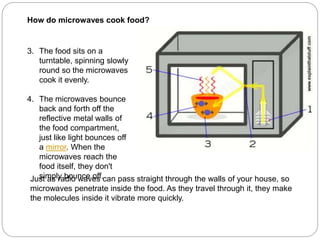
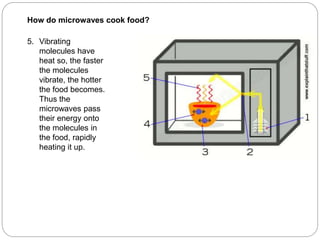
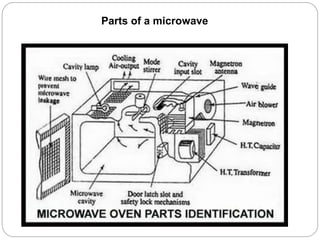
A microwave range hood is a kitchen appliance that combines a microwave oven and range hood into a single unit to save space. It allows the microwave to be installed above the cooktop instead of taking up counter space. Microwaves work by using electromagnetic waves to vibrate water molecules in food, generating heat. Key components include the magnetron which generates the microwaves, waveguide which directs them, and the cooking cavity which contains the microwaves for safe cooking. Microwave range hoods provide a space-saving option for kitchens with limited counter space.