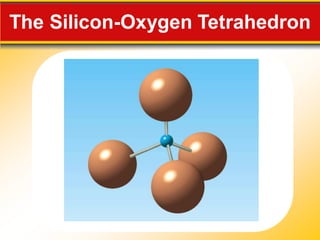
Minerals are naturally occurring solid substances with an orderly crystalline structure and definite chemical composition that are generally considered inorganic. Minerals form through processes like crystallization from magma, precipitation, and changes in pressure and temperature including from hydrothermal solutions. Minerals can be classified into groups based on their composition including silicates containing silicon and oxygen, carbonates containing carbon, oxygen, and metals, oxides containing oxygen and metals, sulfates and sulfides containing sulfur, halides containing halogens, and native elements existing in relatively pure form. The properties of minerals that can be used for identification include color, streak, luster, crystal form, hardness, cleavage, fracture, density, and other distinctive properties.