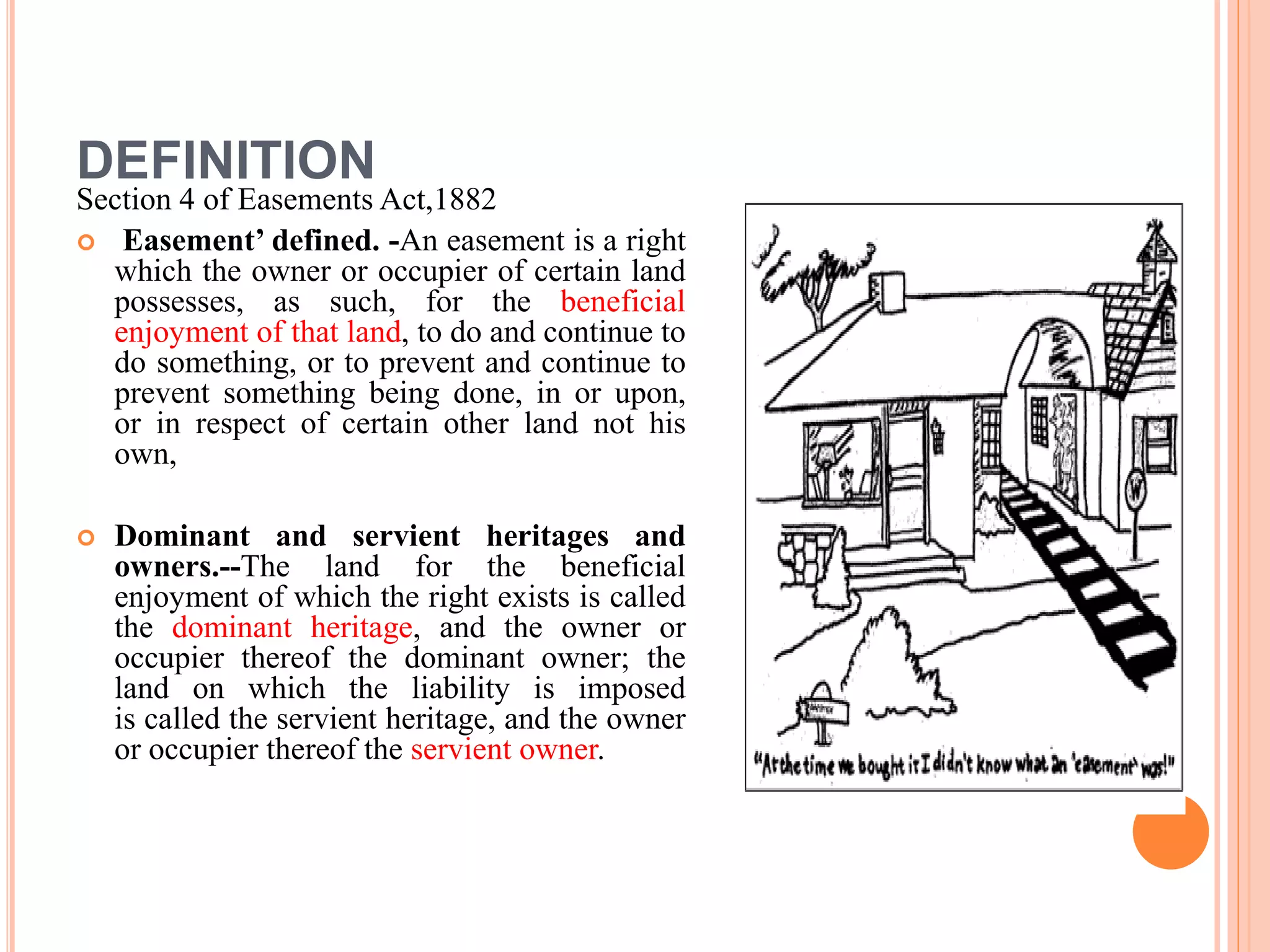
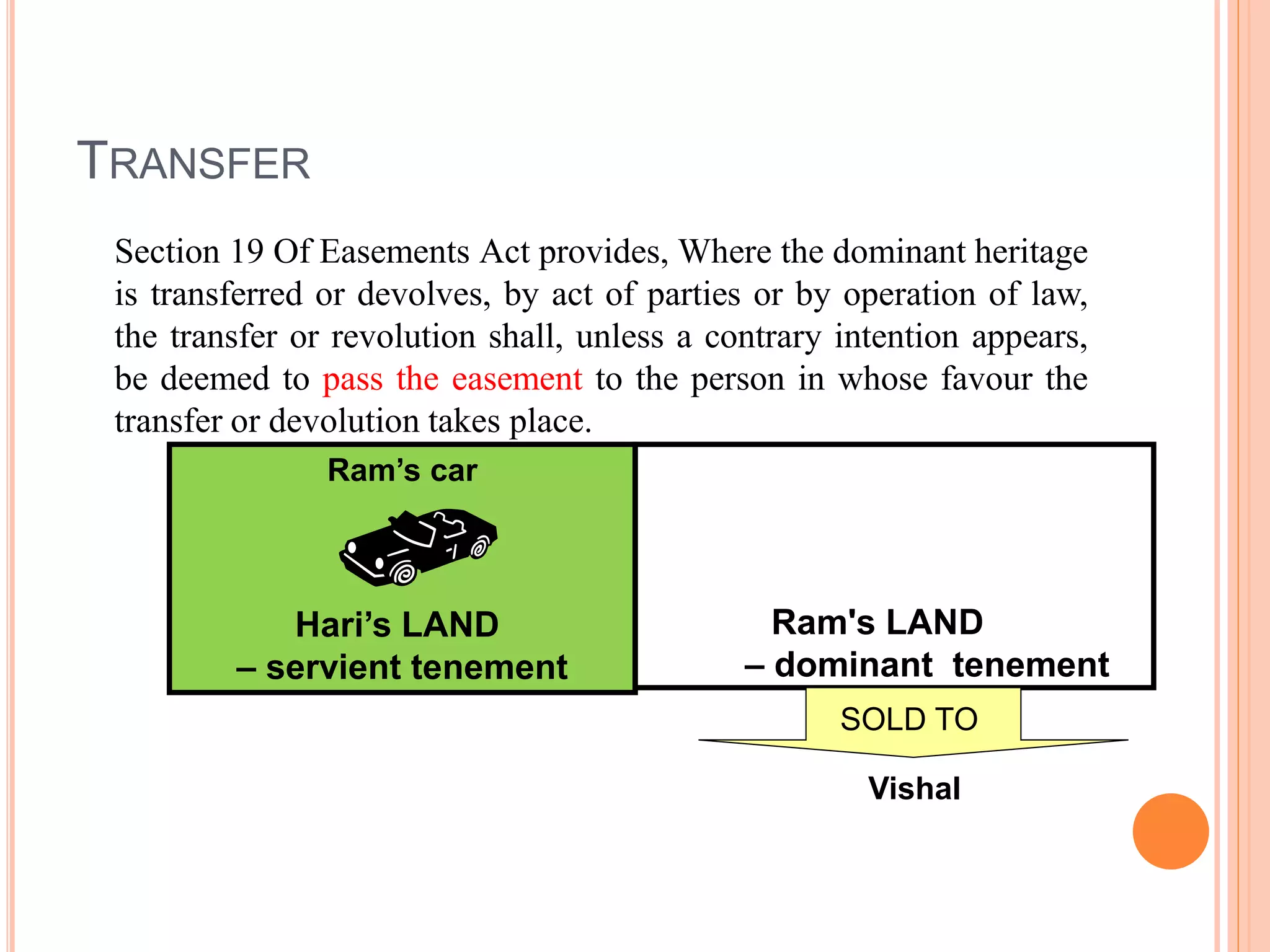
This document discusses the various modes of acquisition of easements under Indian law. It defines an easement and outlines the key elements. Easements can be acquired through grant, prescription after 20 years of peaceful use, operation of law, necessity upon severance of property, prior quasi-easements, customary use, or court decision. The types of easements include appurtenant easements that run with the land and easements in gross for personal use. Easements can also be transferred with the dominant land automatically unless stated otherwise.