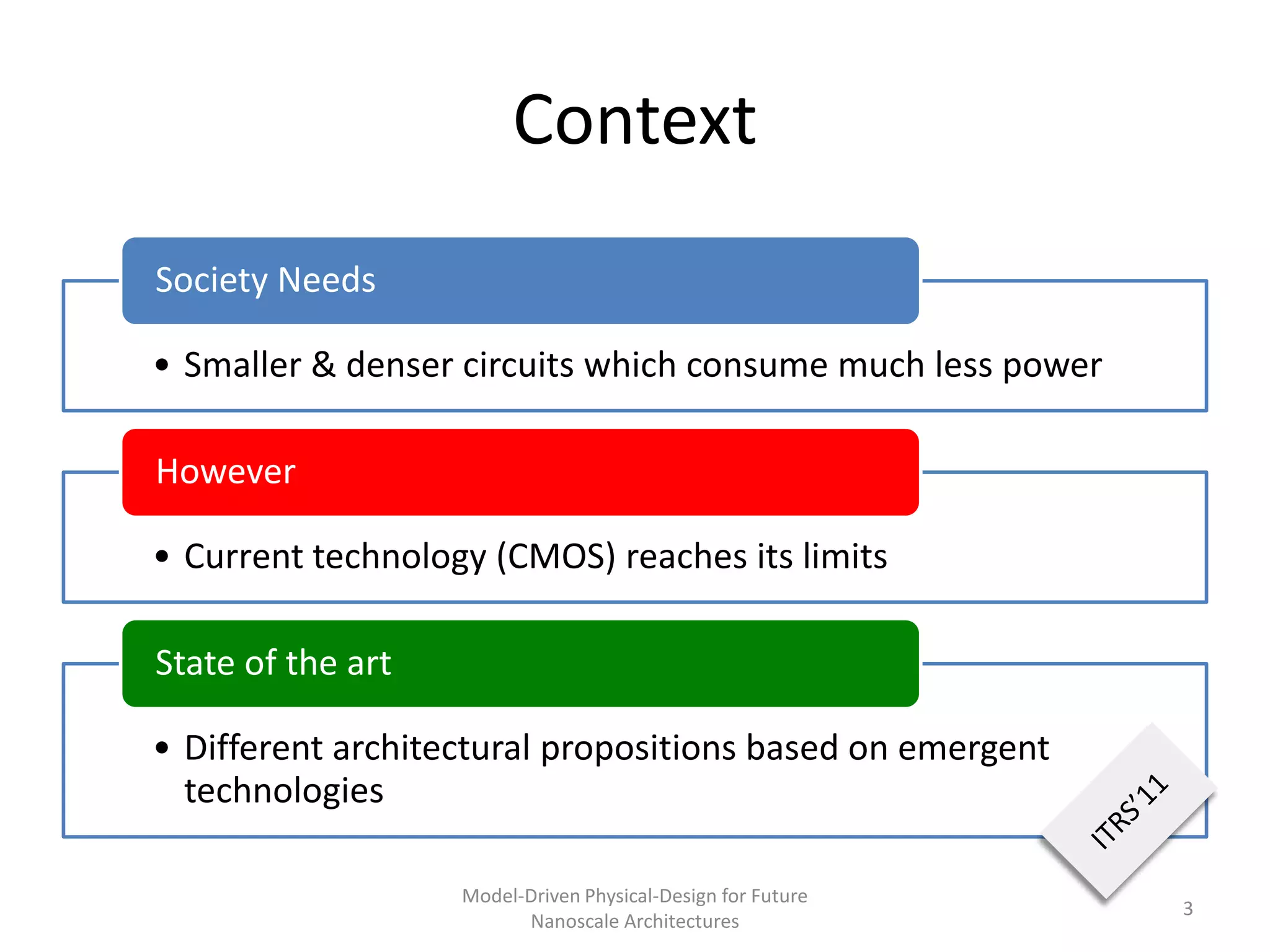
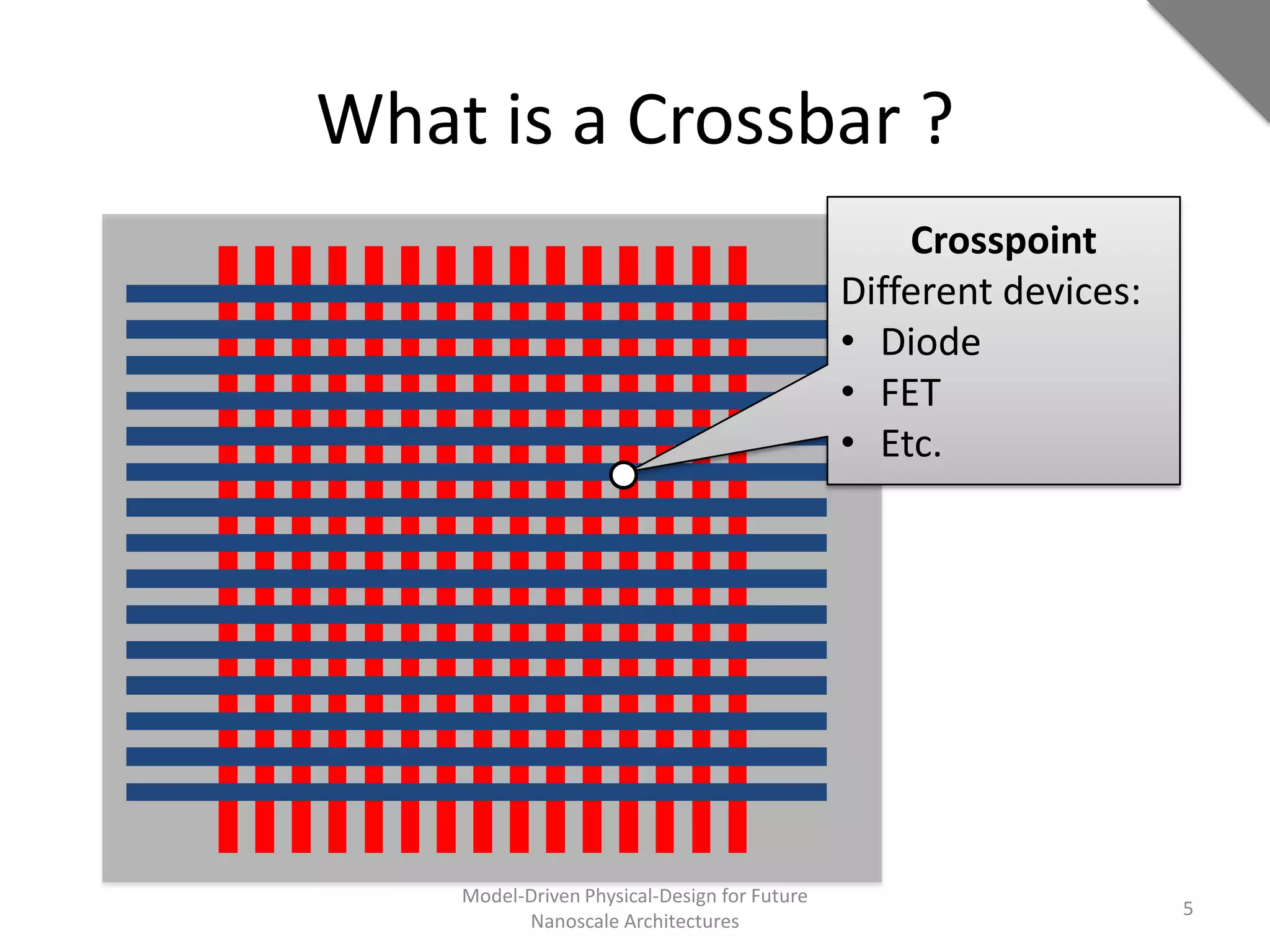
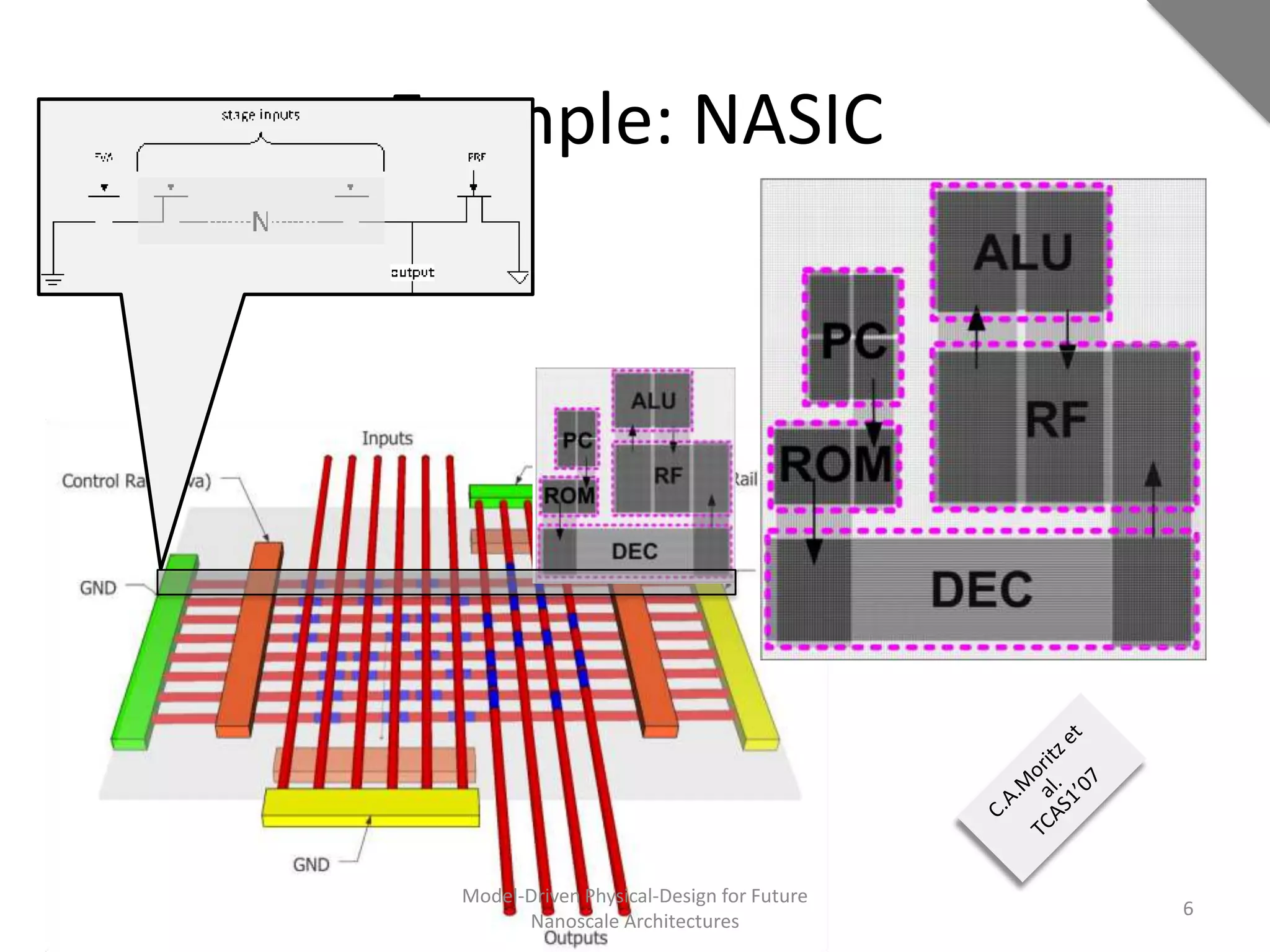
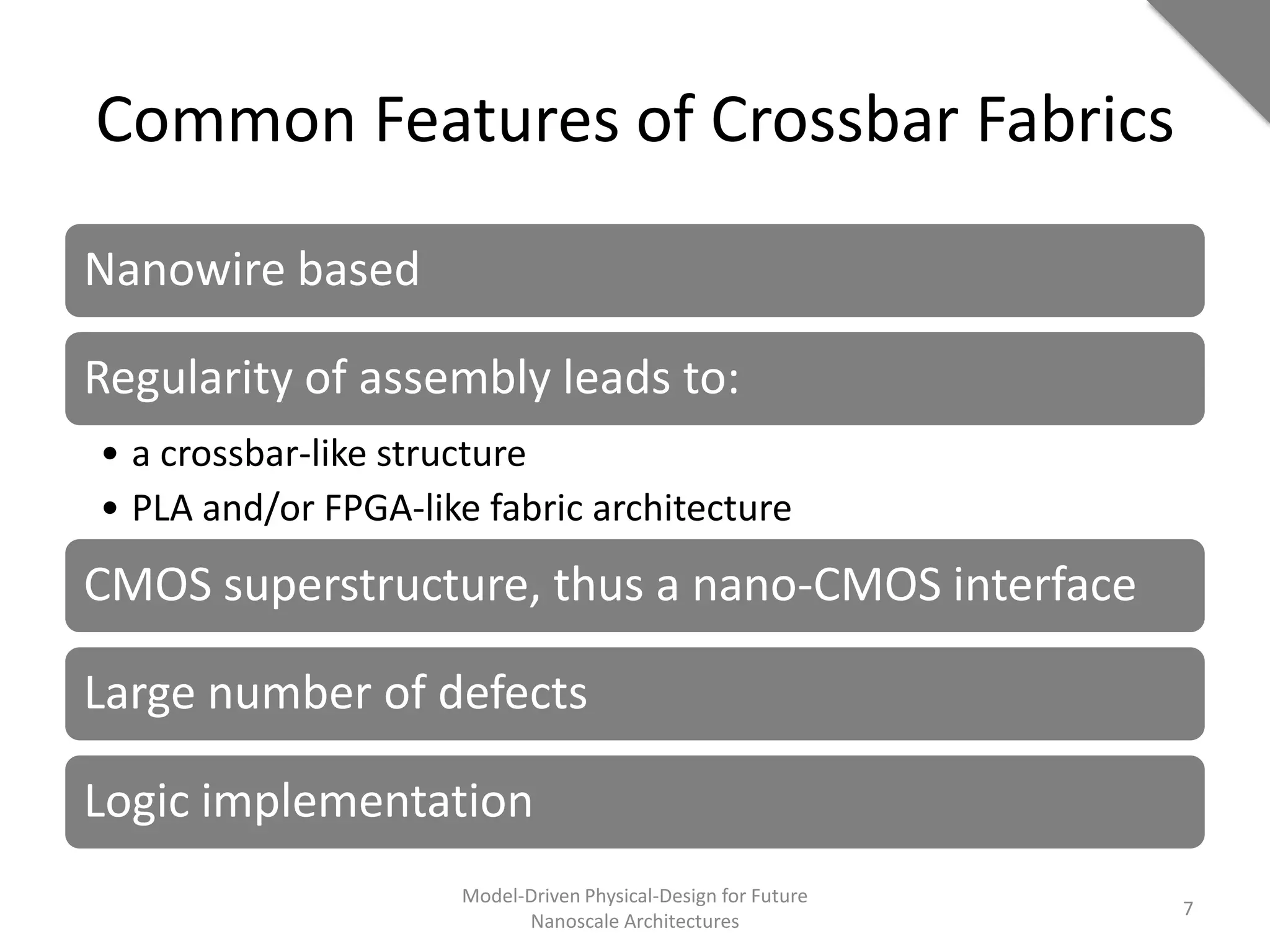
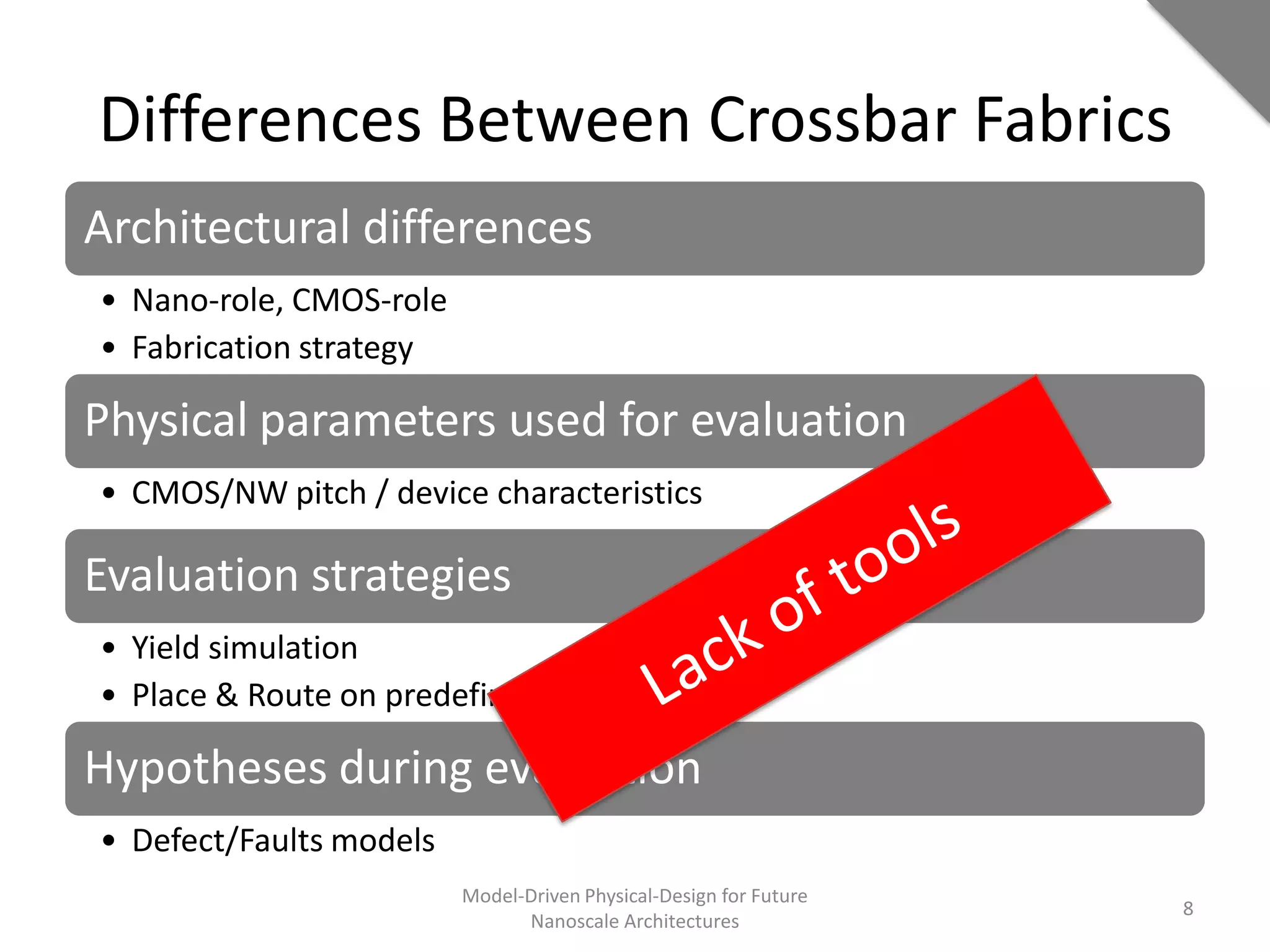
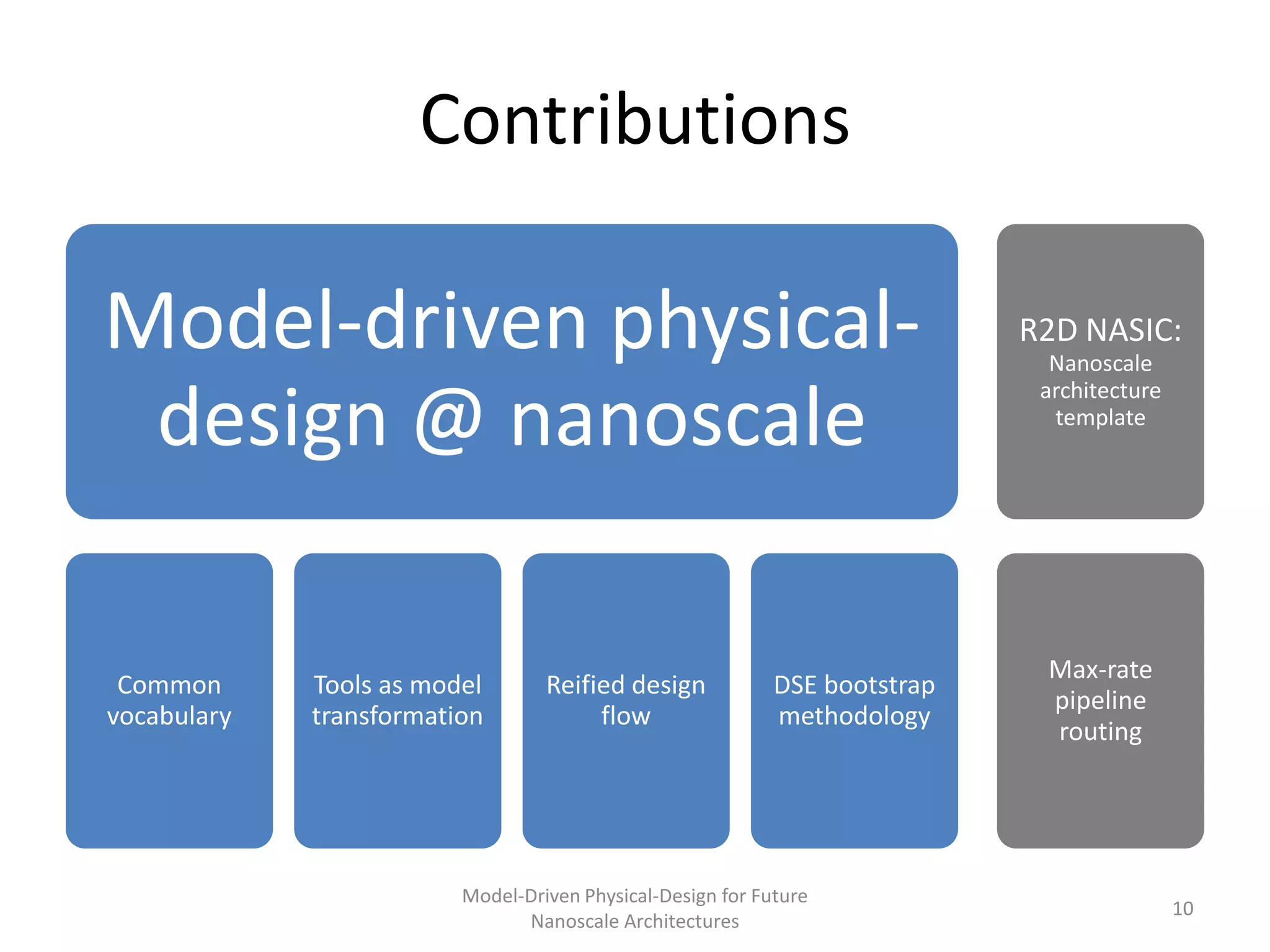
