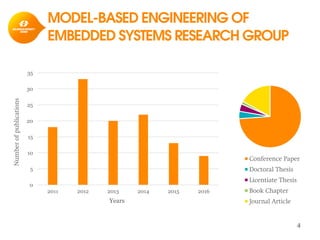
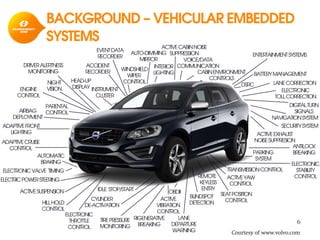
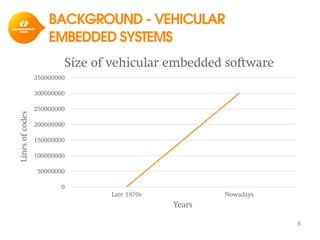
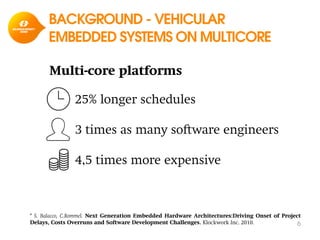
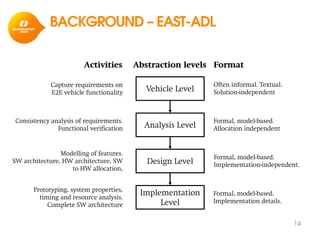
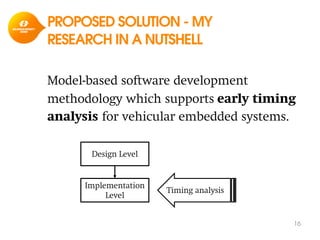
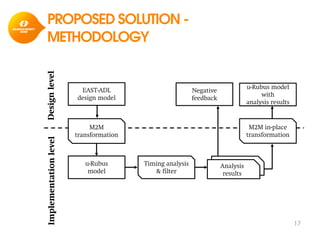
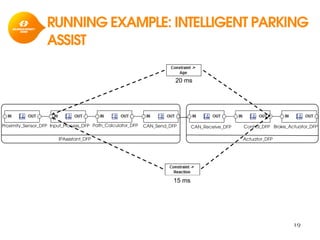
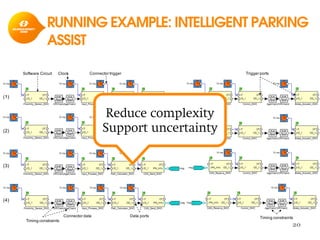
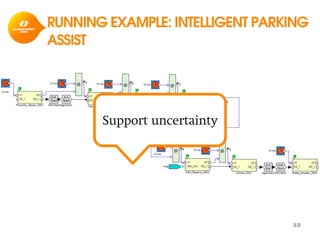
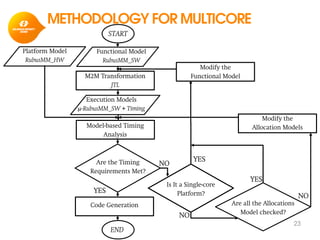
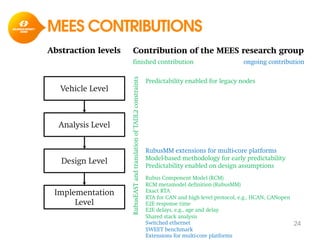
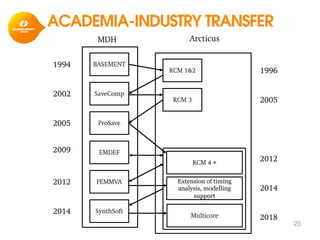
The document discusses model-based development for vehicular embedded systems. It outlines the Model-based Engineering of Embedded Systems research group, which has 16 research projects and focuses on model-based engineering and real-time systems design. The document then discusses the background of vehicular embedded systems, noting their increasing complexity, size of code, and challenges of multi-core platforms. It proposes a solution of a model-based software development methodology supporting early timing analysis. Key aspects are reducing accidental complexity, early timing verification, and support for uncertainty and multi-core platforms. An example of an intelligent parking assist system is used to illustrate the methodology.