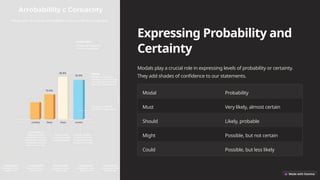
The document discusses modals and auxiliary verbs, highlighting their significance in enhancing sentence meaning and expression. It categorizes modals into various types such as those for ability, permission, obligation, and possibility, while explaining their role in conveying probability and constructing sentences in different tenses. Additionally, it provides guidance on negation, question formation, common expressions, and includes practice exercises for applying modal knowledge.