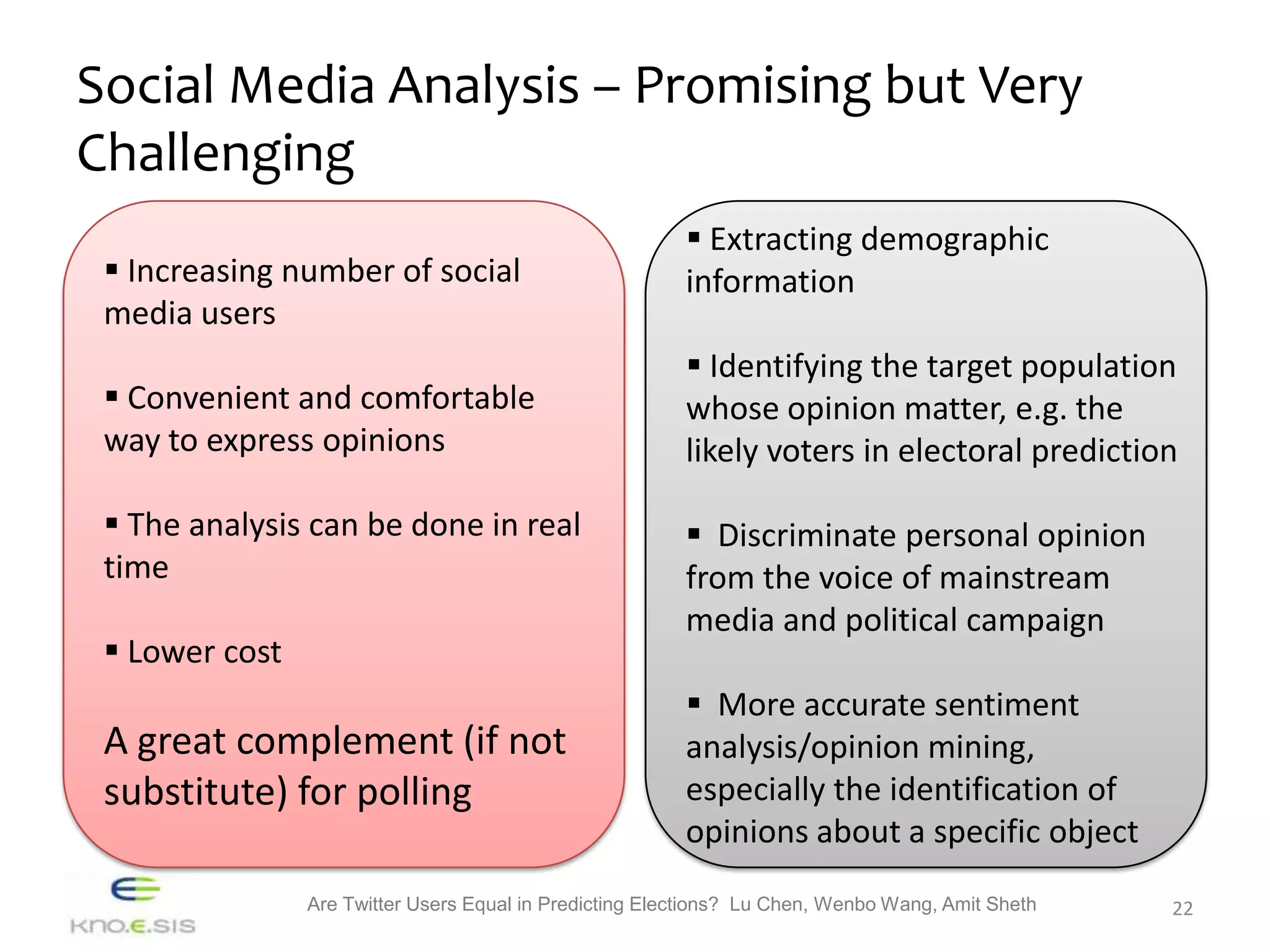
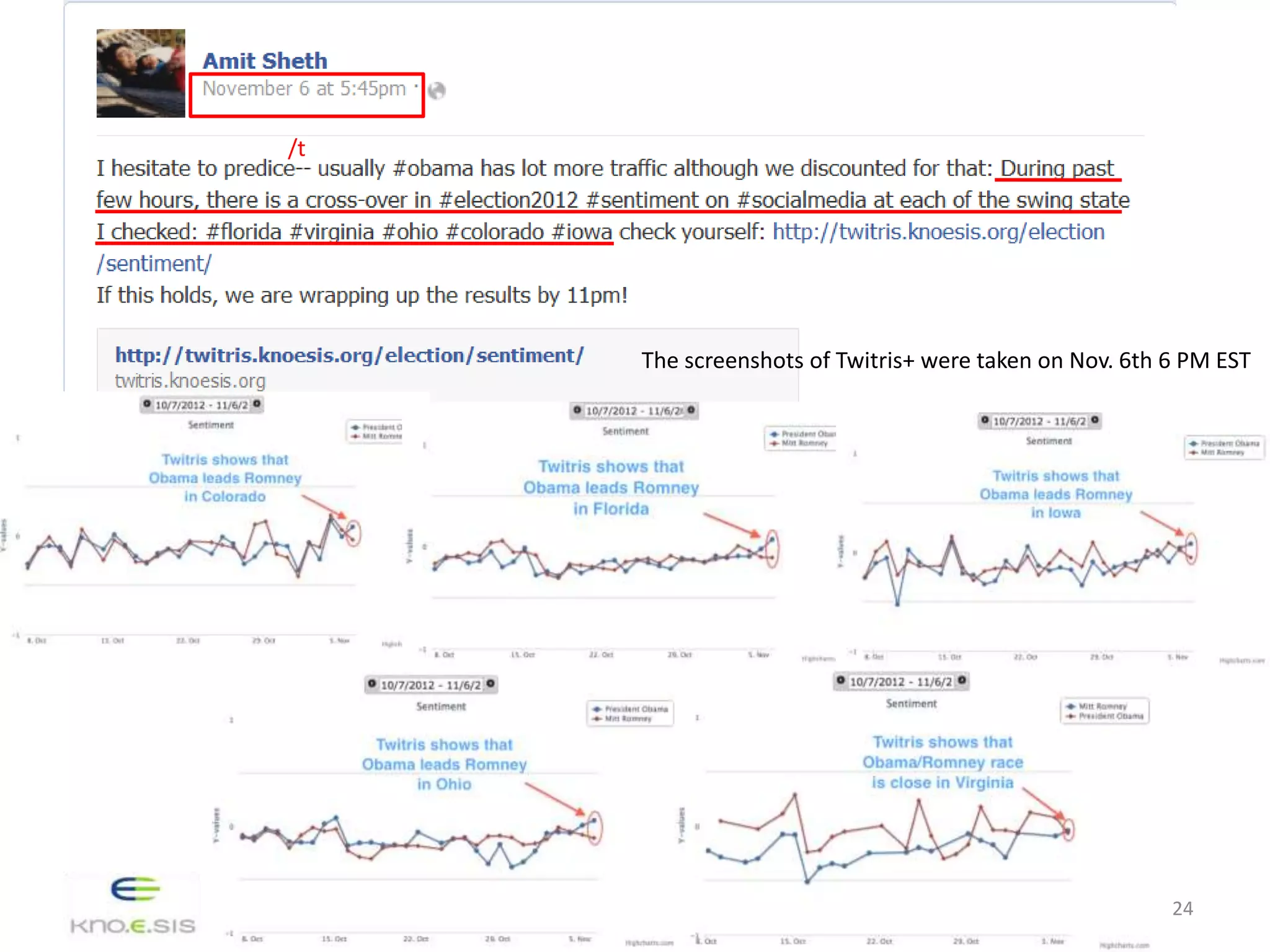
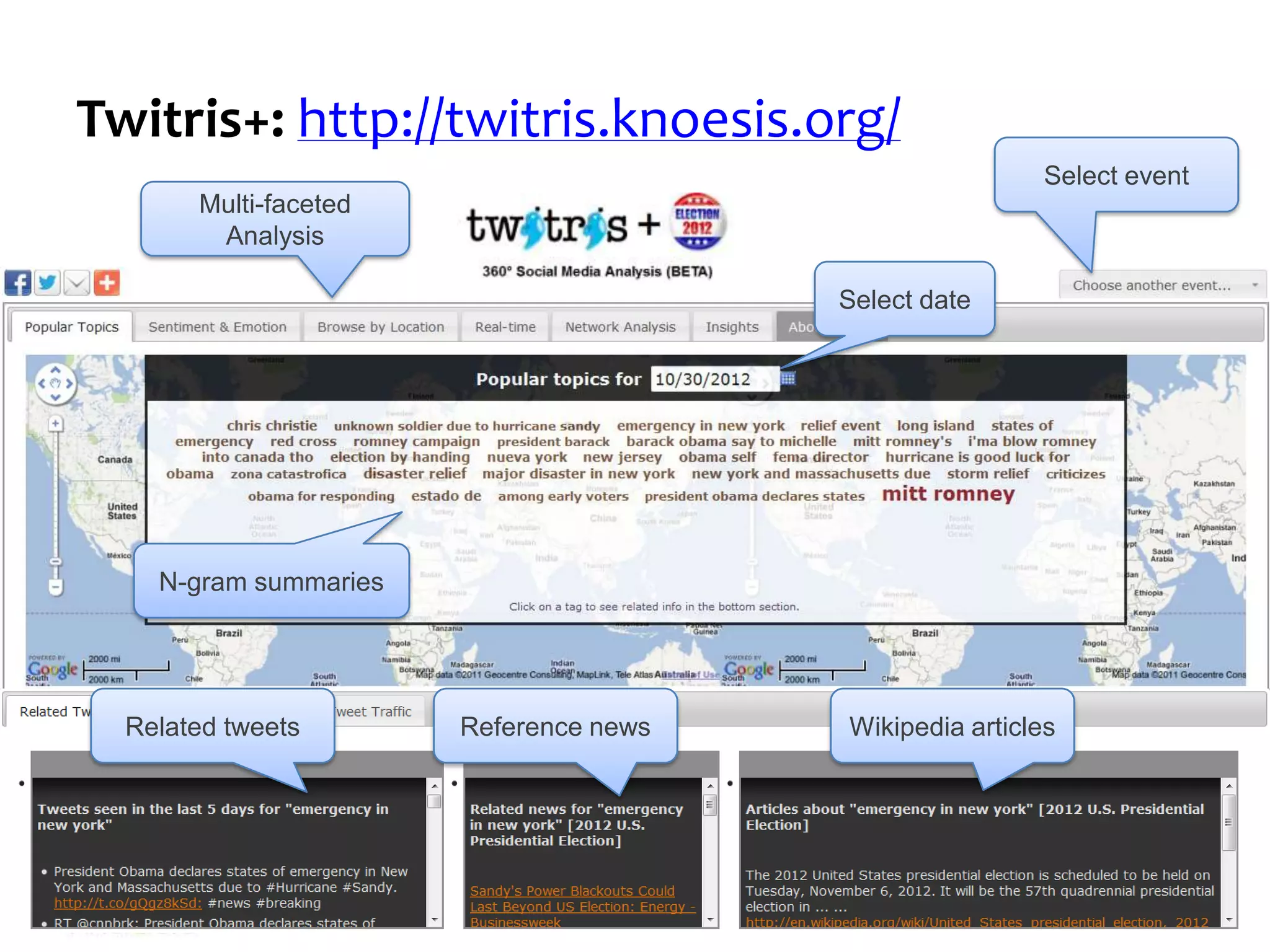
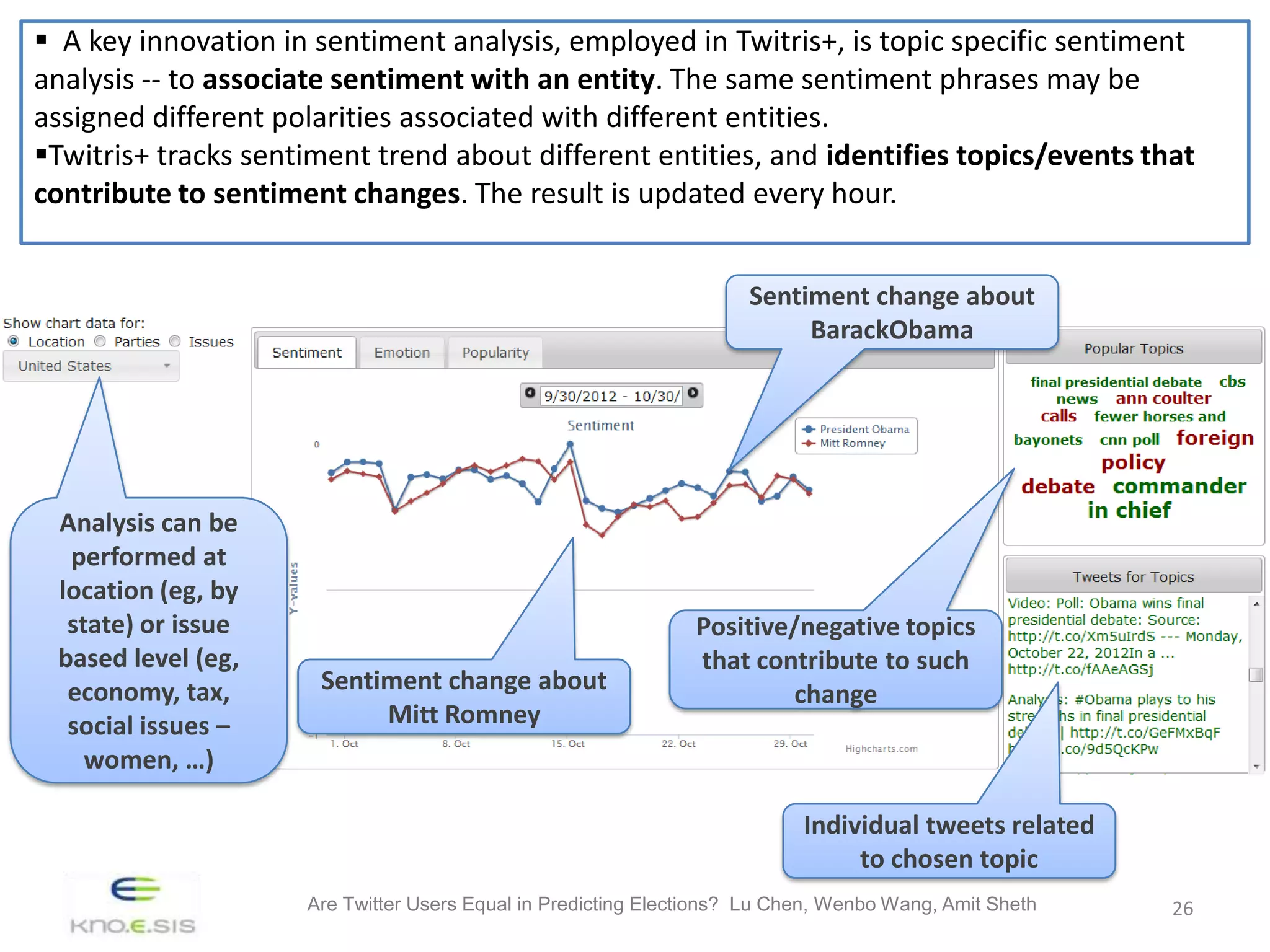
