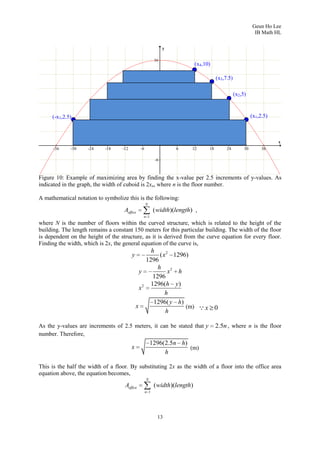
1. The document discusses specifications for building stability and aesthetics, including a maximum height of 75% and minimum of 50% of the width.
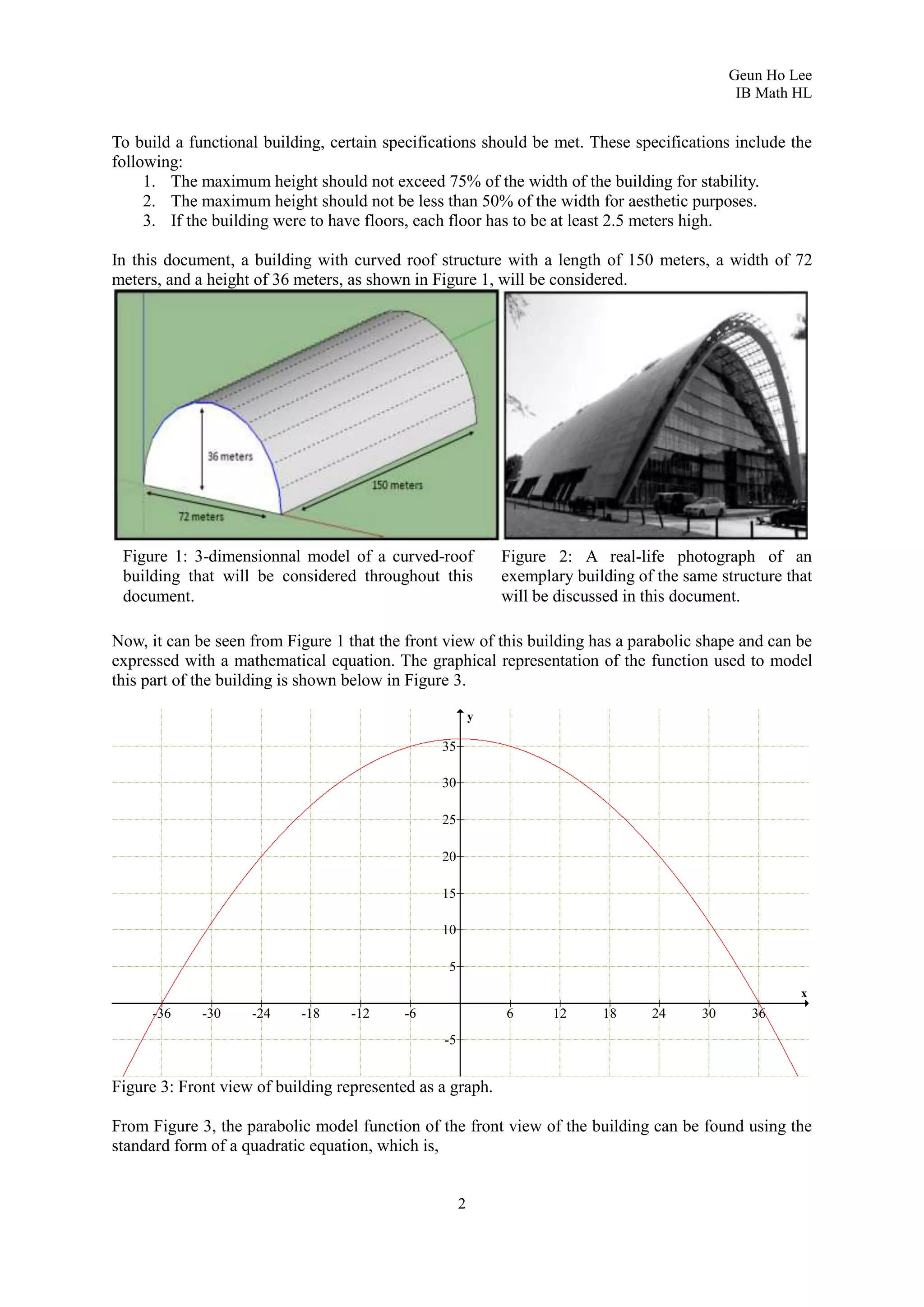
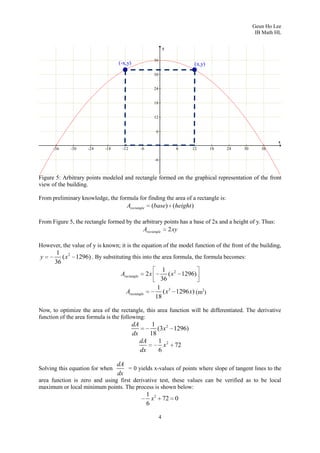
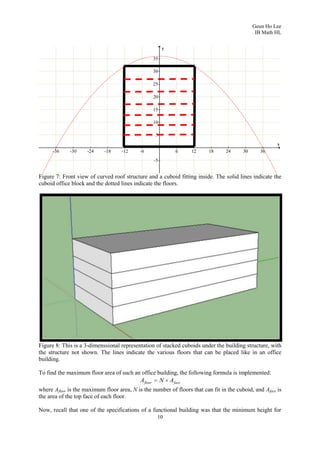
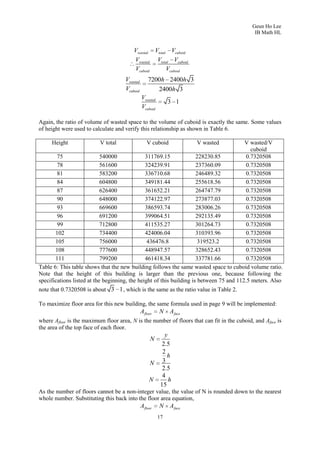
2. It analyzes a specific building with a curved roof that is 150m long, 72m wide, and 36m high, modeling its front face as a parabolic function.
