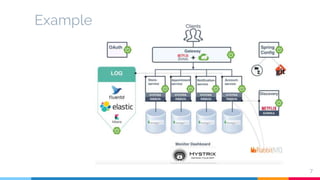
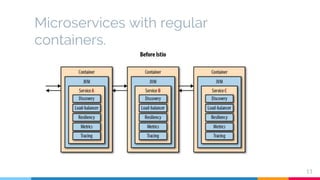
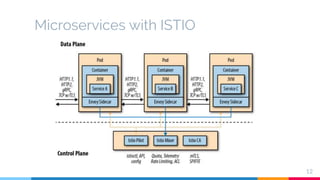
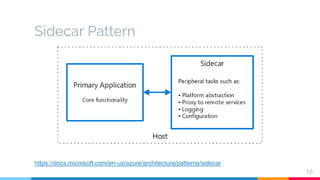
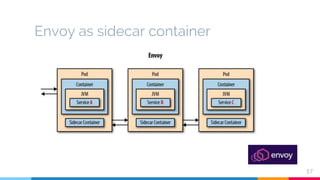
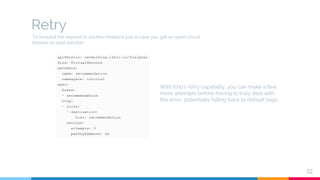
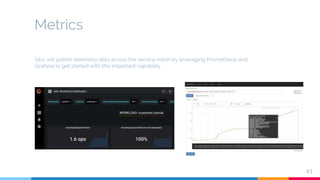
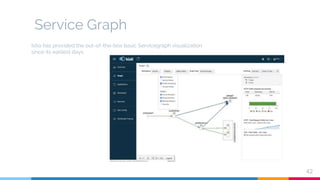
The document presents a detailed overview of microservices architecture with a focus on service mesh concepts, particularly emphasizing Istio as a solution for managing microservices communication. Key topics include traffic control, service resilience, chaos testing, observability, and security within microservices using patterns and tools such as Spring Cloud, Envoy, and various Istio components. The presentation also highlights deployment strategies like canary deployments and discusses Istio's security features like mutual TLS and role-based access control.