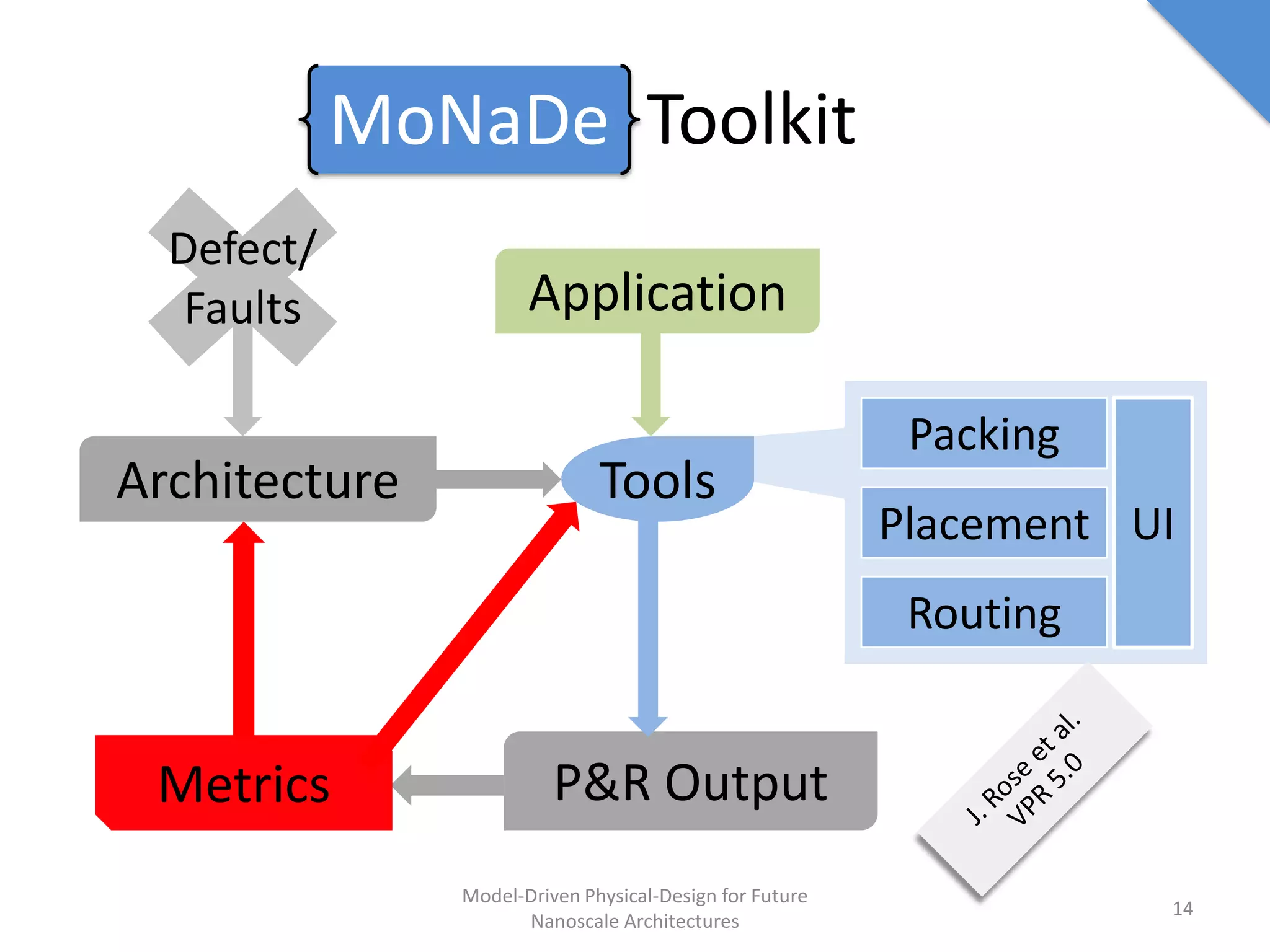
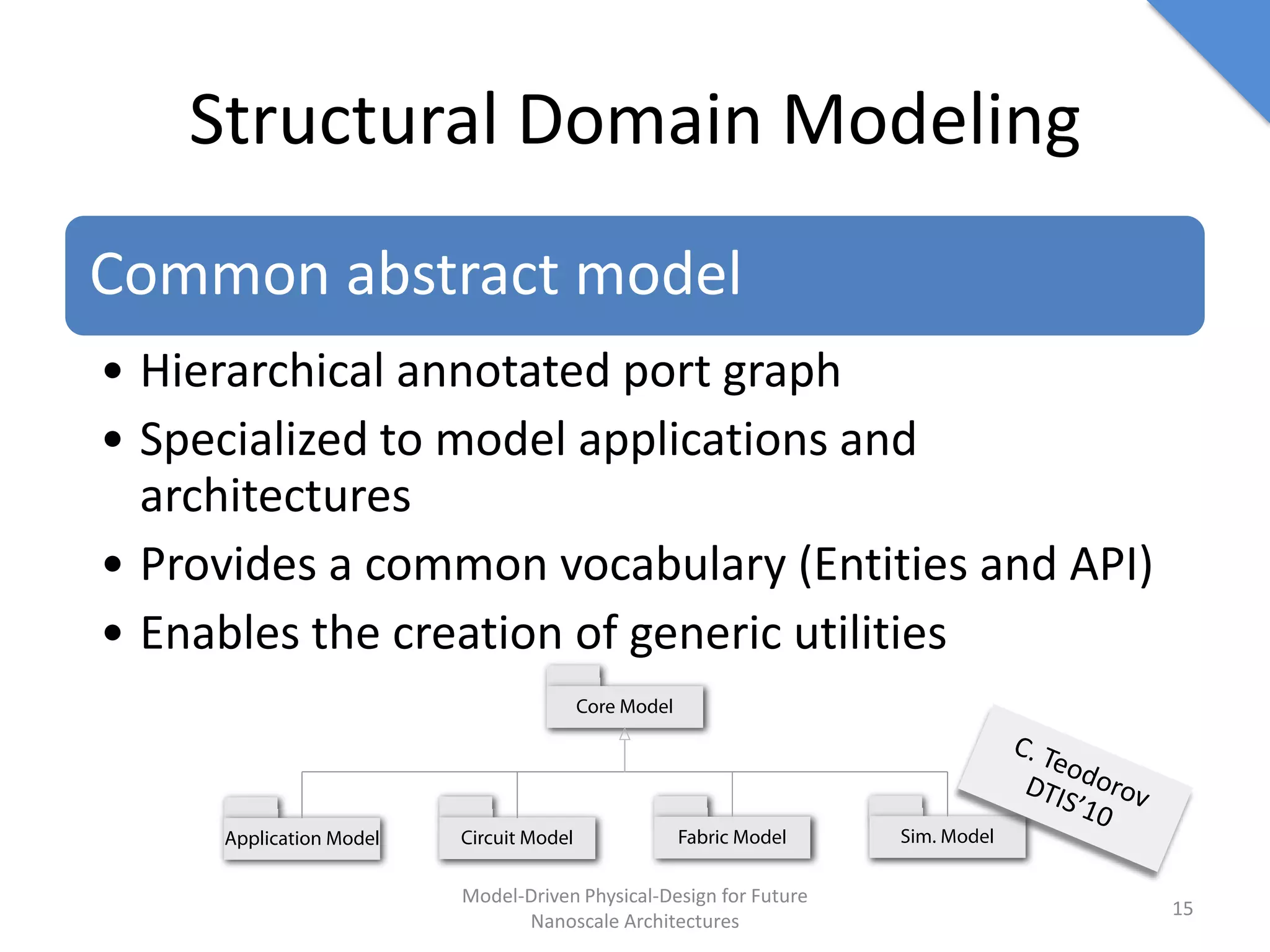
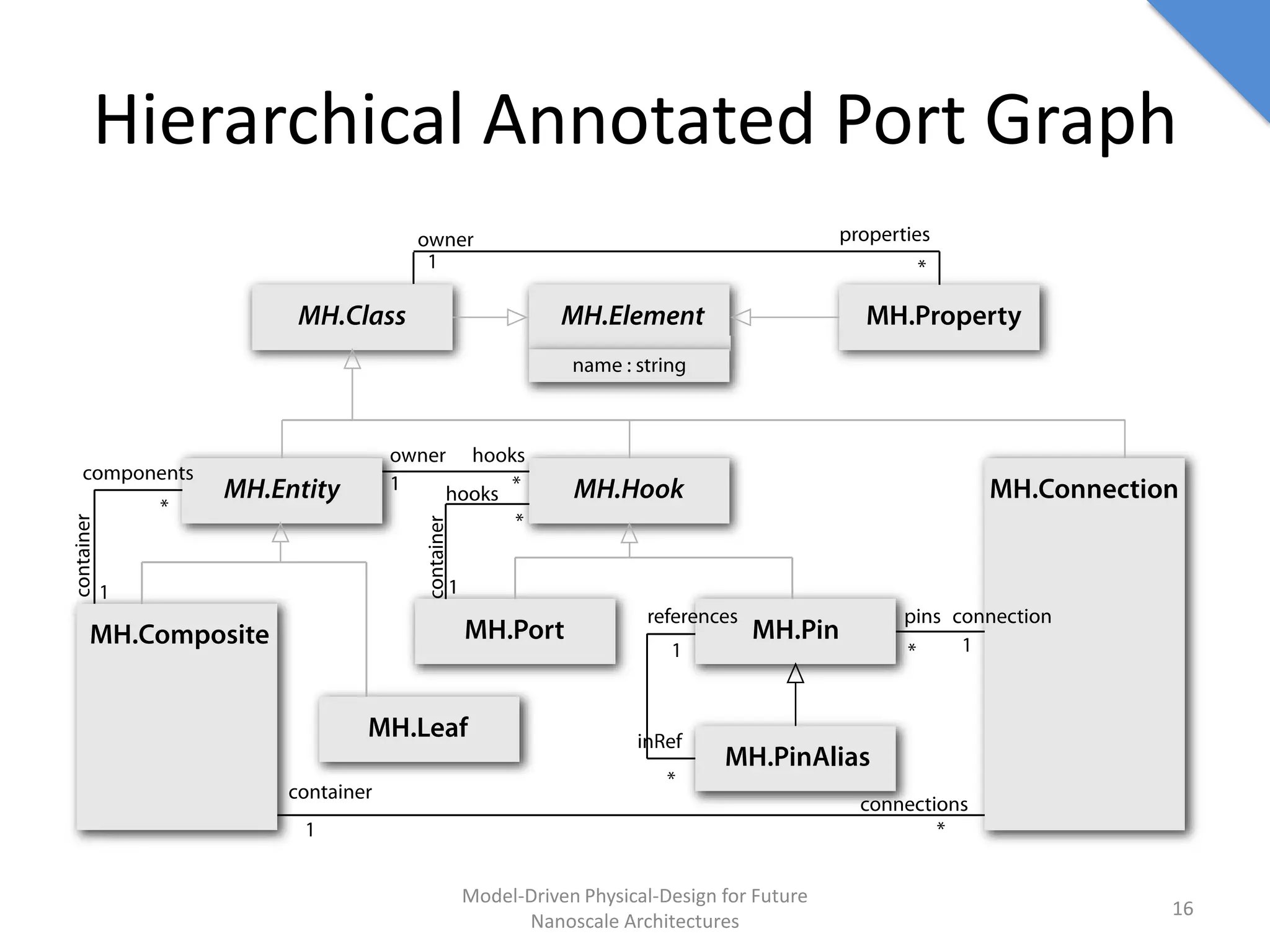
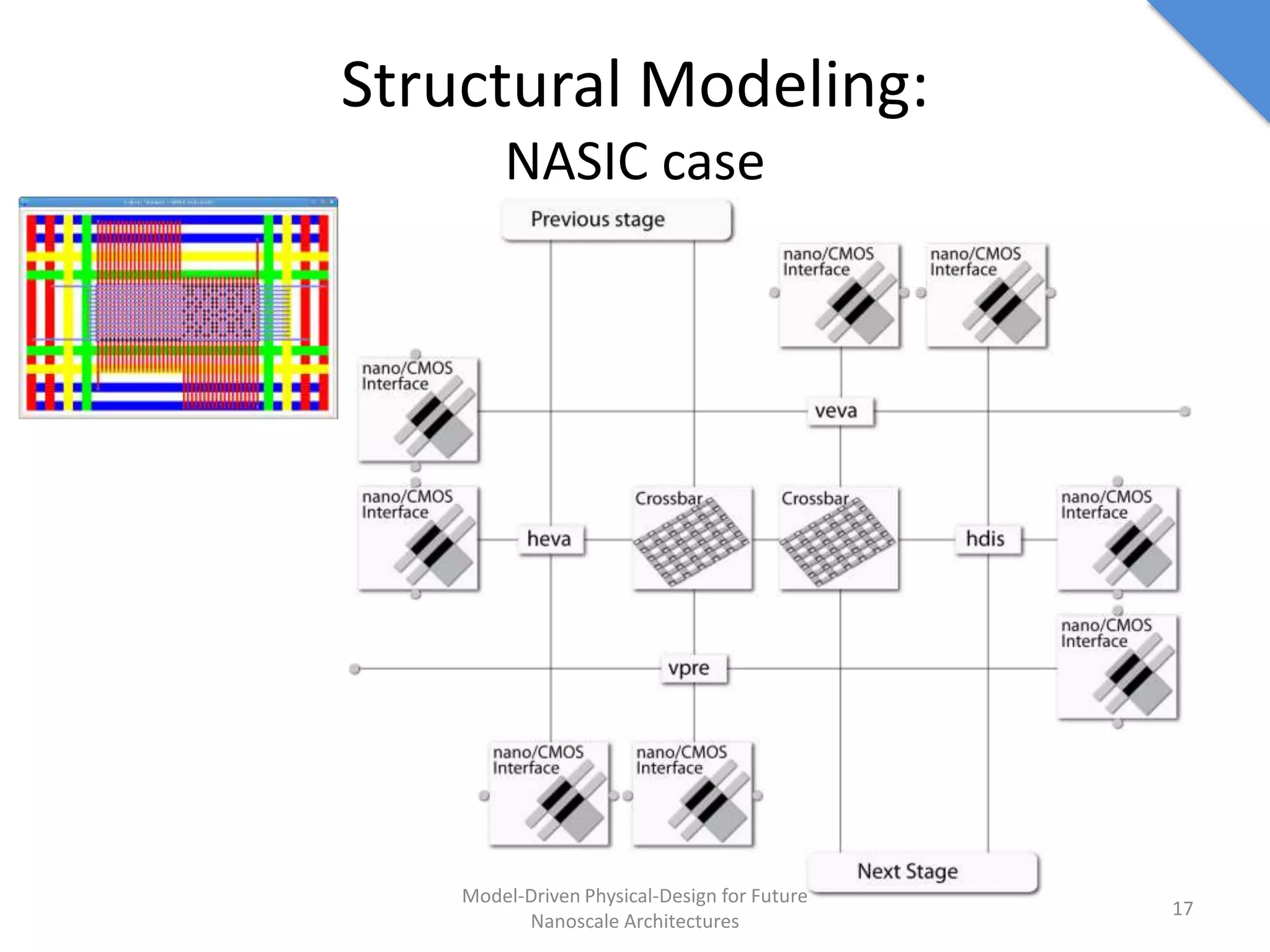
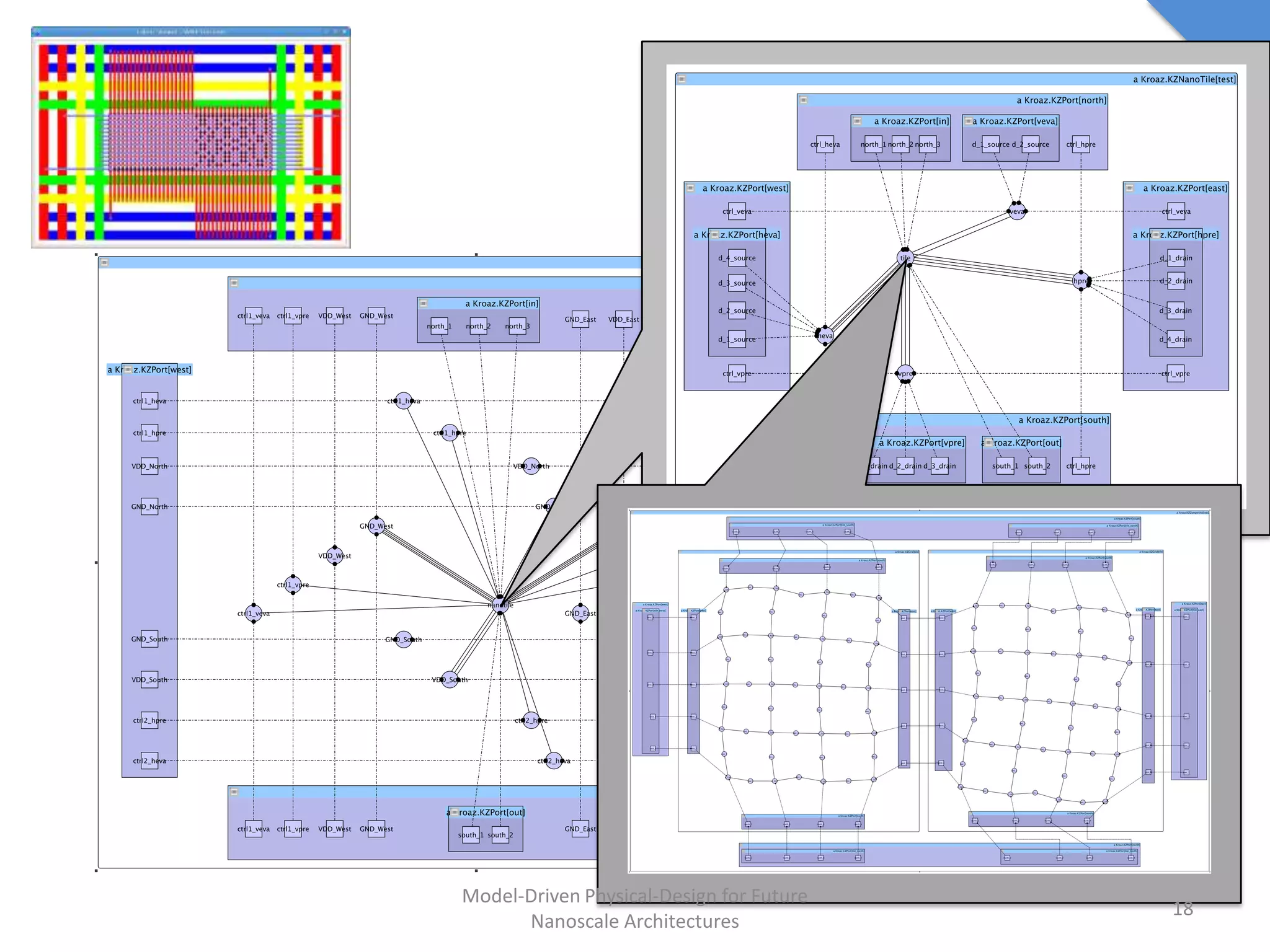
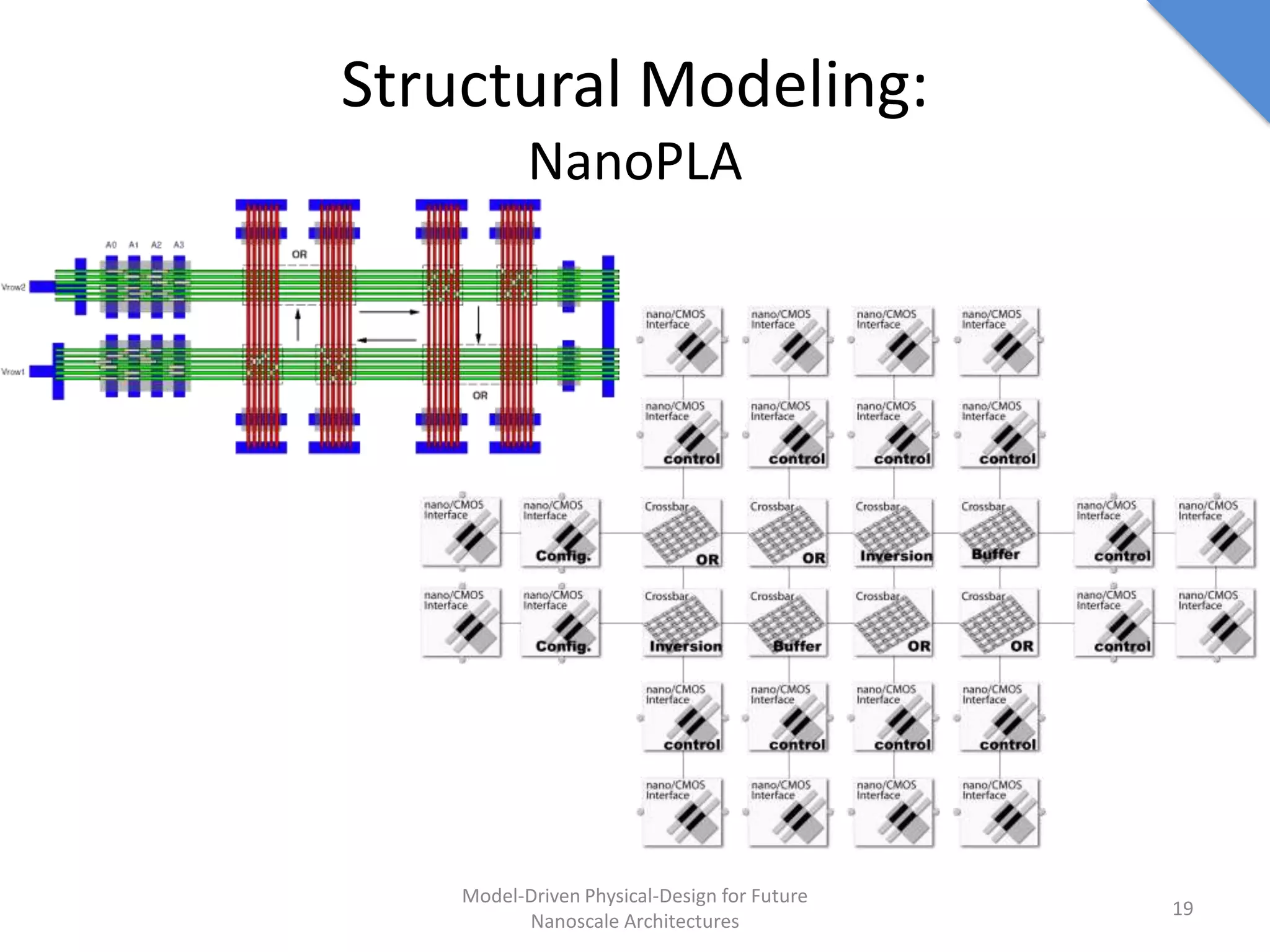
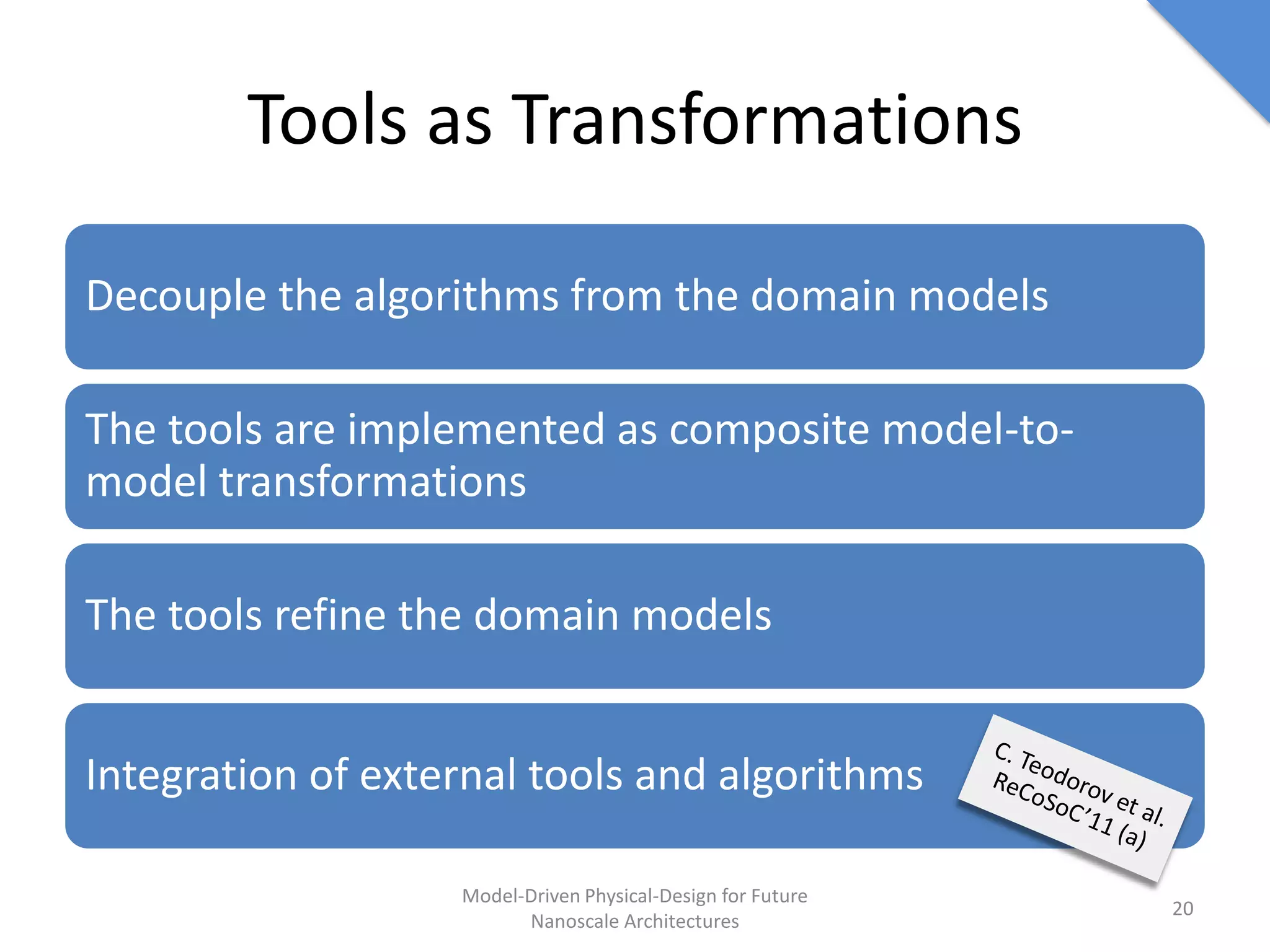
