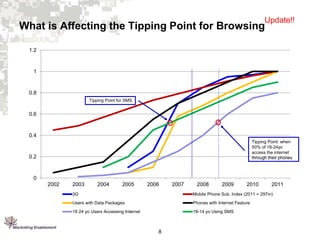
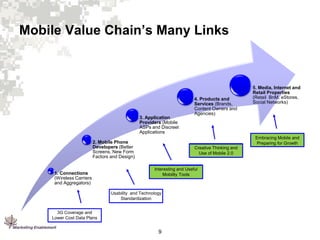
1. Mobile browsing and application use is growing, especially among younger users, and will continue to grow rapidly with improvements in mobile technology and data plans.
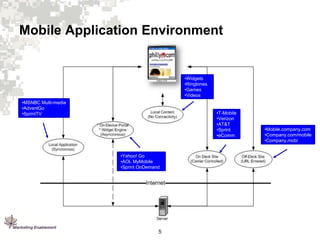
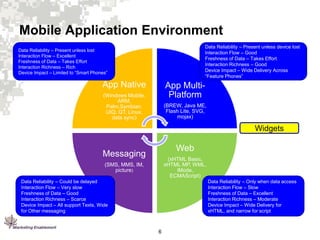
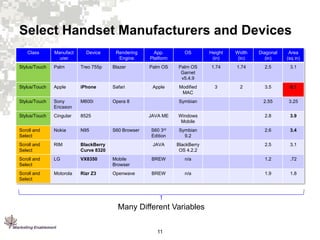
2. Mobile devices have varying capabilities and operate differently than desktops due to their mobile nature.
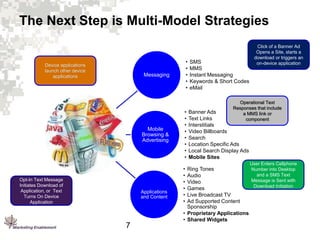
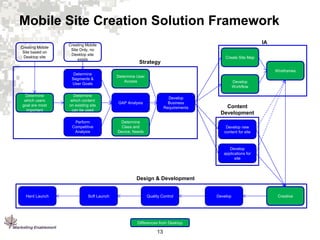
3. Marketing Enablement has developed a framework and best practices for mobile direct marketing focused on the user experience for different mobile environments.