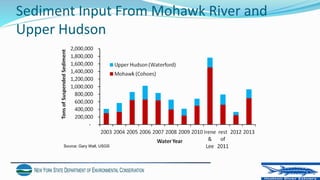
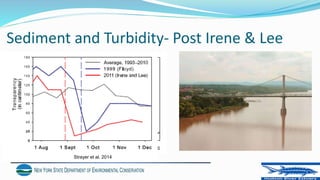
The document discusses the impact of extreme weather events, particularly Hurricane Irene and Tropical Storm Lee, on the Hudson River estuary's ecosystem, noting acute short-term effects on water quality and fish populations. It emphasizes the importance of sediment input and the ongoing recovery of submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV) as key factors in restoring ecosystem resilience. The findings suggest that while immediate effects were observed, long-term recovery efforts are essential as the frequency of such storms is predicted to increase.