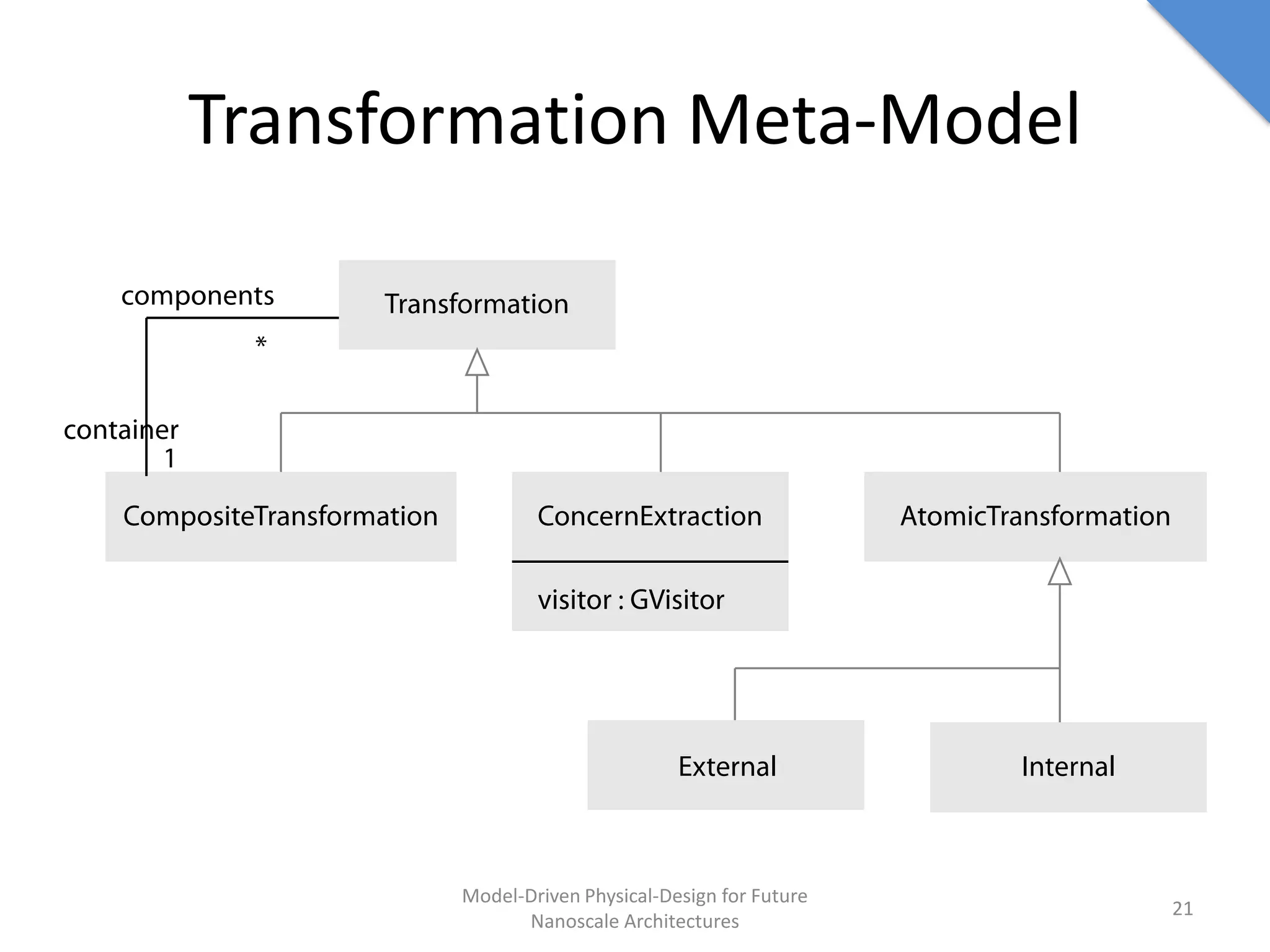
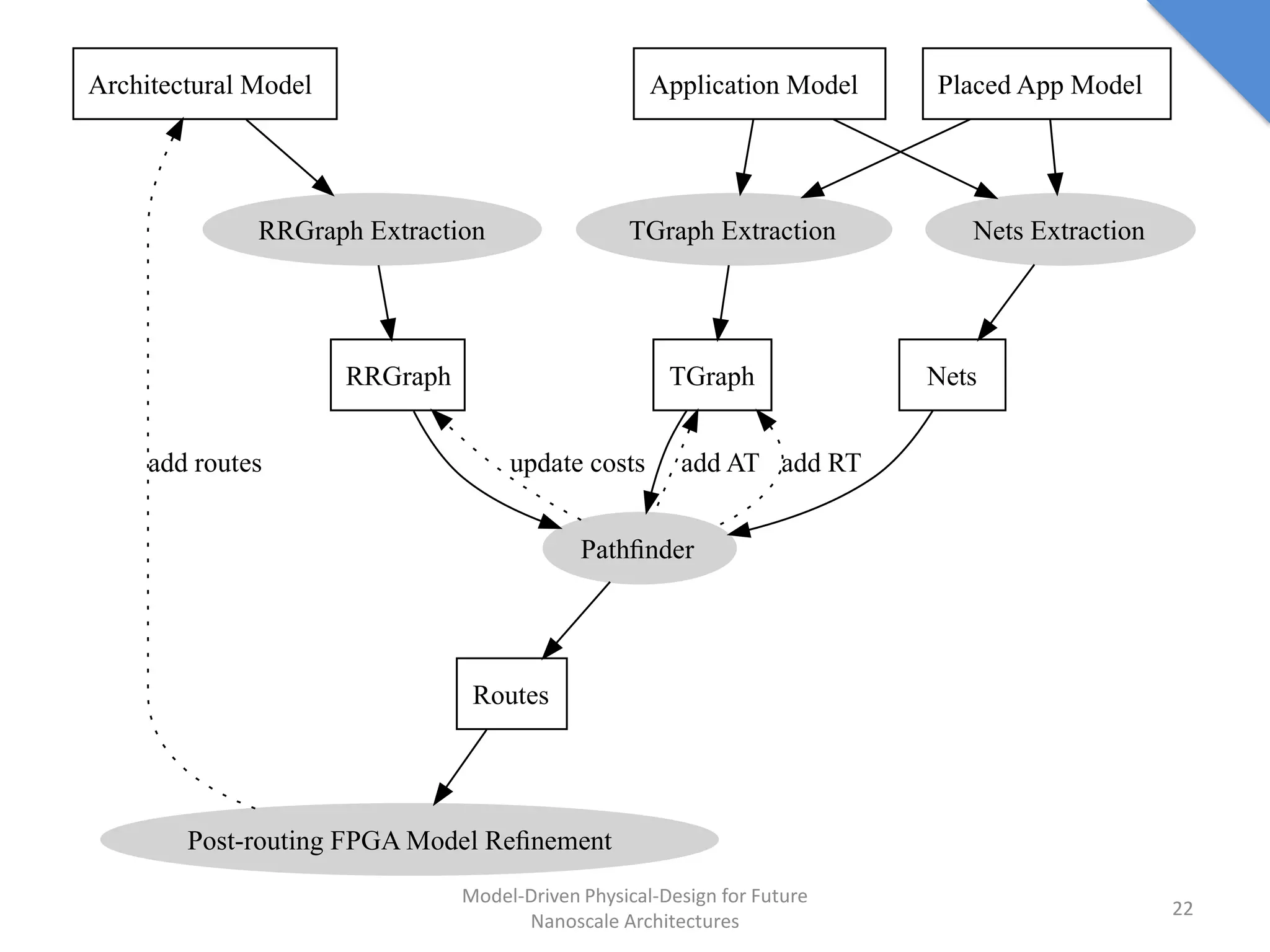
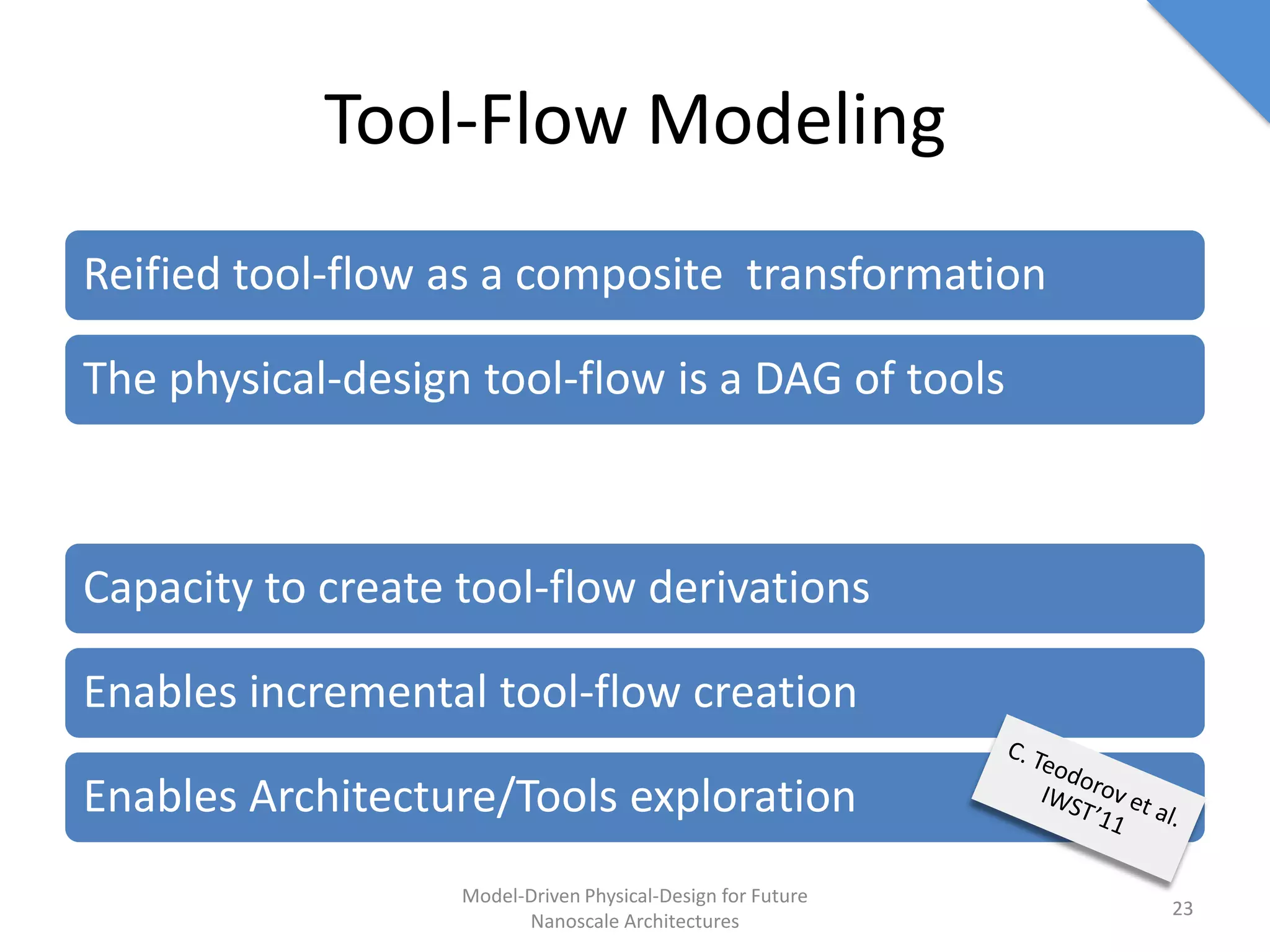
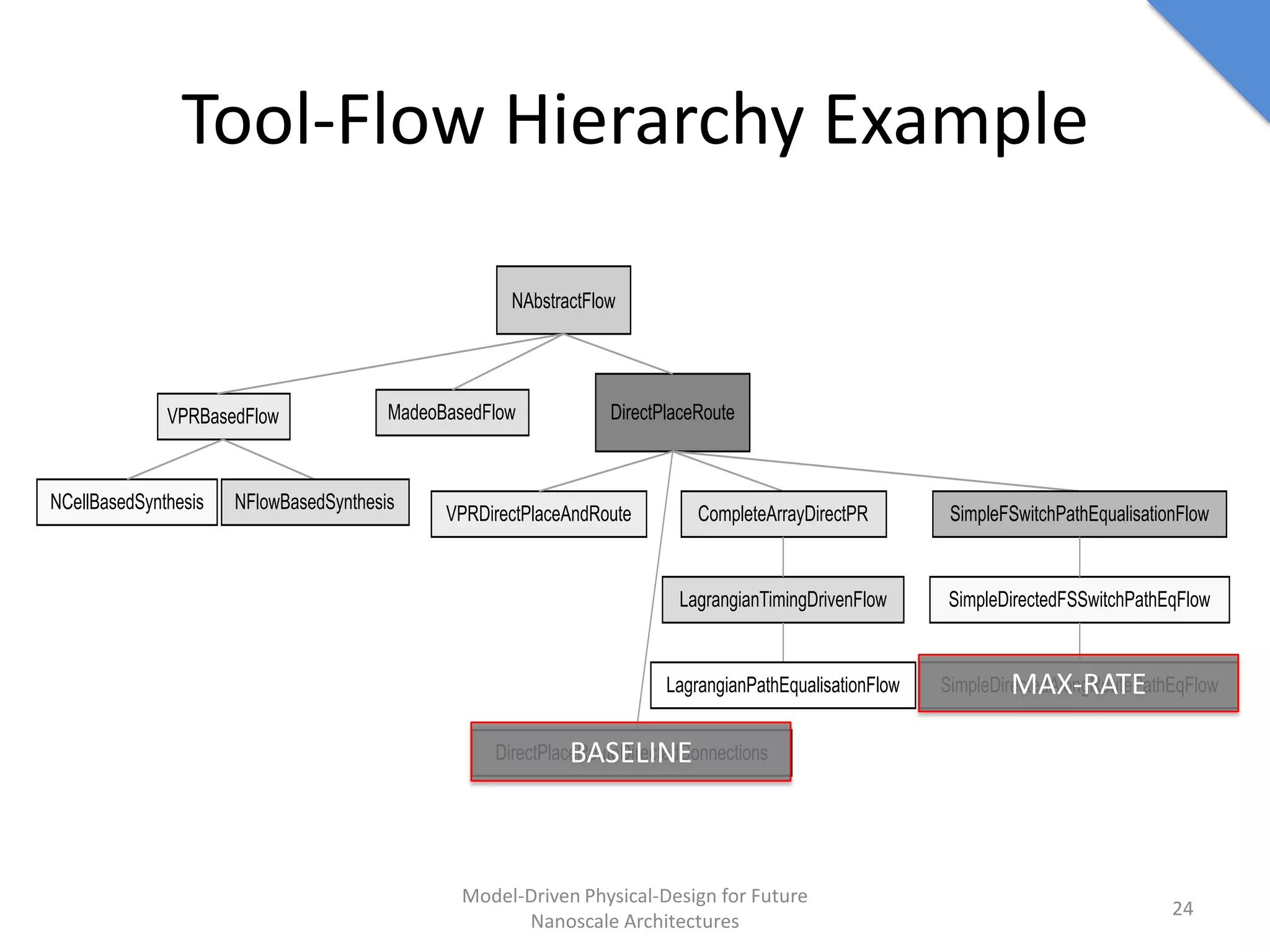
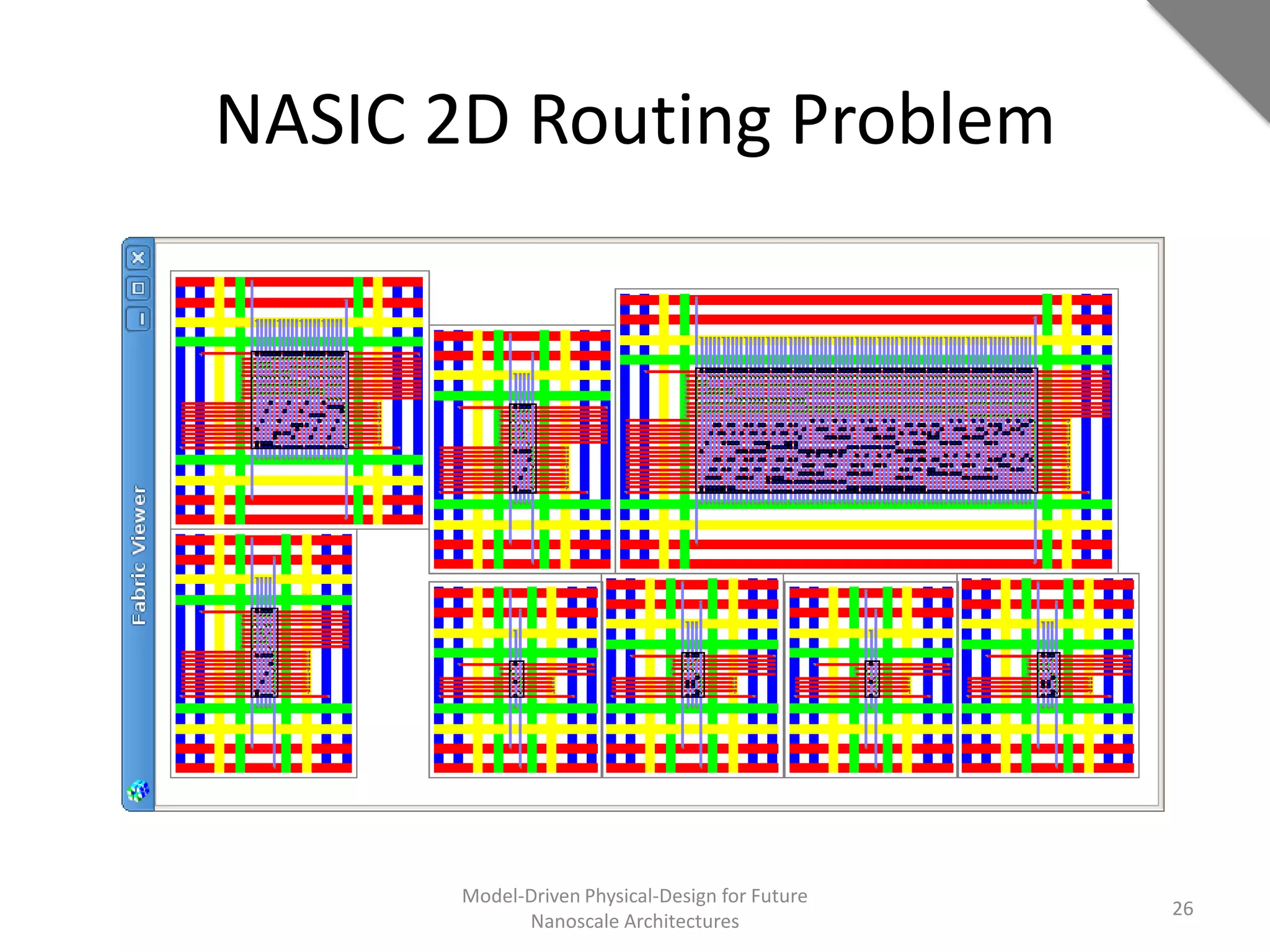
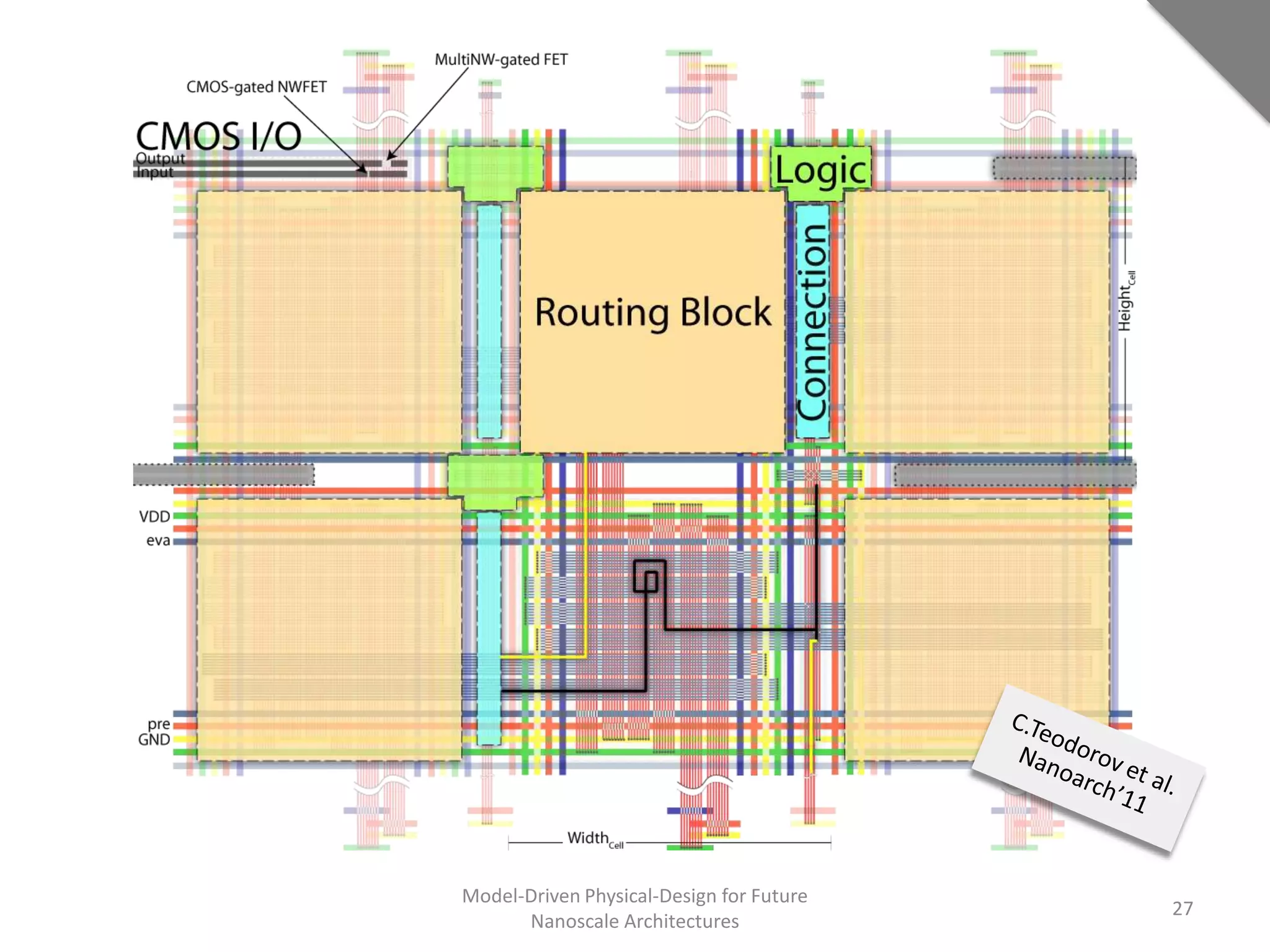