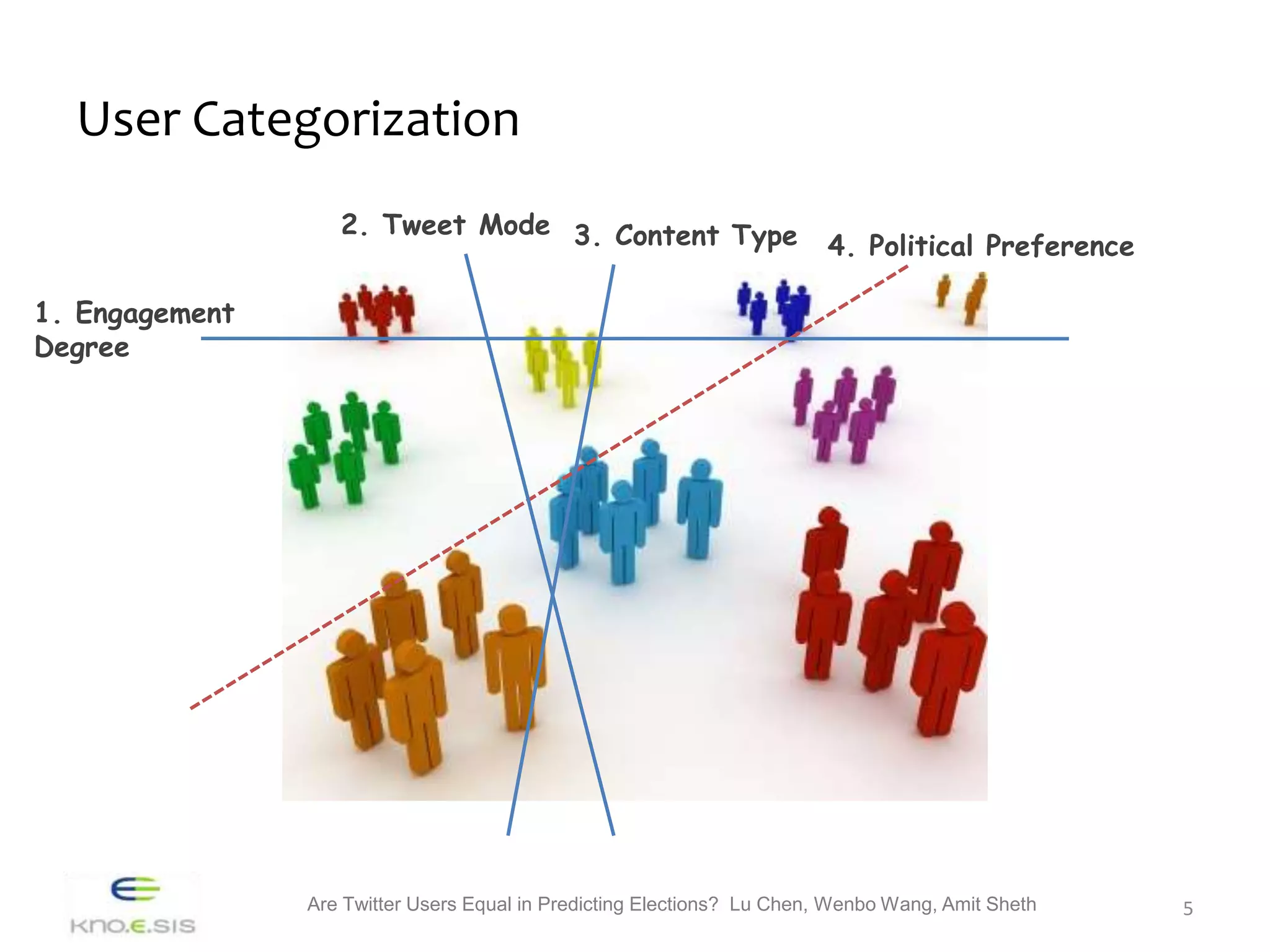
The study investigates whether different groups of Twitter users are equally effective in predicting election outcomes during the 2012 U.S. Republican presidential primaries. By analyzing over 6 million tweets, the research categorizes users based on engagement levels and political preferences, revealing that right-leaning users show greater involvement and predictive accuracy than left-leaning users. The findings emphasize that user engagement and sentiment significantly influence the ability to accurately forecast election results, suggesting that not all Twitter users hold equal predictive power.








