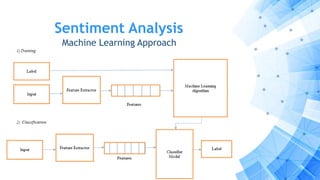
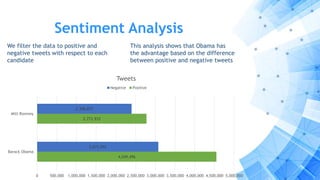
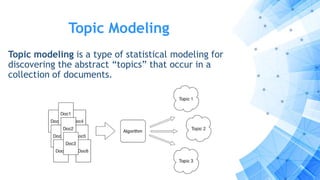
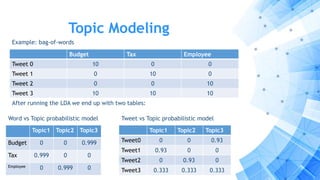
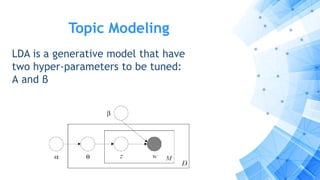
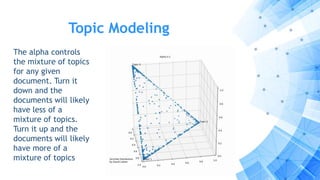
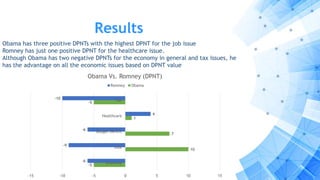
The paper discusses a computational approach to public opinion mining related to economic issues during the 2012 U.S. presidential election using social media data, specifically Twitter. It analyzes a dataset of 24 million tweets through sentiment analysis and topic modeling, revealing that Barack Obama had a significant advantage over Mitt Romney in terms of public sentiment on economic issues. Ultimately, the findings align with the election results, showing Obama won with a substantial lead in both popular and electoral votes, highlighting the importance of economic issues in voter decision-making.