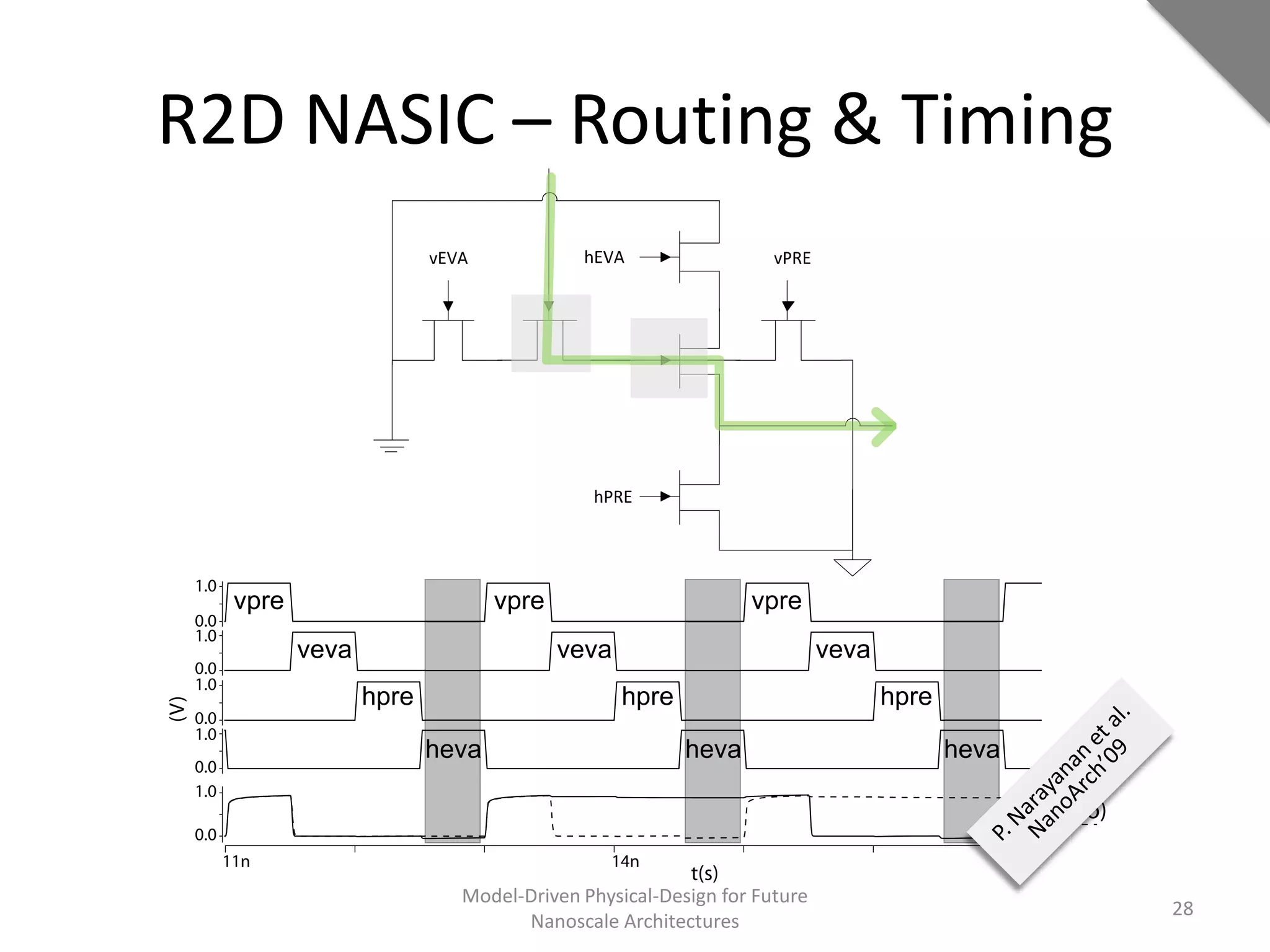
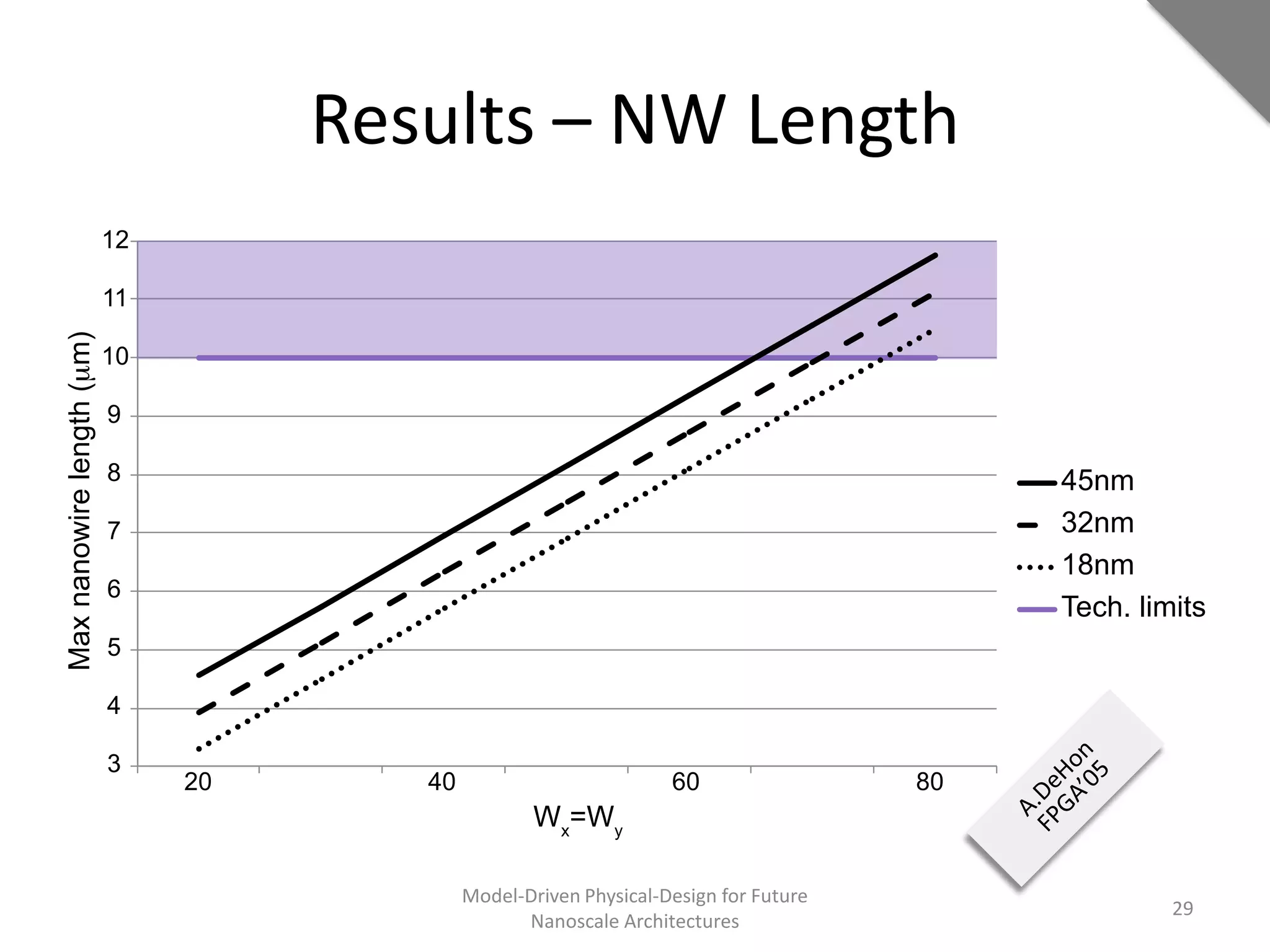
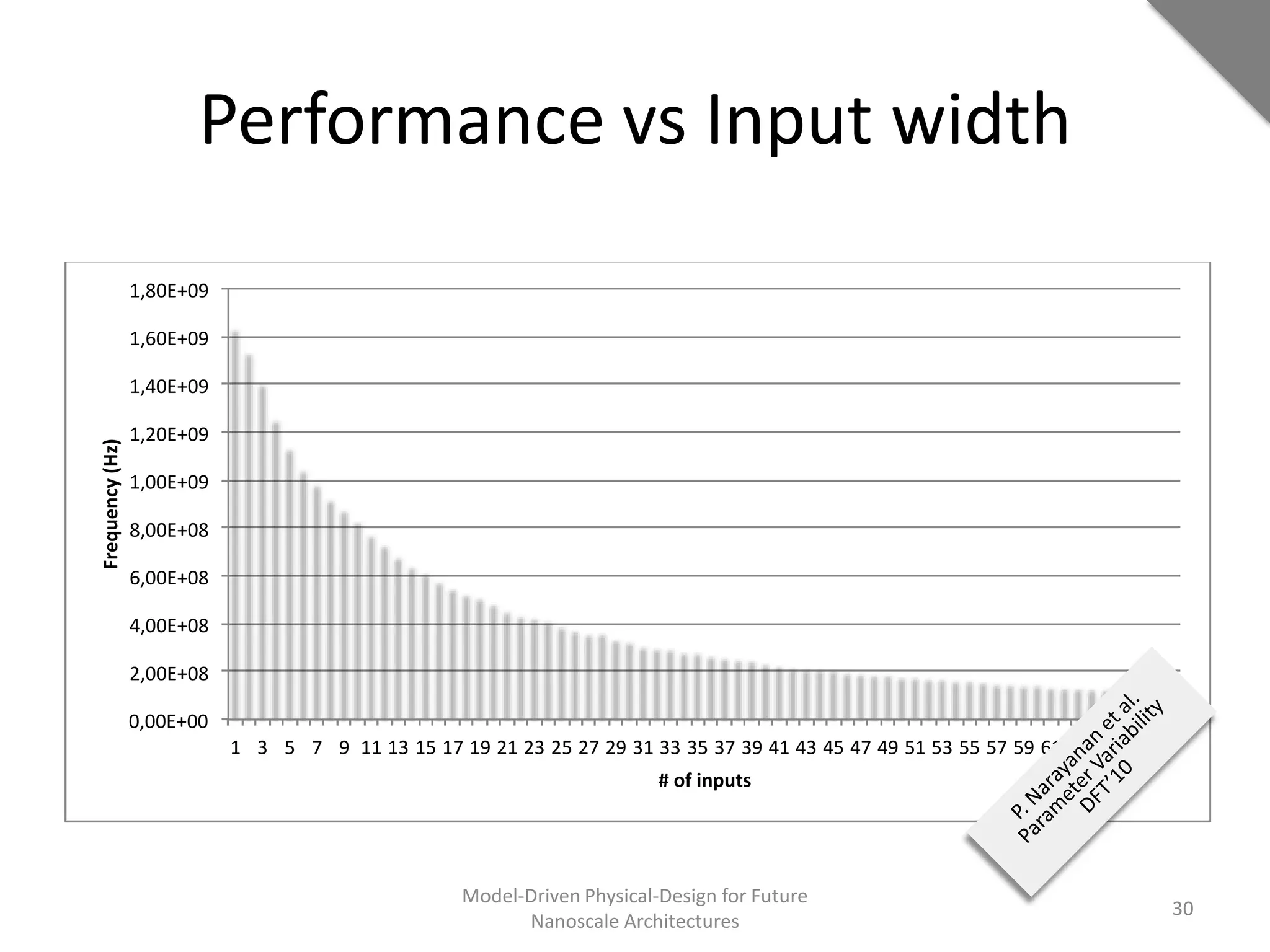
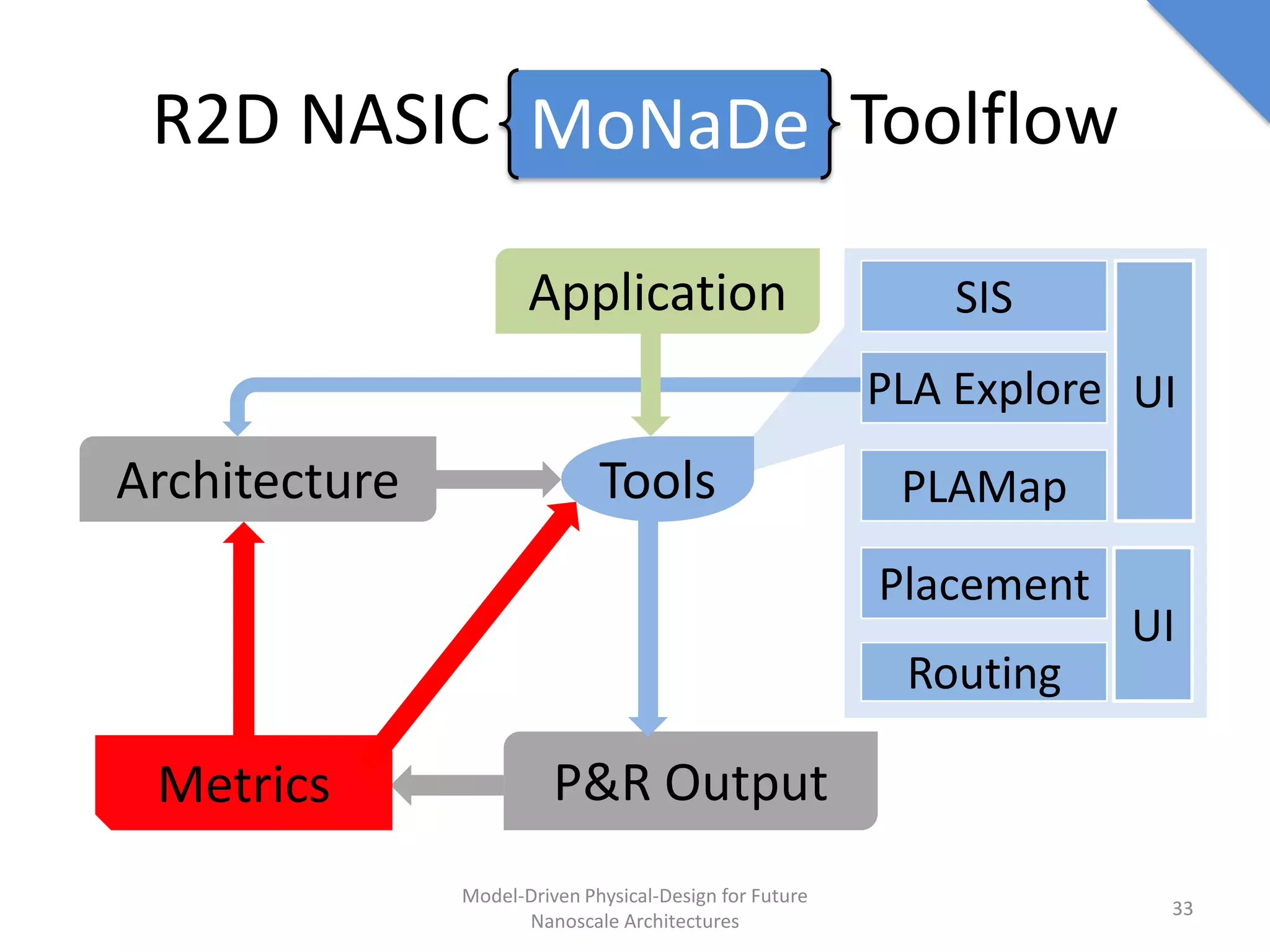
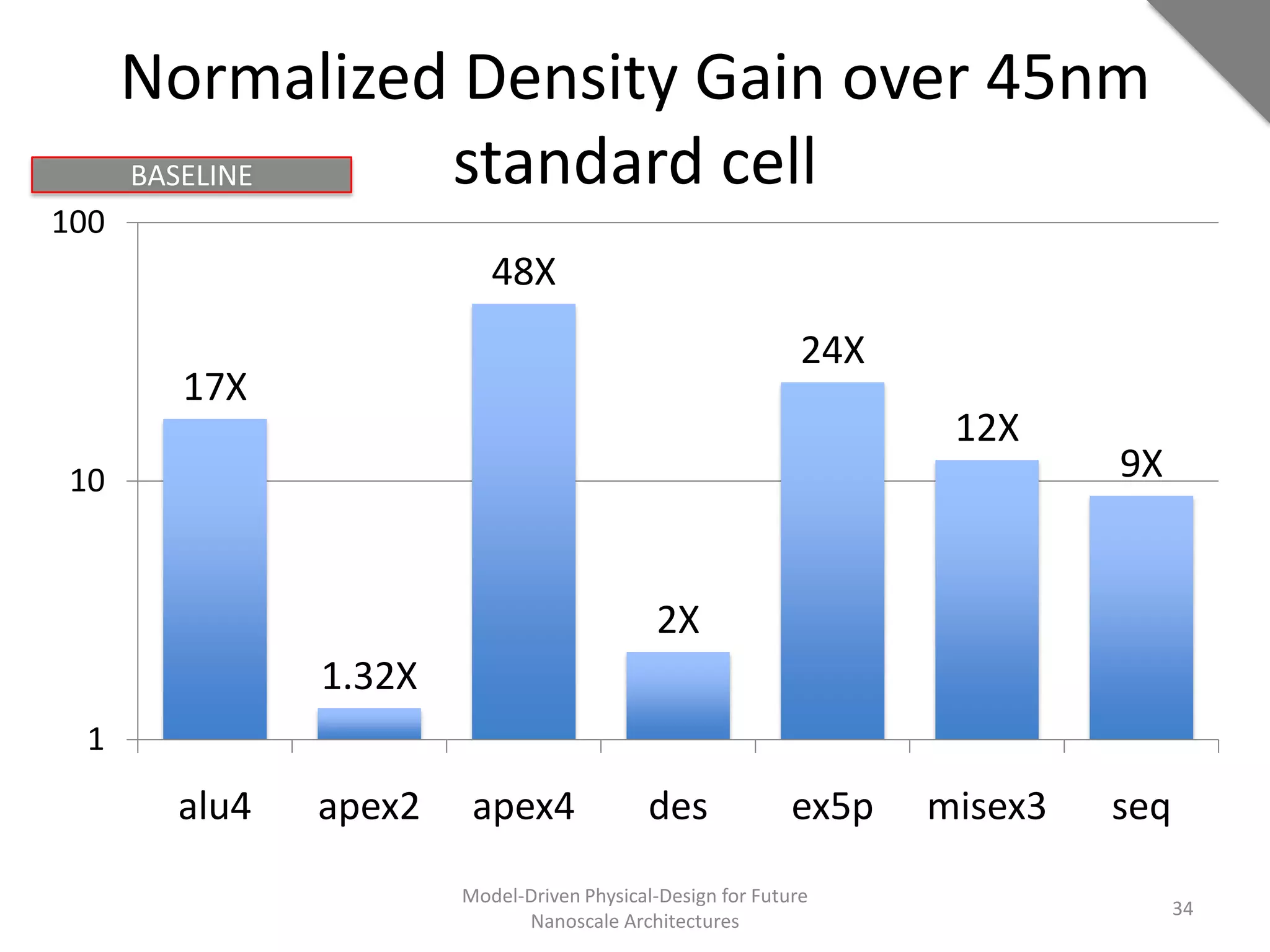
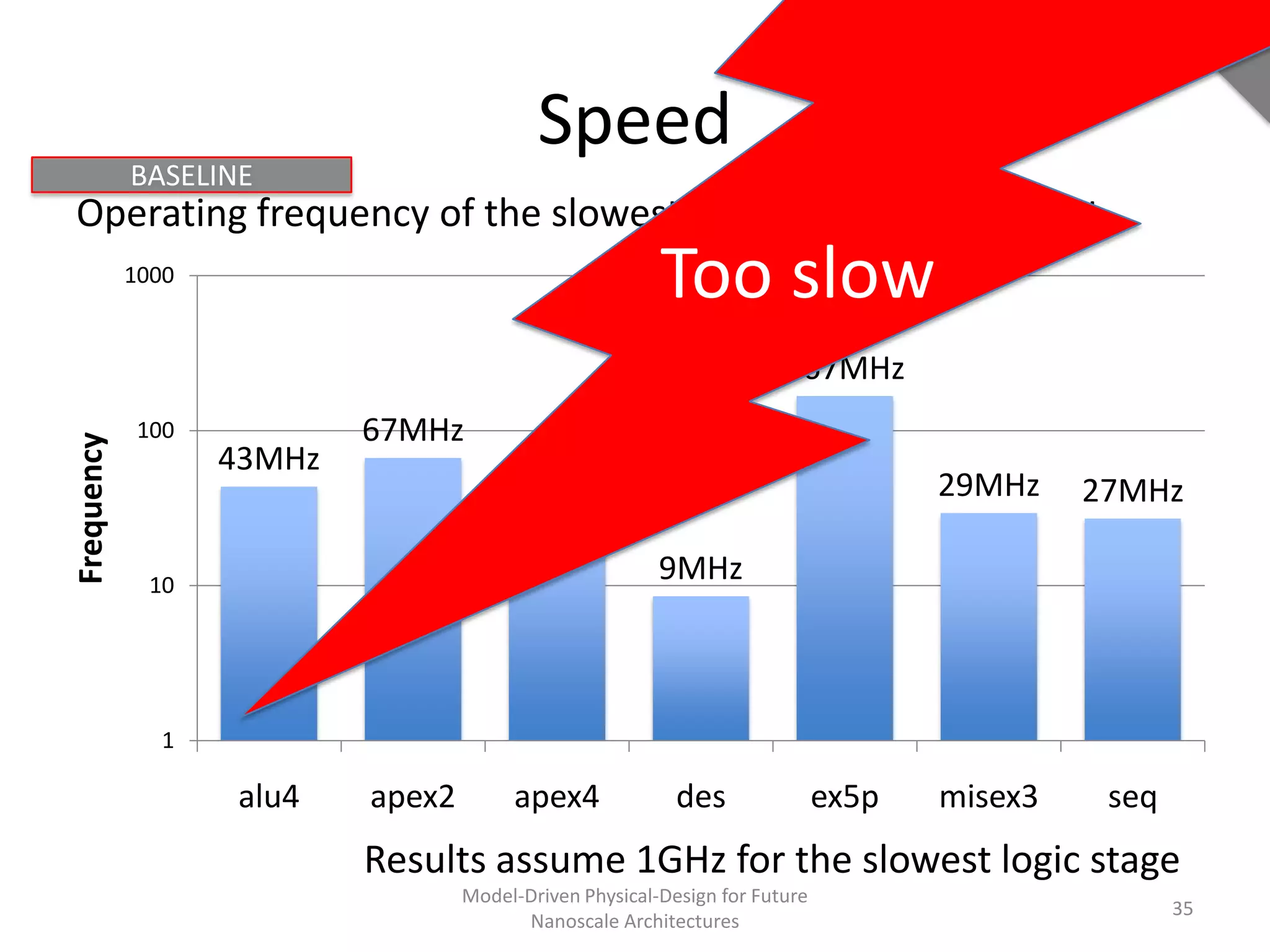