![2 Representative of the Target Population
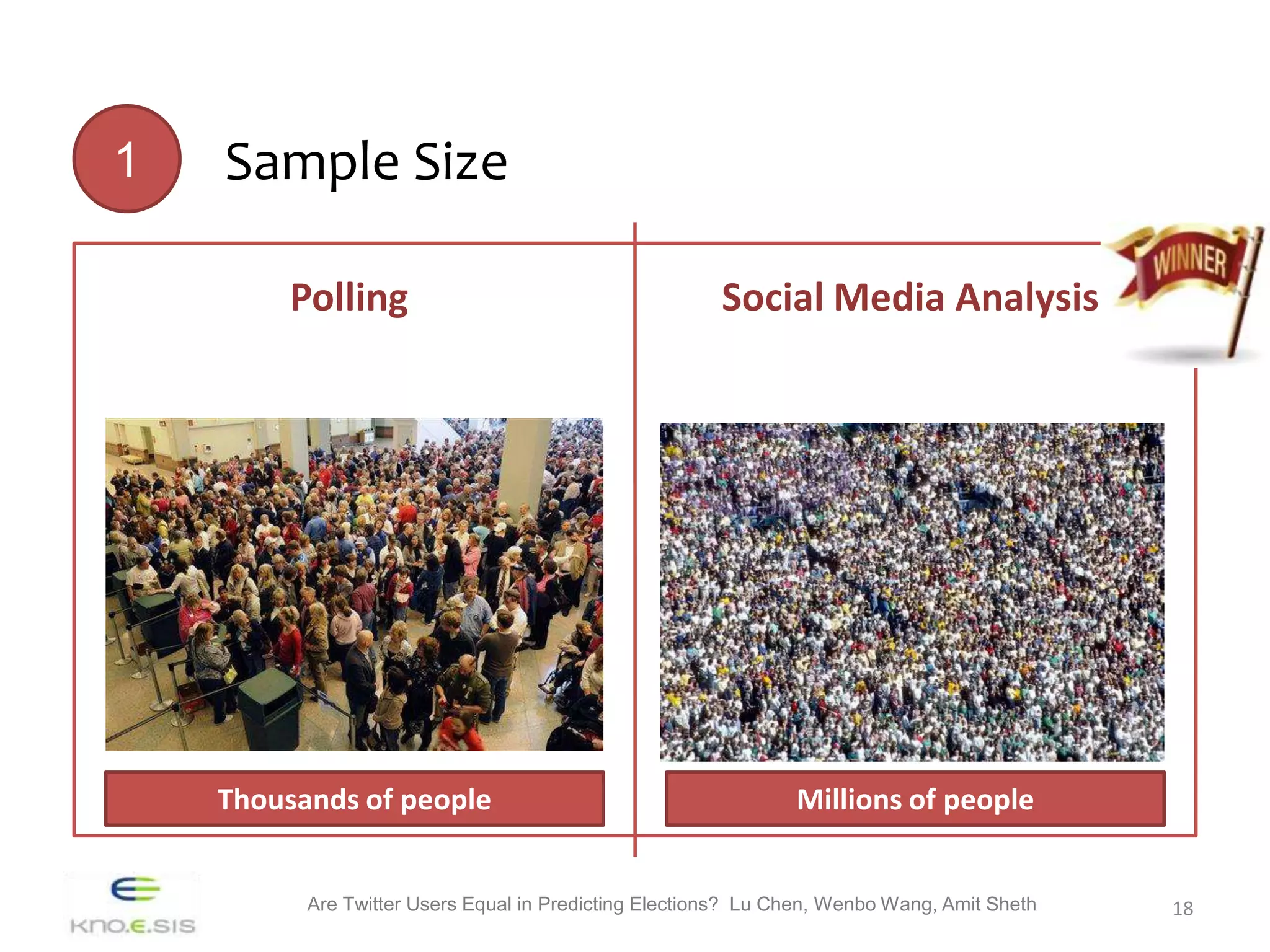
Polling Social Media Analysis
About 95% of US homes can be
reached by landline telephone and
cell phone. About 60% of American adults
Sampling the target population use social networking sites.
randomly. Difficult to do random sampling.
Weighting the sample to census Limited demographic data
estimates for demographic (although with some work, can be
characteristics (gender, race, age, improved).
educational attainment, and
region).
[1] Can Social Media Be Used for Political Polling? http://www.radian6.com/blog/2012/07/can-social-media-be-used-for-political-polling/
Are Twitter Users Equal in Predicting Elections? Lu Chen, Wenbo Wang, Amit Sheth 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/socinfo2012-electionprediction-dec-2012-121202195132-phpapp02/75/Are-Twitter-Users-Equal-in-Predicting-Elections-Insights-from-Republican-Primaries-and-2012-General-Election-19-2048.jpg)