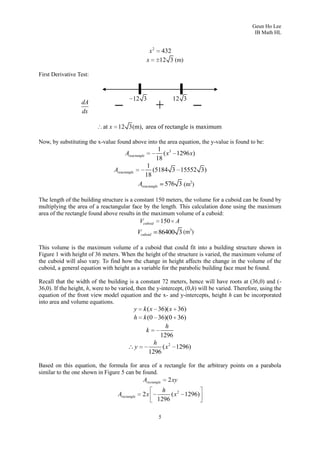
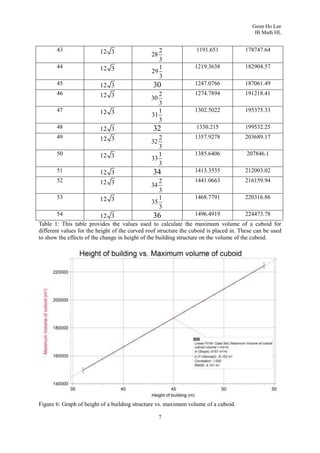
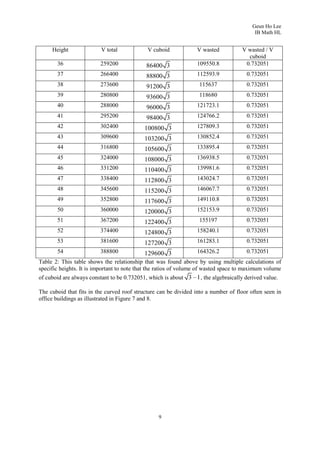
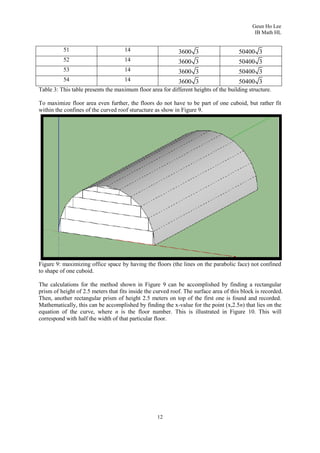
3. To find the maximum volume cuboid that can fit inside, it derives the area function of a rectangle on the parabolic face, finds where it is maximized, and calculates the maximum volume as 86,400 cubic meters.