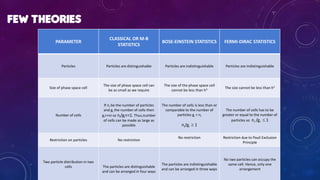
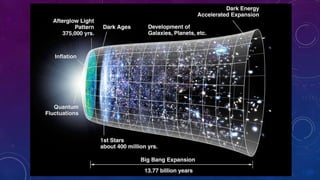
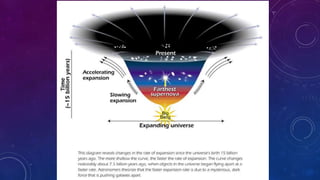
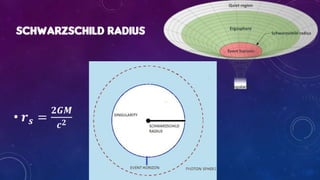
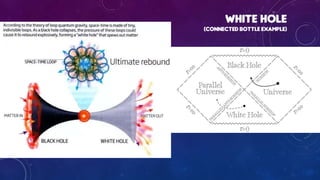
Classical physics deals with non-extreme conditions where quantum mechanics (QM) and Einstein's theory of relativity (ER) are not needed. Modern physics incorporates elements of QM or ER, or both, and is needed when dealing with extreme conditions like very small distances, high velocities, or large distances. Key differences between classical and modern physics include: particles being distinguishable versus indistinguishable, the size of the phase space cell, restrictions on particles due to principles like Pauli Exclusion, and possible arrangements of particles in cells.