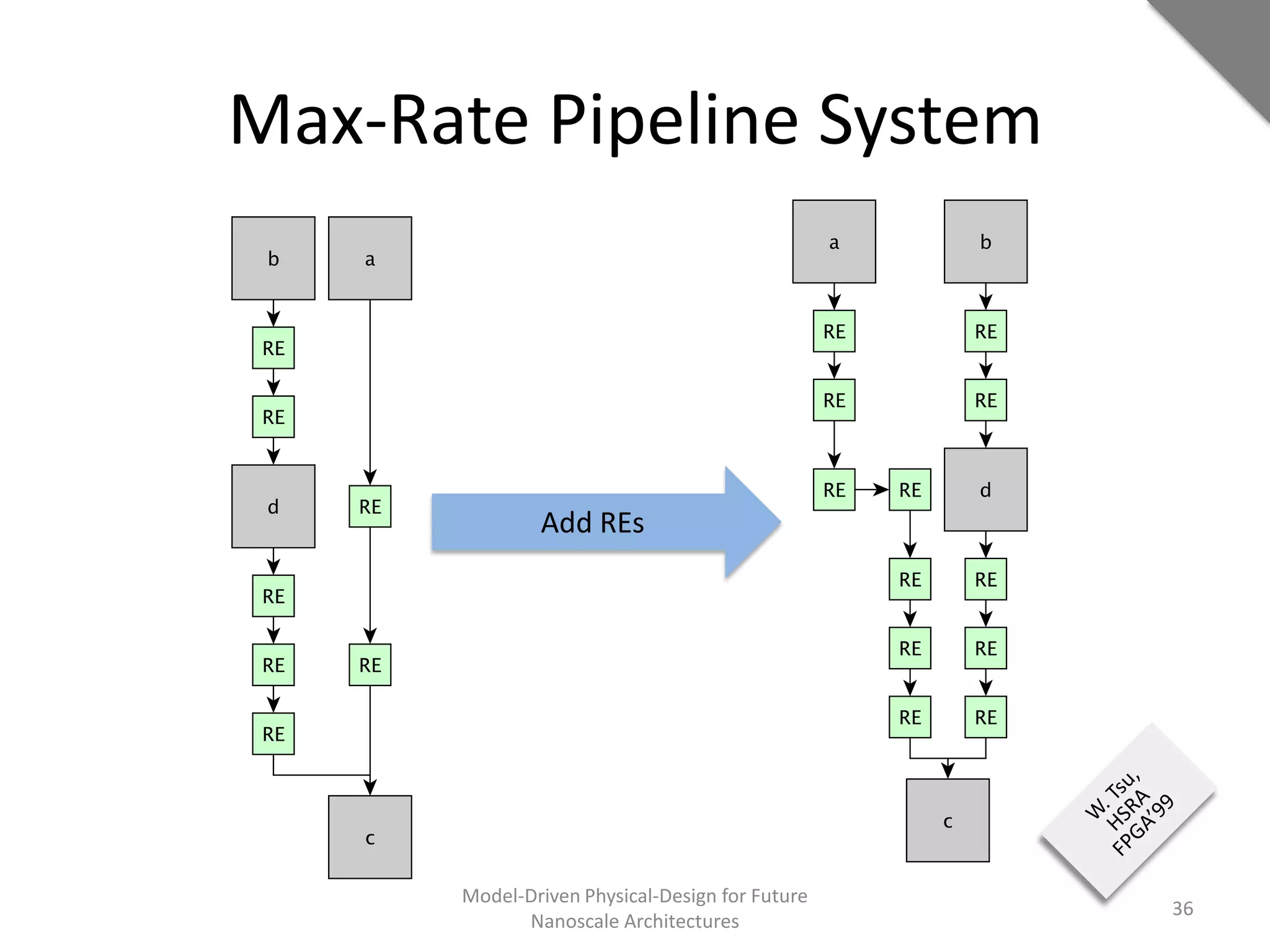
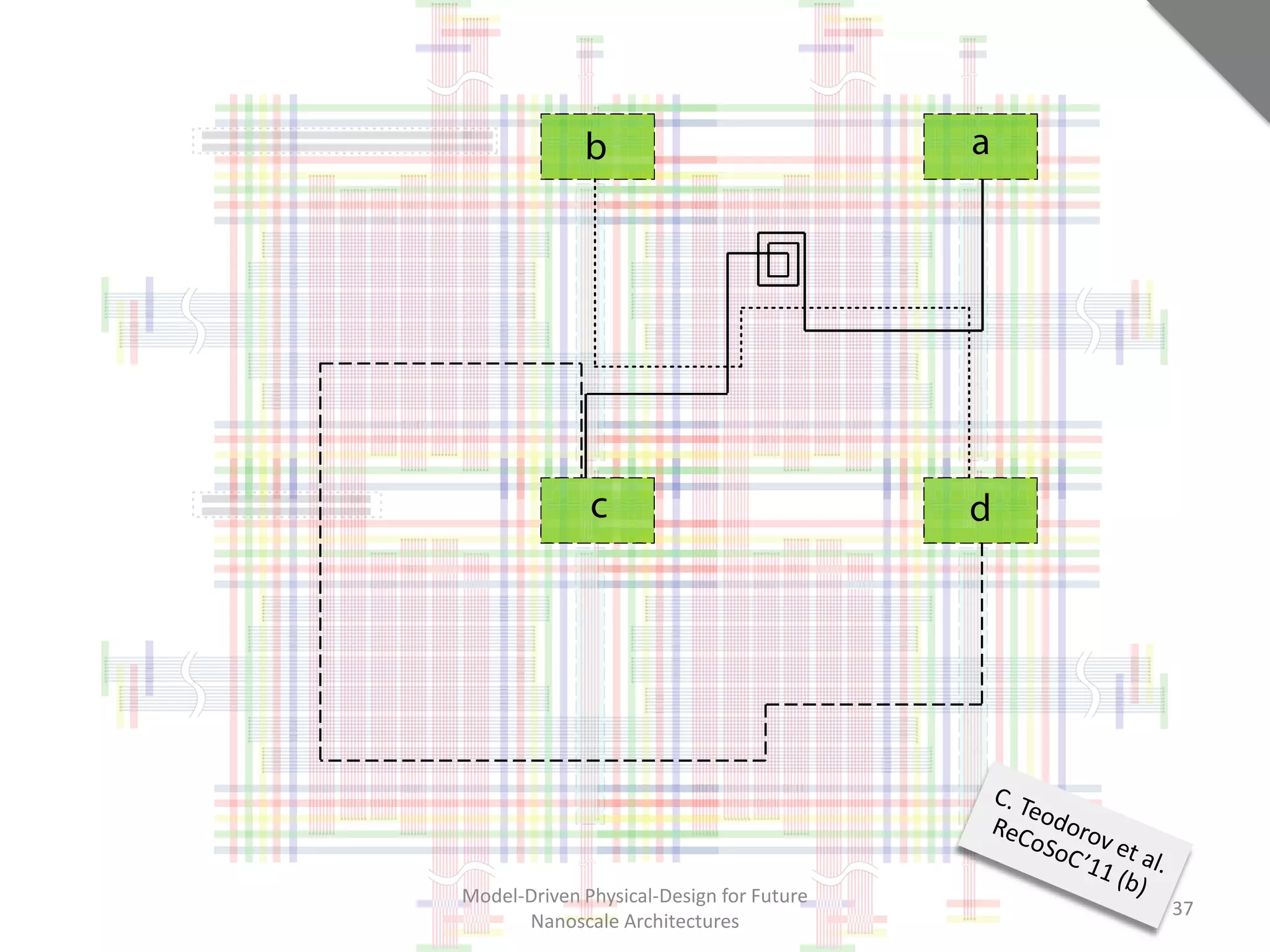
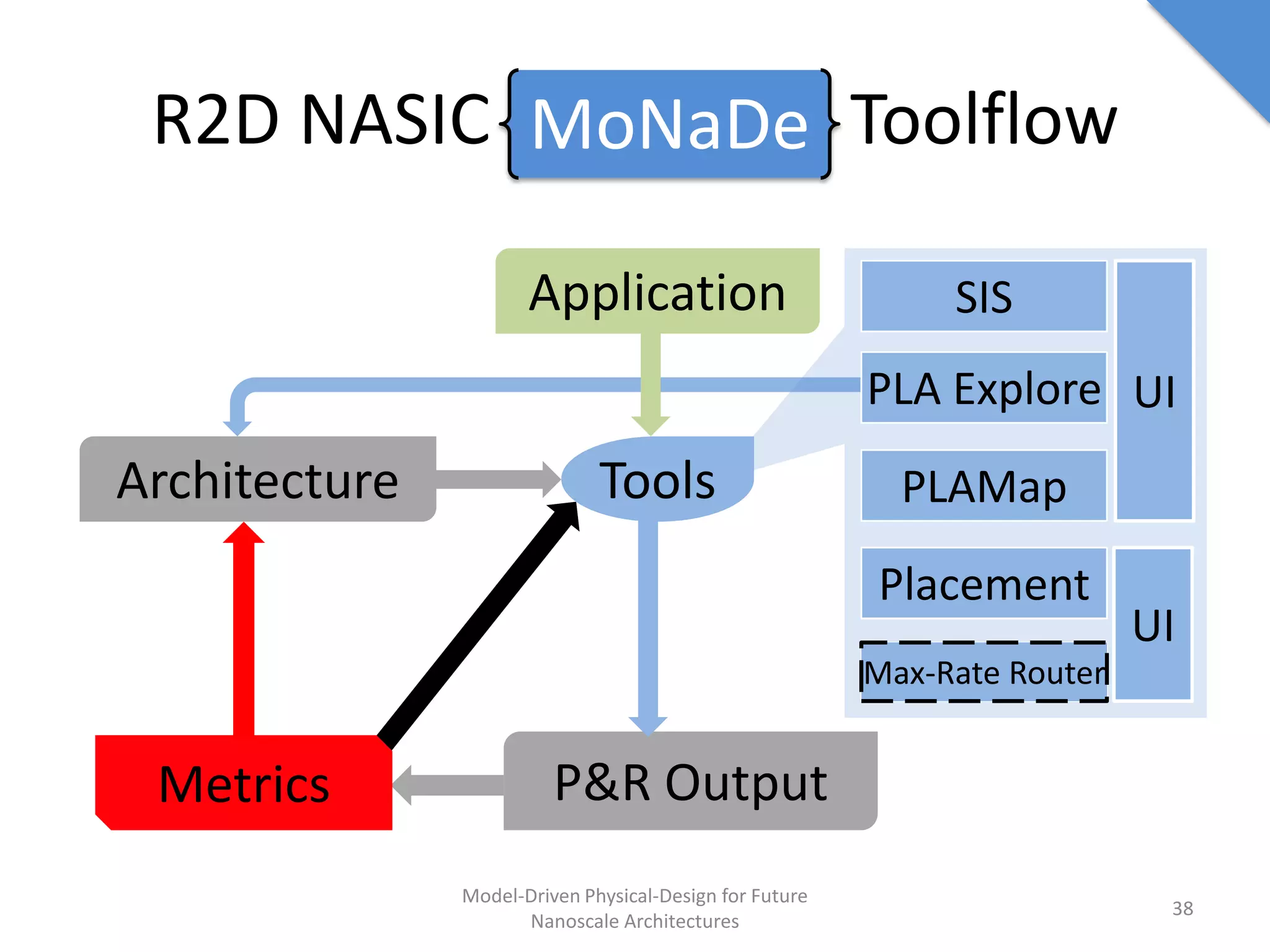
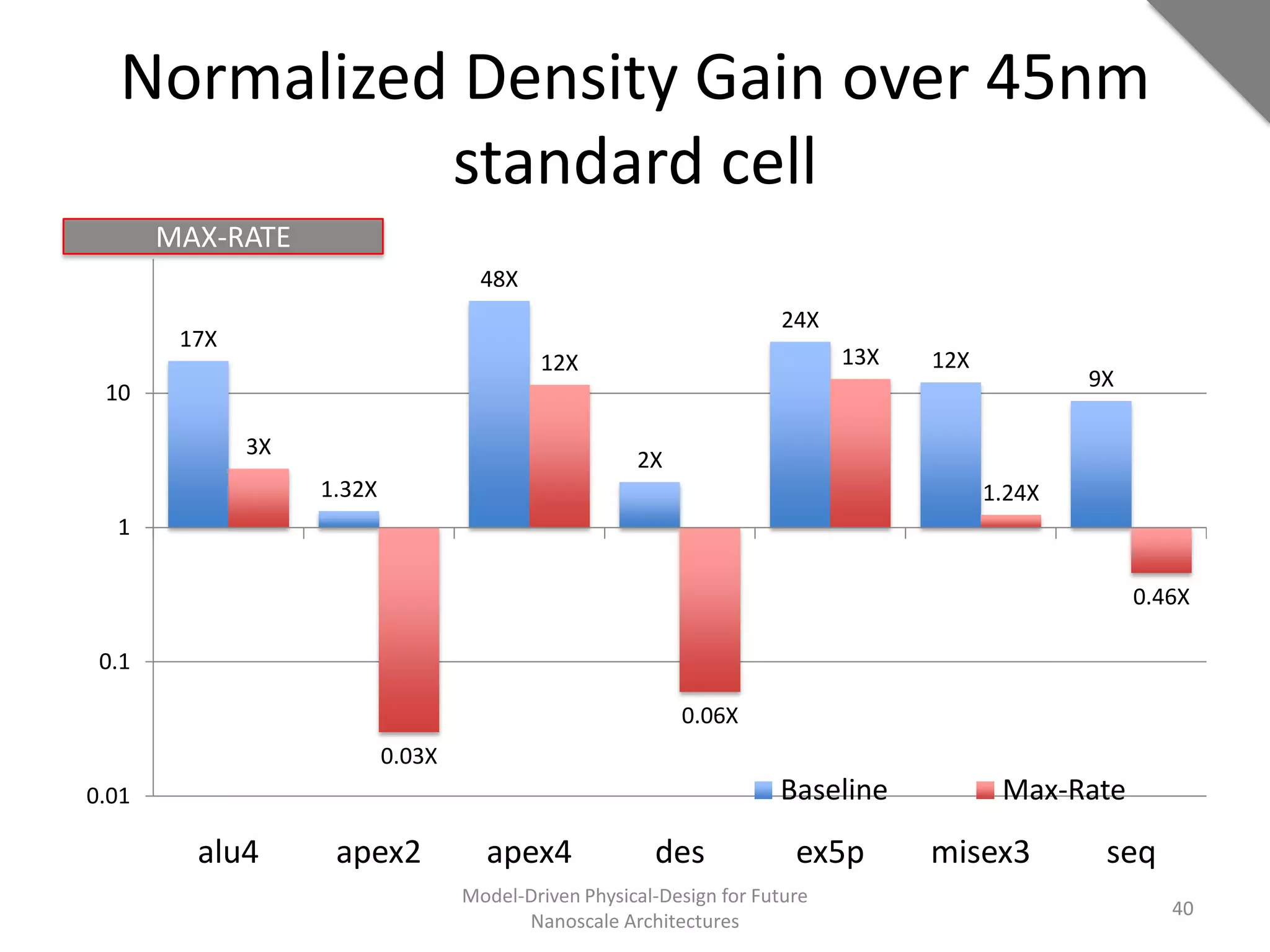
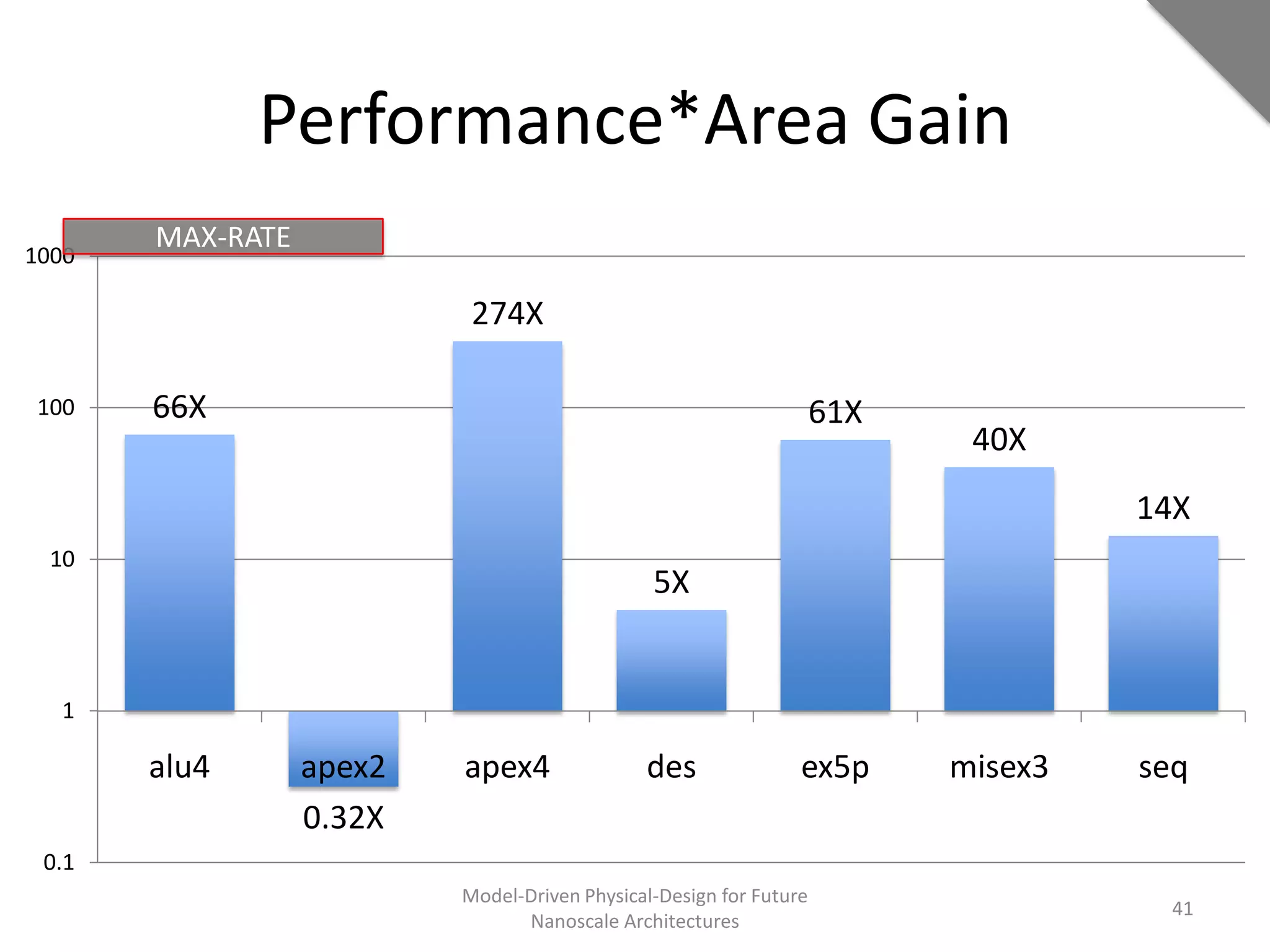
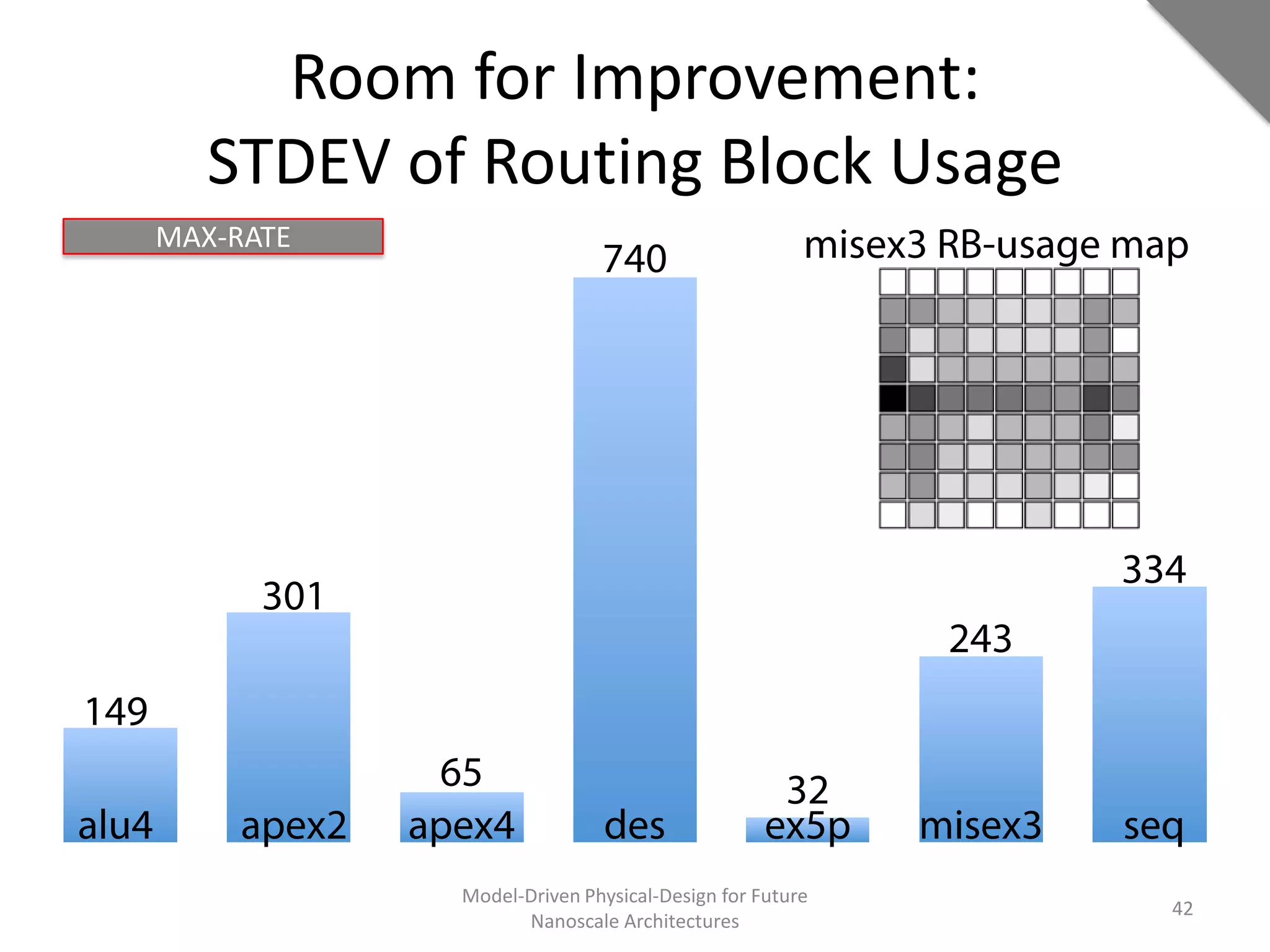
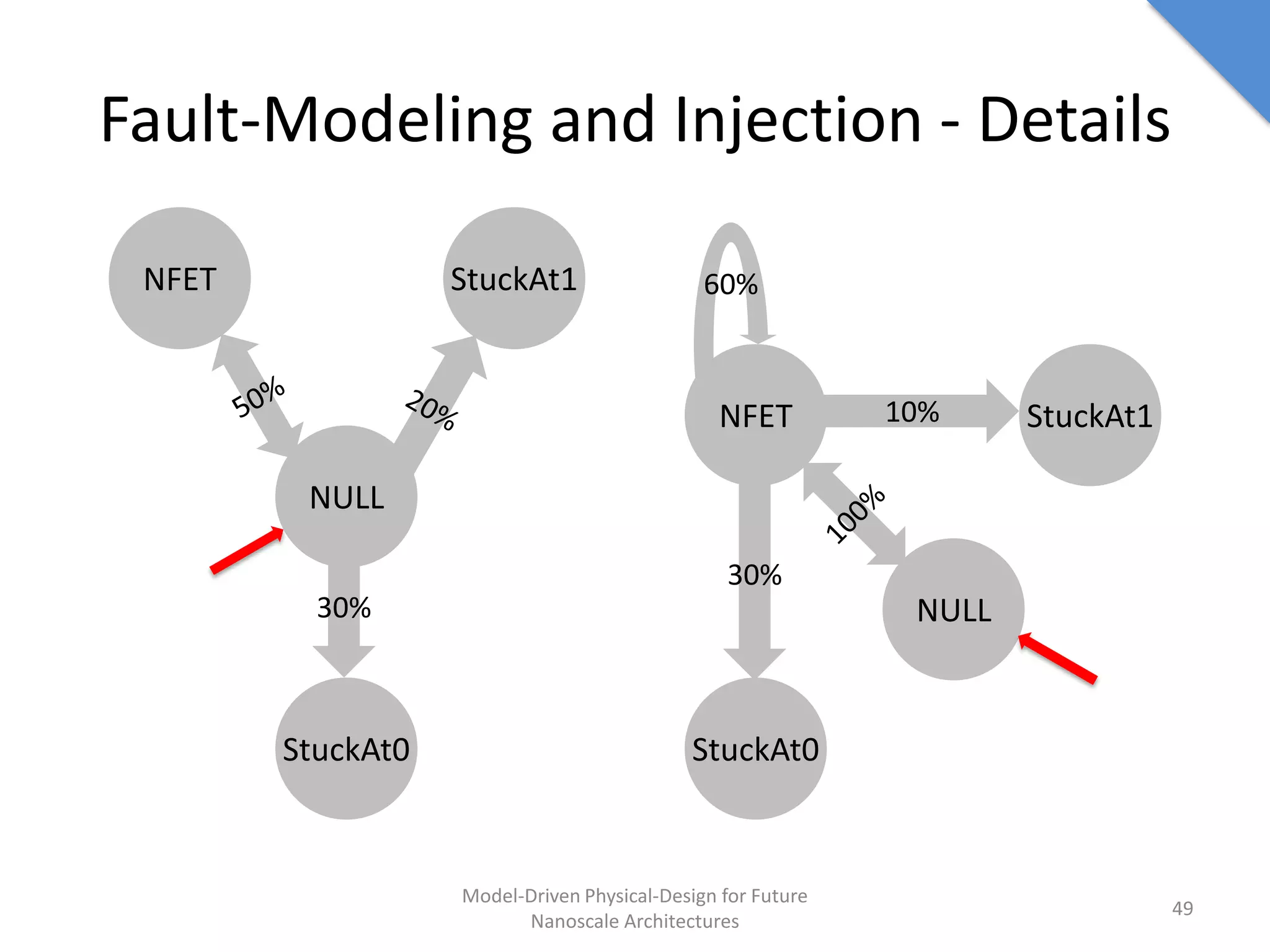
This document discusses model-driven physical design approaches for future nanoscale architectures. It proposes a generic physical design framework based on a common structural domain model. This model-based approach aims to maximize tool reuse across different nanoscale technologies. It also separates algorithmic and architectural concerns by modeling tools as model transformations. An example nanoscale architecture template called R2D NASIC is developed using this framework and evaluated. Results show improvements in density, performance and max throughput pipelines compared to a baseline. Overall, the model-driven approach seeks to provide a common vocabulary and design flow for tackling challenges in physical design for emerging nanotechnologies.