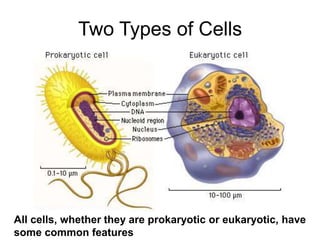
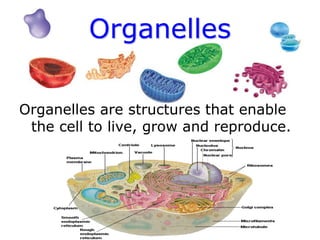
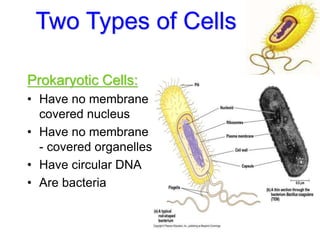
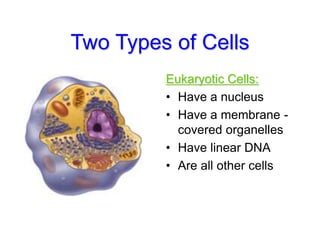
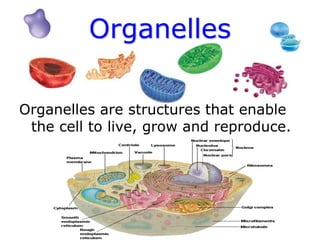
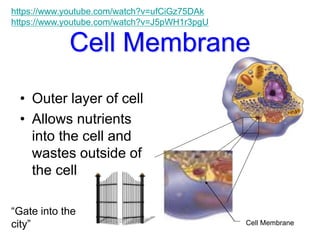
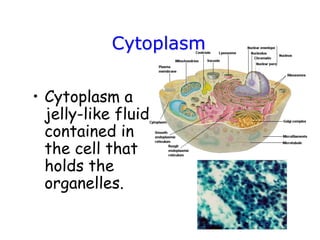
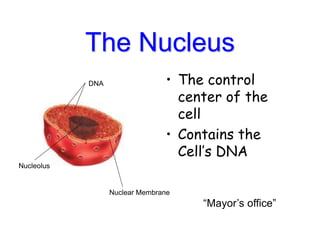
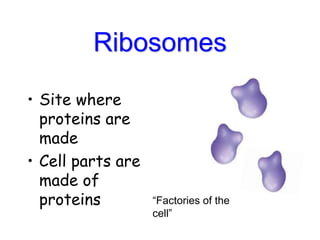
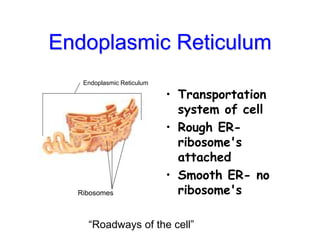
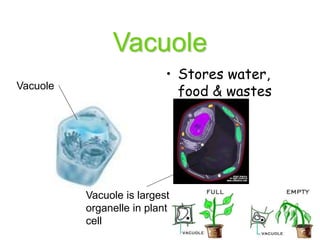
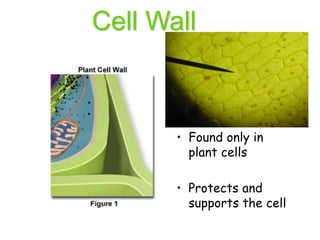
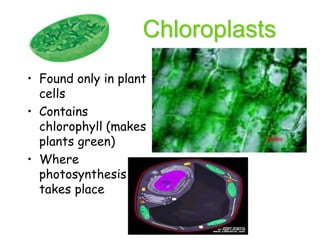
Cells are the fundamental units of structure and function in living organisms, with all living things made up of cells. The document discusses the discovery of cells, types of microscopes, cell theory, and distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, along with their organelles and functions. Key organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, and chloroplasts, which support the cell's ability to live and reproduce.