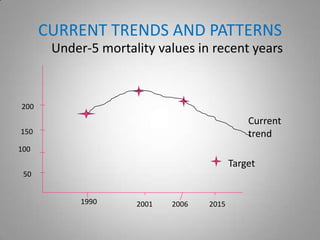
This document analyzes Nigeria's progress toward Millennium Development Goal 4 of reducing child mortality. It finds that while policies aim to reduce under-5 mortality, challenges like poor infrastructure, cultural beliefs, and inadequate funding mean the target of a two-thirds reduction by 2015 is unlikely to be achieved. Current annual declines in under-5 mortality are less than half of what is required. The goal may be possible in later years if governance and resources improve.