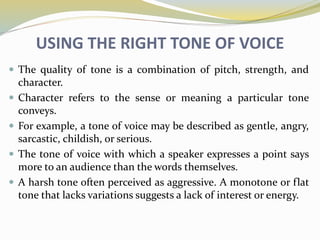
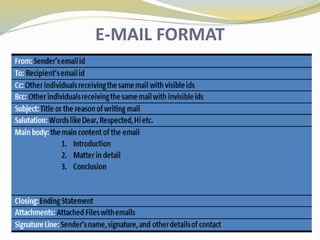
The document discusses various aspects of business etiquette and workplace etiquette. It covers topics such as the importance of business etiquette, appropriate personal appearance and dress code in the workplace, etiquette for different business occasions, using the right tone of voice, and the significance of etiquette in the modern globalized business world. It emphasizes how etiquette builds relationships, trust and communication skills, and promotes a positive work environment.