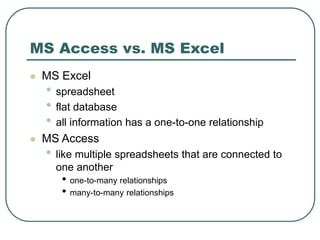
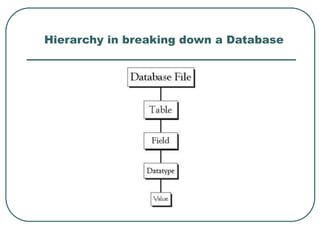
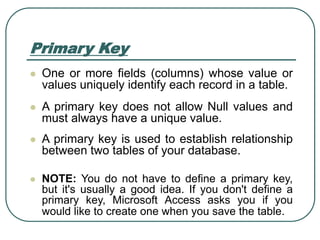
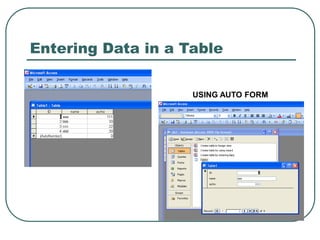
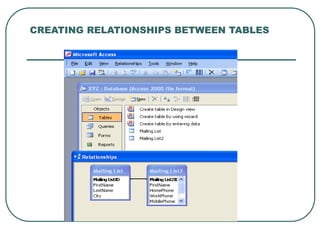
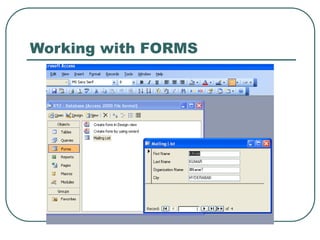
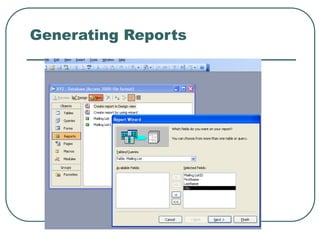
This document provides an introduction to Microsoft Access. It describes Access as a database management system (DBMS) that allows users to create and modify databases. It compares Access to Excel, noting that Access can manage one-to-many and many-to-many relationships while Excel is limited to one-to-one relationships. The document then outlines the hierarchy of an Access database, including the database file, tables, fields, and data types. It provides instructions for creating databases, tables, and relationships between tables in Access.