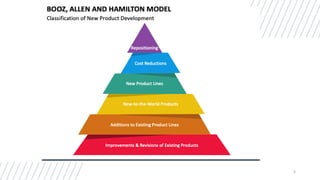
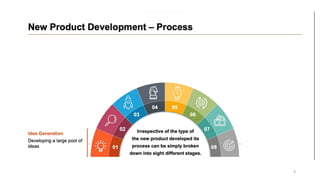
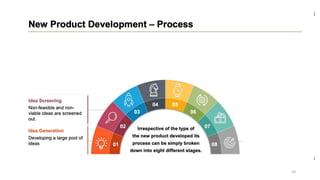
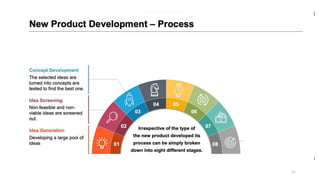
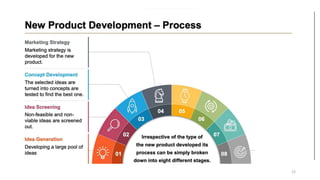
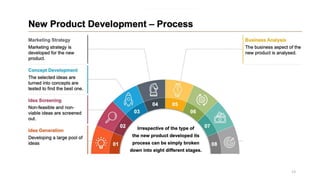
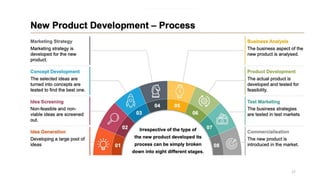
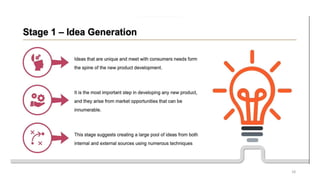
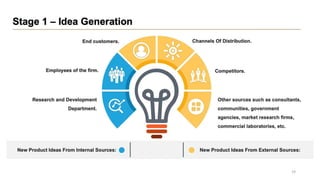
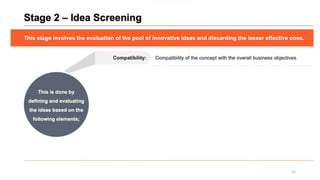
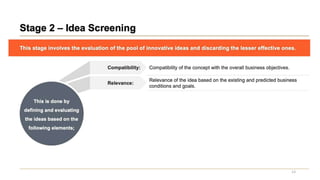
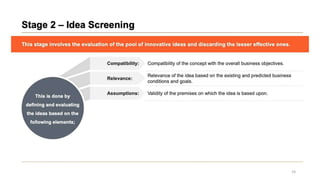
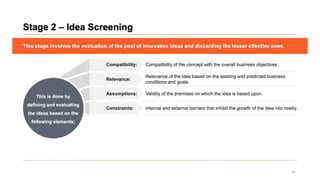
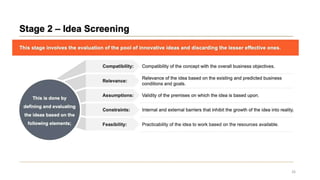
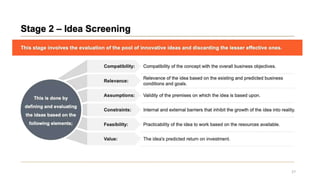
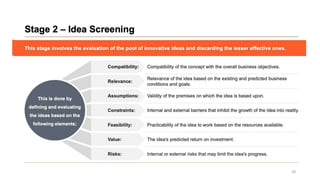
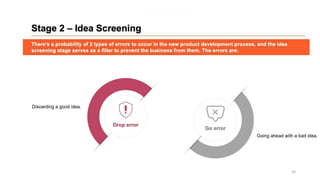
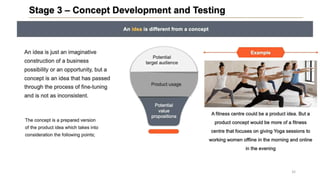
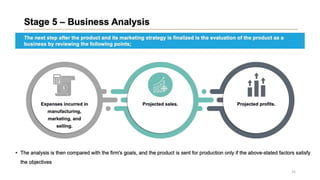
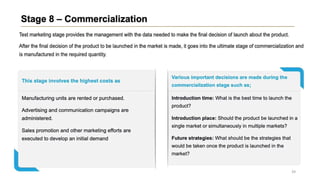
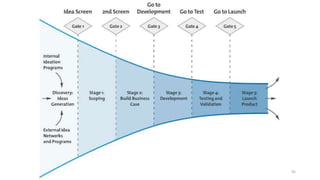
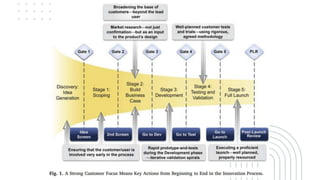
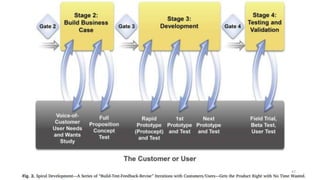
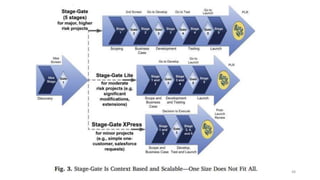
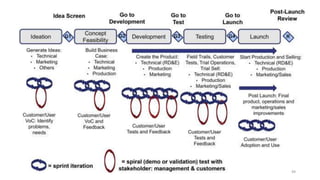
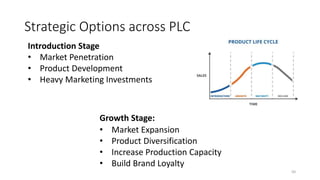
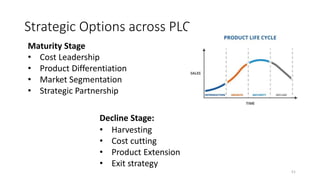
This document discusses marketing strategy decisions for new product development and the product lifecycle. It defines new products from both a customer and firm perspective. Common reasons for developing new products include market differentiation, meeting customer needs, and revenue growth. Statistical data shows that only a small percentage of new product ideas are successfully launched and many launched products fail. Common pitfalls leading to failure include misinterpreting customer requirements, poor product design, and launching at the wrong time. Success in new product development depends on factors like developing products with unique benefits, incorporating customer feedback, and properly executing launch marketing plans. Strategic decisions must be made throughout the different stages of the product lifecycle from introduction to decline. Both bringing new products to market and scaling existing