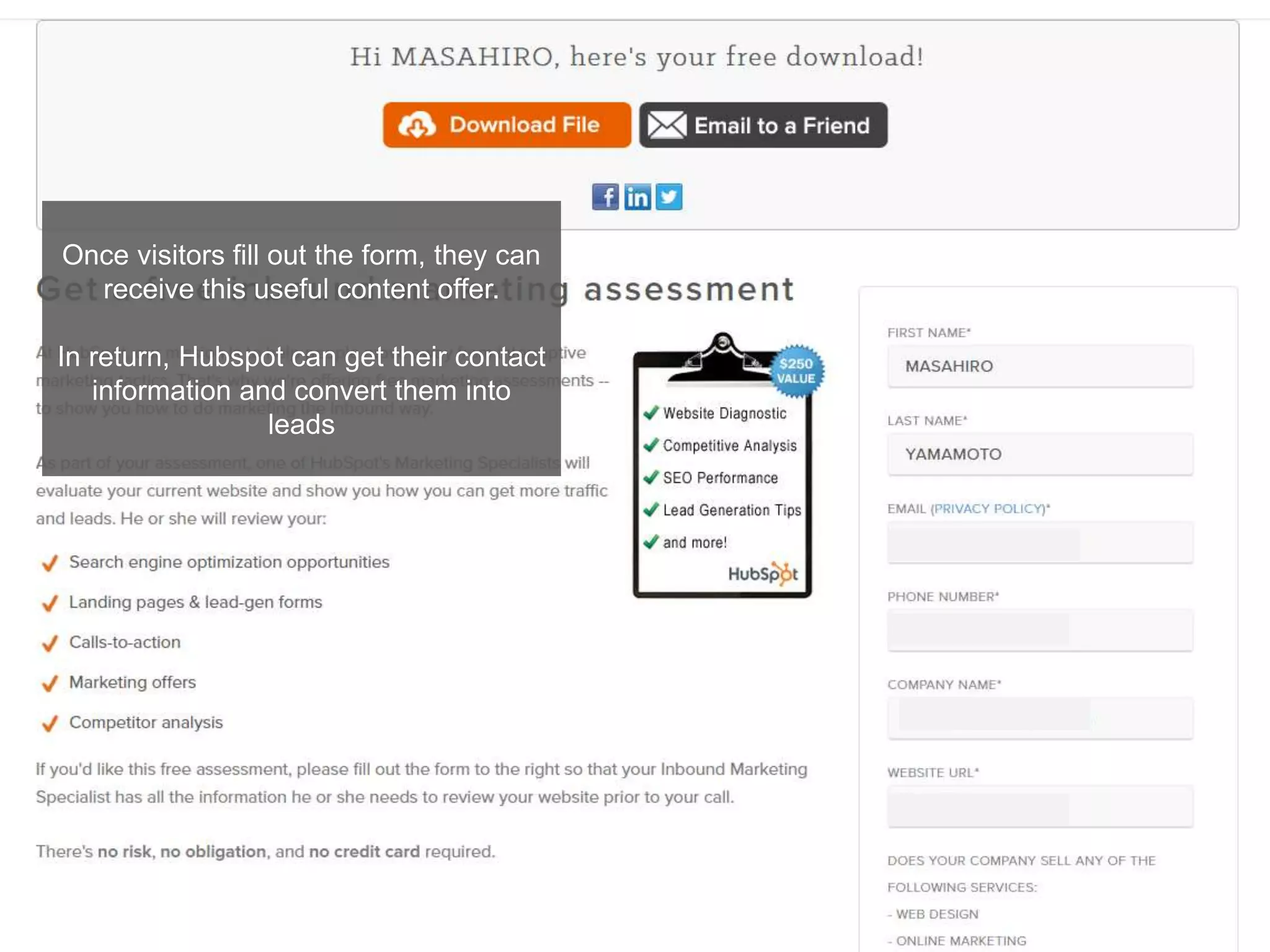
The document provides an overview of digital media strategy and inbound marketing. It defines key terms like public relations, advertising, and marketing communication. It explains that inbound marketing focuses on attracting customers by creating useful content rather than interrupting them with sales messages. The process includes attracting visitors with content, converting them to leads by collecting contact information, closing leads into customers through targeted communication, and delighting customers to become promoters. An example of using blog content and forms to guide visitors through this process to hire a business communication service is also provided. The document stresses creating relevant content at each stage and integrating owned, earned and paid media.










![EXAMPLE
Using the contact information, you can send personalized emails to
persuade these leads to hire your business communication service.
For example…
Hi xxx,
Thanks for downloading our 10 Marketing Resume Templates! We hope you
found them helpful!
Crafting a resume and cover letter that attract hiring mangers’ interest is difficult.
Over the years, we developed effective writing and self-branding techniques that
have helped our clients successfully land jobs they desired.
If you want to know more about what we do, go to this page [link] and schedule a
30 minute video chat. Don’t hesitate to ask anything. We would be happy to
answer any questions you might have!
Best wishes,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulenotes1anoverviewofdigitalmediastrategy-190605062202/75/Module-1-An-Overview-of-Digital-Media-Strategy-24-2048.jpg)