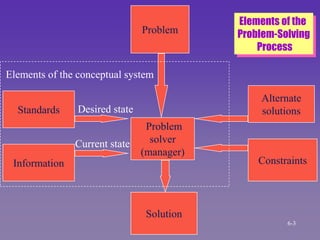
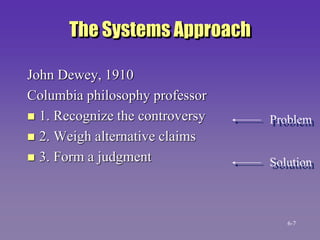
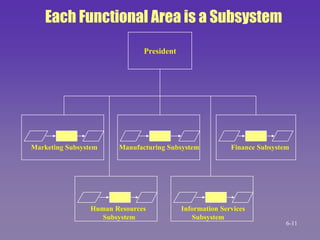
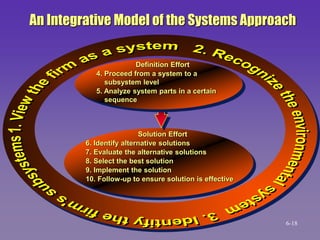
The document discusses the systems approach to problem solving. It describes the elements of the problem solving process which include the desired state, current state, constraints, and standards. It also outlines the 10 steps of the systems approach which involve preparation, definition, and solution efforts. These steps include identifying subsystems, analyzing system parts, identifying alternative solutions, evaluating alternatives, selecting the best solution, implementing it, and following up. The systems approach views the organization as a system and breaks problems down into their components to systematically address issues.










![Definition Effort [cont.]
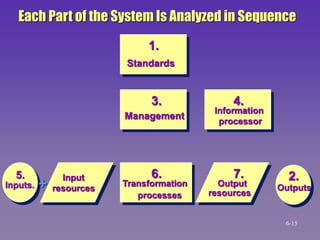
Step 5: Analyze System Parts in a Certain
Sequence
1. Evaluation standards. They must be valid,
realistic, understandable, measurable
2. Compare system outputs with standards
3. Evaluate management
4. Evaluate the information processor
5. Evaluate the inputs and input resources
6. Evaluate the transformation processes
7. Evaluate the output resources
6-14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/miswk-5-220926081149-62fc520b/85/MIS-Wk-5-ppt-14-320.jpg)




![Summary [cont.]
Management by exception
Managerial problem solving
Classification of problems
– Structured
– Unstructured
Use of the systems approach
6-21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/miswk-5-220926081149-62fc520b/85/MIS-Wk-5-ppt-21-320.jpg)