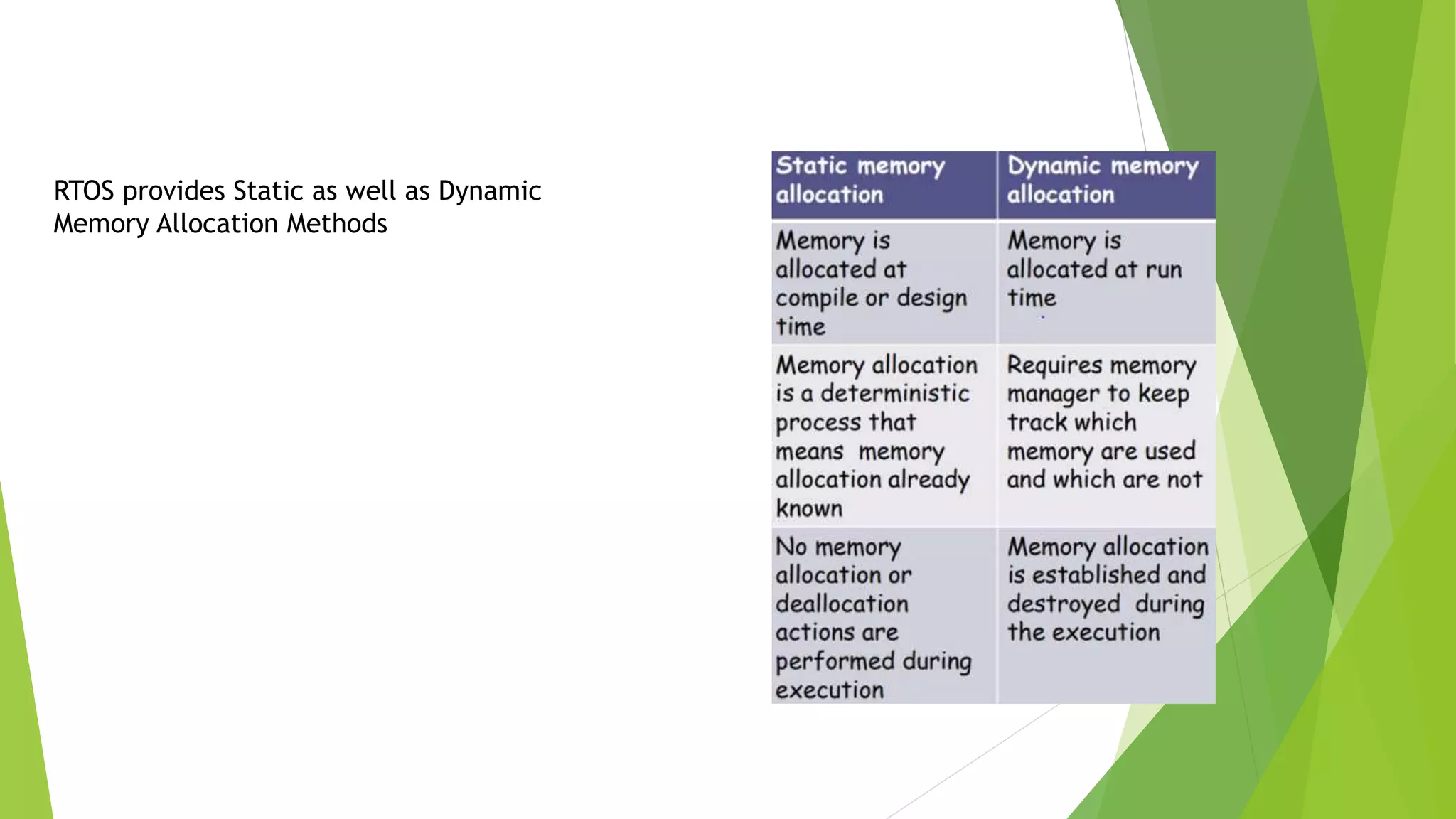
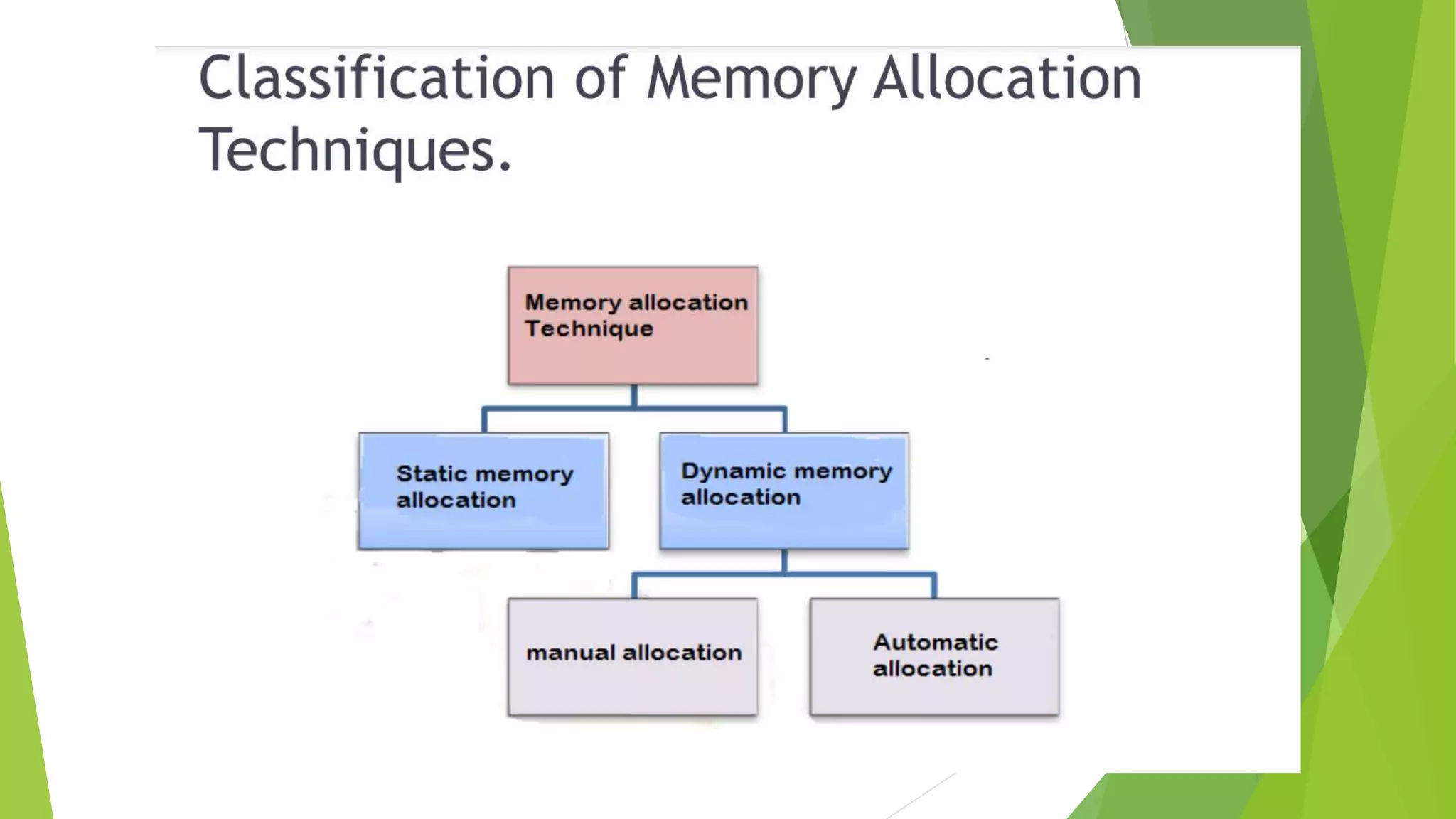
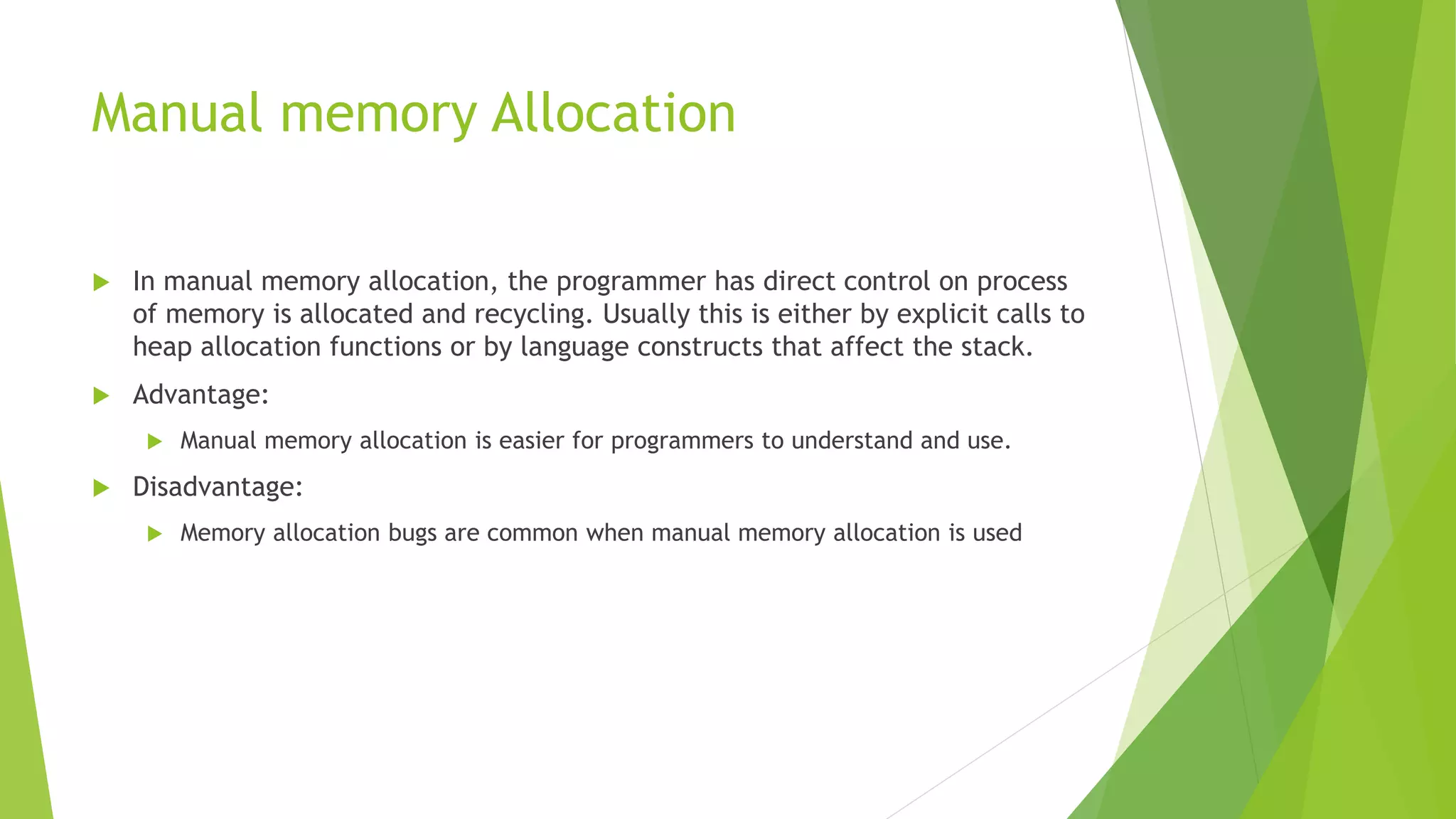
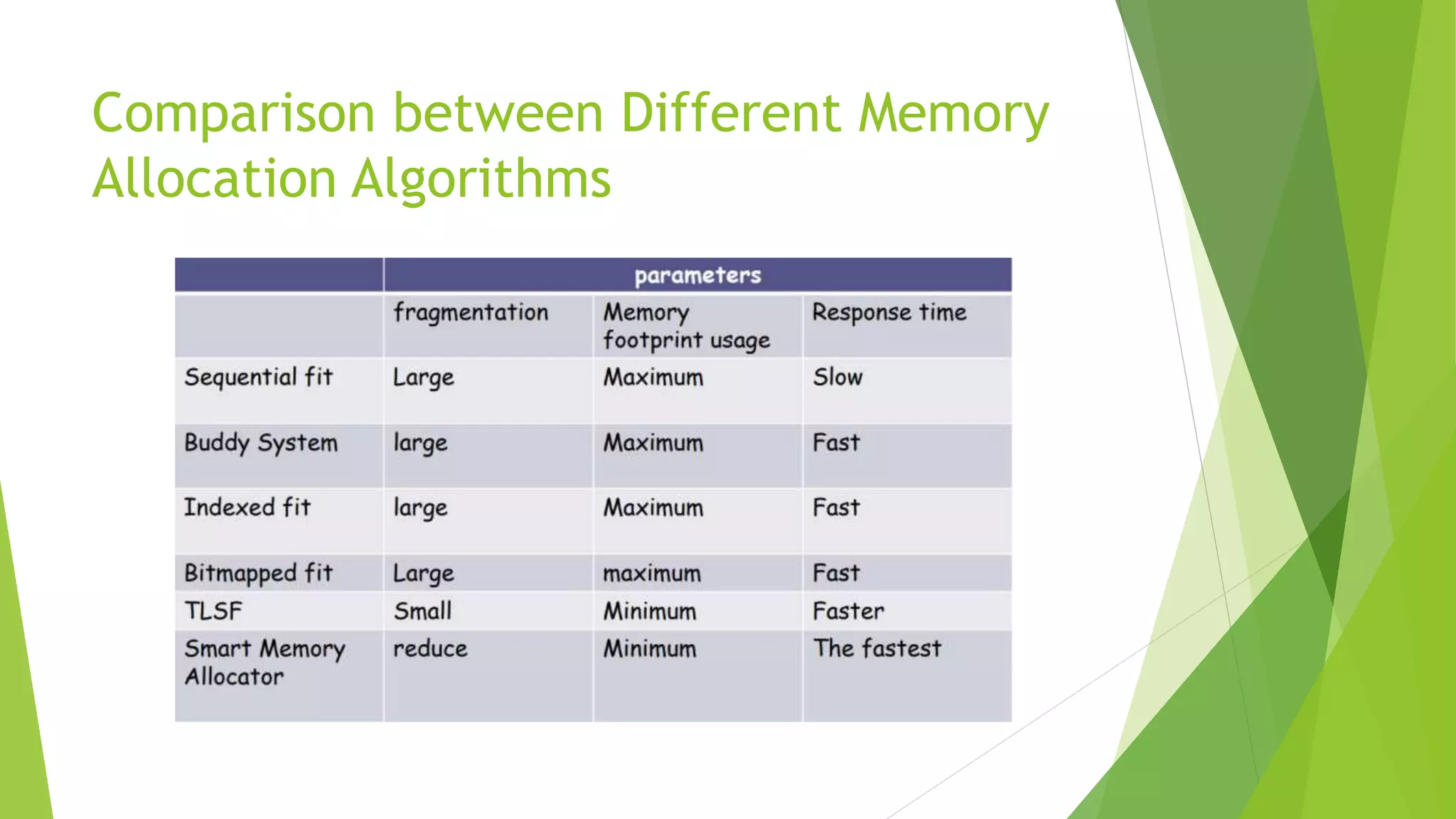
Memory management in RTOS is different than in general purpose operating systems. RTOS focuses on predictable timing and deterministic behavior, compromising effectiveness of memory allocation. RTOS uses block-based allocation of fixed-size blocks from a free buffer queue, rather than dynamic allocation. Most RTOS kernels allow tasks to access any memory without protection for predictability, assuming the design is proven correct. Some RTOS kernels provide optional memory protection and fail-safe modes for illegal access. Dynamic allocation algorithms like first-fit and best-fit are used to allocate from memory blocks.